Authenticity is the foundation of building trust and meaningful connections in both personal and professional relationships. Embracing your true self fosters confidence and attracts genuine opportunities aligned with your values. Discover how embracing authenticity can transform your life by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
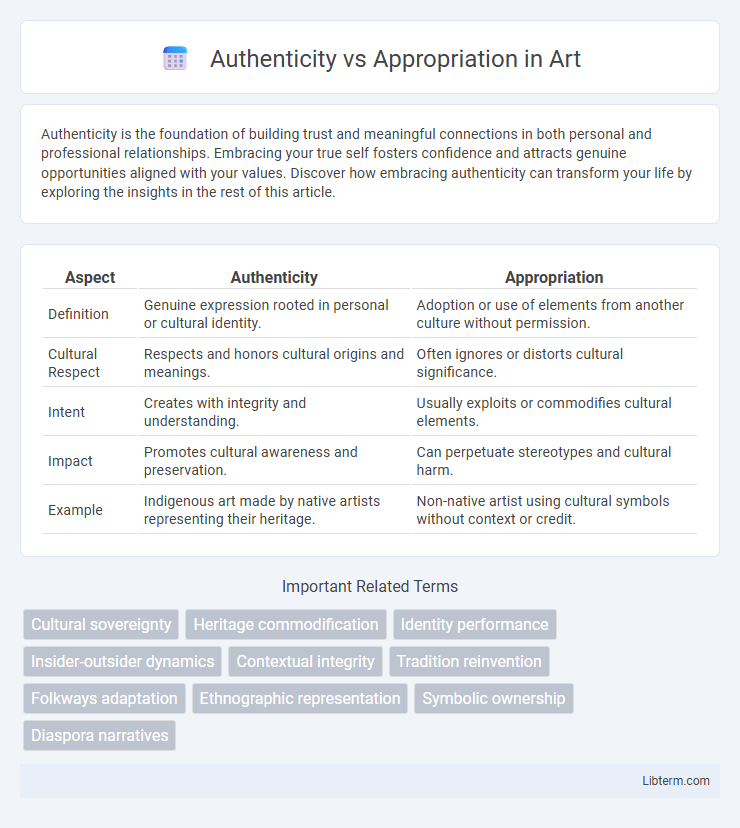
| Aspect | Authenticity | Appropriation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Genuine expression rooted in personal or cultural identity. | Adoption or use of elements from another culture without permission. |
| Cultural Respect | Respects and honors cultural origins and meanings. | Often ignores or distorts cultural significance. |
| Intent | Creates with integrity and understanding. | Usually exploits or commodifies cultural elements. |
| Impact | Promotes cultural awareness and preservation. | Can perpetuate stereotypes and cultural harm. |
| Example | Indigenous art made by native artists representing their heritage. | Non-native artist using cultural symbols without context or credit. |
Understanding Authenticity in Culture
Authenticity in culture involves genuine expression rooted in the traditions, values, and lived experiences of a community, preserving its unique identity across generations. It requires an in-depth understanding of historical context, symbolic meanings, and the socio-cultural dynamics that shape cultural artifacts and practices. Recognizing authenticity helps prevent cultural appropriation, where elements are misrepresented or exploited without respect for their original significance.
Defining Cultural Appropriation
Cultural appropriation involves the adoption of elements from one culture by members of another culture, often without understanding, respect, or acknowledgment of its original context and significance. Authenticity emphasizes honoring the source culture's values and meanings, ensuring representations remain true to their origins rather than being commodified or stereotyped. Discerning cultural appropriation requires recognizing power imbalances and the implications of exploiting marginalized cultures for aesthetic or commercial gain.
Historical Contexts of Cultural Exchange
Historical contexts of cultural exchange reveal complex dynamics between authenticity and appropriation, as intertwined cultures influence art, language, and traditions over centuries. Authenticity often centers on preserving original cultural meanings, while appropriation involves adopting elements without understanding or respecting their origins. Examining colonization, trade routes, and migration patterns highlights how cultural exchanges have both enriched societies and sparked debates on ownership and representation.
The Fine Line: Inspiration Versus Imitation
The fine line between authenticity and appropriation involves discerning genuine cultural inspiration from exploitative imitation, where intent and respect play crucial roles. Authentic inspiration credits original sources and fosters cultural appreciation, while appropriation often involves borrowing elements without acknowledgment or context, leading to cultural misrepresentation. Understanding this distinction requires awareness of power dynamics, historical context, and meaningful engagement with the culture in question.
Power Dynamics in Cultural Borrowing
Power dynamics in cultural borrowing often determine the fine line between authenticity and appropriation, where dominant groups extract cultural elements from marginalized communities without permission or understanding. This process perpetuates historical inequalities by commodifying and distorting cultural symbols while erasing their original significance. True authenticity respects the source culture's context, voices, and rights, challenging exploitative practices and fostering equitable cultural exchange.
Impacts of Appropriation on Marginalized Communities
Cultural appropriation often results in the commodification and distortion of marginalized communities' traditions, undermining their cultural significance and erasing historical contexts. This exploitation perpetuates stereotypes and reinforces social inequalities by benefiting dominant groups at the expense of marginalized voices. The emotional and psychological harm caused by appropriation fosters feelings of disenfranchisement and cultural dislocation among affected communities.
Celebrating Culture Respectfully
Celebrating culture respectfully involves honoring the true roots and meanings behind traditions, avoiding superficial or commodified representations that lead to cultural appropriation. Authenticity requires engaging with cultural practices through education, consent, and acknowledgment of their significance to the originating community. Emphasizing respect and understanding helps preserve cultural integrity while fostering genuine appreciation across diverse groups.
The Role of Intent and Context
Authenticity in cultural expression is often determined by the intent behind the act, where respectful appreciation contrasts with appropriation marked by exploitation or misrepresentation. Context plays a crucial role, as understanding historical background, power dynamics, and cultural significance helps differentiate meaningful engagement from harmful cultural borrowing. Recognizing the purpose and situational factors ensures respectful cultural exchange while preventing the perpetuation of stereotypes or cultural harm.
Examples: When Appropriation Crosses the Line
Cultural appropriation occurs when elements like traditional clothing, symbols, or rituals are taken out of context and used disrespectfully or commercially without understanding their significance. For instance, wearing Native American headdresses as fashion statements at music festivals disregards their sacred meaning and ceremonial importance. Similarly, using sacred religious symbols from Hinduism or other faiths as trendy tattoos or costumes can offend practitioners by stripping these items of their spiritual value.
Moving Forward: Embracing Authenticity in Global Society
Embracing authenticity in a global society requires recognizing cultural expressions' origins and respecting their significance, avoiding cultural appropriation that dilutes or misrepresents traditions. Prioritizing genuine engagement and collaboration promotes inclusivity and honors diverse identities, fostering mutual understanding across cultures. Moving forward, global communities benefit from valuing authenticity as a foundation for ethical cultural exchange and social cohesion.
Authenticity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com