Graphite is a naturally occurring form of carbon known for its excellent conductivity and lubricating properties, making it essential in industries such as electronics, manufacturing, and energy storage. Its layered structure allows electrons to move freely, contributing to its widespread use in batteries, pencils, and thermal management applications. Discover how graphite's unique characteristics can impact your technology and industrial needs by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
