Portrait painting captures the unique essence and personality of a subject through skillful brushwork and attention to detail. Mastery of light, shadow, and composition transforms a simple likeness into a compelling narrative that resonates with viewers. Discover the techniques and history behind this timeless art form by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
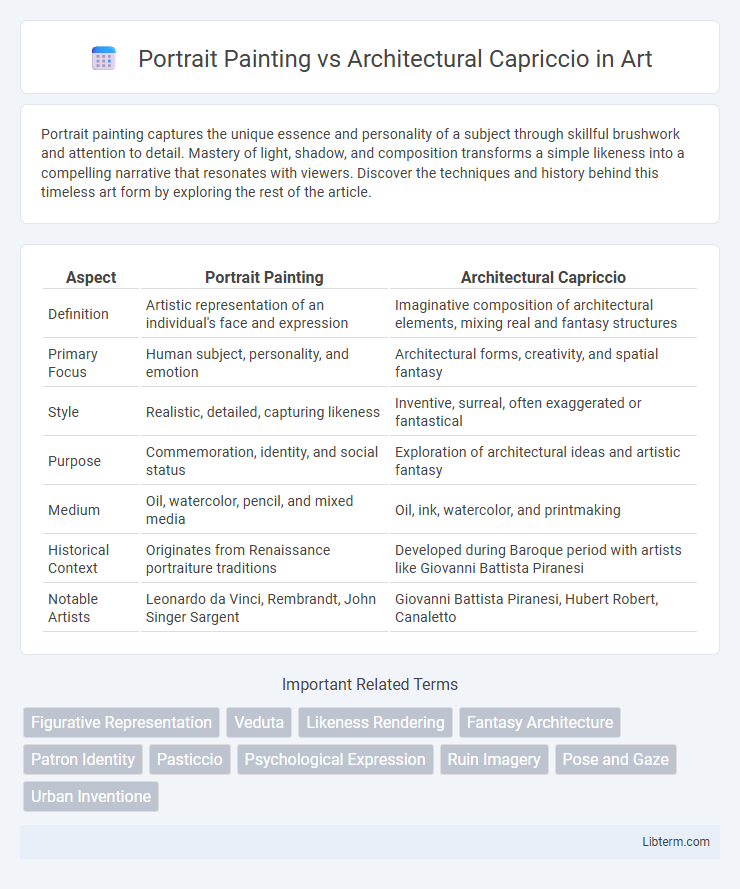
| Aspect | Portrait Painting | Architectural Capriccio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic representation of an individual's face and expression | Imaginative composition of architectural elements, mixing real and fantasy structures |
| Primary Focus | Human subject, personality, and emotion | Architectural forms, creativity, and spatial fantasy |
| Style | Realistic, detailed, capturing likeness | Inventive, surreal, often exaggerated or fantastical |
| Purpose | Commemoration, identity, and social status | Exploration of architectural ideas and artistic fantasy |
| Medium | Oil, watercolor, pencil, and mixed media | Oil, ink, watercolor, and printmaking |
| Historical Context | Originates from Renaissance portraiture traditions | Developed during Baroque period with artists like Giovanni Battista Piranesi |
| Notable Artists | Leonardo da Vinci, Rembrandt, John Singer Sargent | Giovanni Battista Piranesi, Hubert Robert, Canaletto |
Introduction to Portrait Painting and Architectural Capriccio
Portrait painting captures the unique features and personality of a subject through detailed representation, often emphasizing facial expressions and posture to convey emotion and identity. Architectural capriccio combines real and imaginary buildings into fantastical compositions, blending classical architectural elements to create imaginative scenes that emphasize creativity over accuracy. Both art forms showcase distinct approaches: portrait painting centers on individual likeness and human presence, while architectural capriccio explores imaginative environments and structural fantasy.
Defining Portrait Painting: Essence and Purpose
Portrait painting captures the essence and personality of an individual through detailed facial expressions, mood, and attire, emphasizing realism and emotional connection. Its primary purpose is to preserve identity and convey status, character, or psychological depth of the subject. Unlike architectural capriccio, which blends imaginative urban or architectural elements, portrait painting remains anchored in the truthful representation of human subjects.
Unveiling the World of Architectural Capriccio
Architectural Capriccio unveils a fantastical fusion of real and imagined buildings, contrasting sharply with the focused individual representation found in portrait painting. This genre invites viewers into an imaginative exploration of architectural forms and spatial illusions, highlighting creativity over realism. Emphasizing intricate details and dramatic perspectives, architectural capriccio transforms architectural elements into a dynamic visual narrative.
Historical Evolution: Origins and Milestones
Portrait painting originated in ancient civilizations, evolving significantly during the Renaissance with enhanced techniques and psychological depth, marking milestones such as the works of Leonardo da Vinci and Rembrandt. Architectural capriccio emerged in the 17th century, blending imaginative and real architectural elements to create whimsical cityscapes, with key contributions from artists like Giovanni Paolo Panini and Canaletto. Both genres reflect historical shifts in artistic focus: portrait painting centered on individual identity and status, while architectural capriccio emphasized creativity and fantasy within urban contexts.
Key Techniques and Artistic Approaches
Portrait painting emphasizes capturing the subject's personality and expression through detailed facial features, use of light and shadow (chiaroscuro), and precise brushwork to convey realistic textures and emotions. Architectural capriccio employs imaginative compositions that blend real and fantastical architectural elements, utilizing perspective techniques such as linear perspective and atmospheric perspective to create depth and a sense of space. Both art forms require mastery of composition and color theory, but portrait painting prioritizes human anatomy accuracy while architectural capriccio focuses on architectural creativity and spatial illusion.
Subject Matter: From Human Faces to Imaginary Structures
Portrait painting centers on capturing the intricate details of human faces, emphasizing individual personality, expression, and emotion through realistic or stylized representation. Architectural capriccio explores imaginary structures, blending real and fantastical buildings to create visionary, often surreal cityscapes that defy conventional architectural rules. This contrast highlights the shift from the tangible human form to imaginative spatial compositions, reflecting diverse artistic intentions and cultural narratives.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Portrait painting boasts iconic artists like Leonardo da Vinci with the timeless "Mona Lisa" and Rembrandt van Rijn, known for his evocative self-portraits. Architectural capriccio features notable masters such as Giovanni Paolo Panini, celebrated for his imaginative compositions blending ruins and fantastical buildings, and Canaletto, who infused Venetian landscapes with architectural fantasy. Both genres highlight distinct artistic innovations, shaping cultural heritage through their unique visual narratives.
Symbolism and Interpretation in Both Genres
Portrait painting often symbolizes identity, status, and personal narrative through realistic depiction and expressive detail, highlighting individual character and social context. Architectural capriccio utilizes imaginative architectural compositions to evoke emotions, nostalgia, or cultural symbolism, blending real and fantastical elements to interpret space and memory. Both genres rely on symbolism to communicate deeper meanings: portraits emphasize human psychology and social roles, while architectural capriccios explore abstract ideas and historical imagination.
Influence on Contemporary Art Practices
Portrait painting continues to shape contemporary art practices by emphasizing individual identity, emotional depth, and realism, often influencing modern digital portraiture and mixed-media artworks. Architectural capriccio inspires contemporary artists through imaginative combinations of classical architecture and surreal environments, fostering experimental spatial narratives and architectural visualization techniques. Both genres contribute uniquely to contemporary art by blending tradition with innovative expressions and interdisciplinary approaches.
Choosing Between Portrait Painting and Architectural Capriccio
Choosing between portrait painting and architectural capriccio hinges on the desired artistic expression: portrait painting captures individual identity and emotion through detailed human likeness, while architectural capriccio emphasizes imaginative, often fantastical urban landscapes combining real and invented structures. Portrait artists prioritize mastery of facial features, light, and texture to convey personality, whereas capriccio creators focus on perspective, composition, and architectural elements to evoke mood and storytelling. Preference depends on whether the artist values personal narrative or architectural creativity as the central theme of their work.
Portrait Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com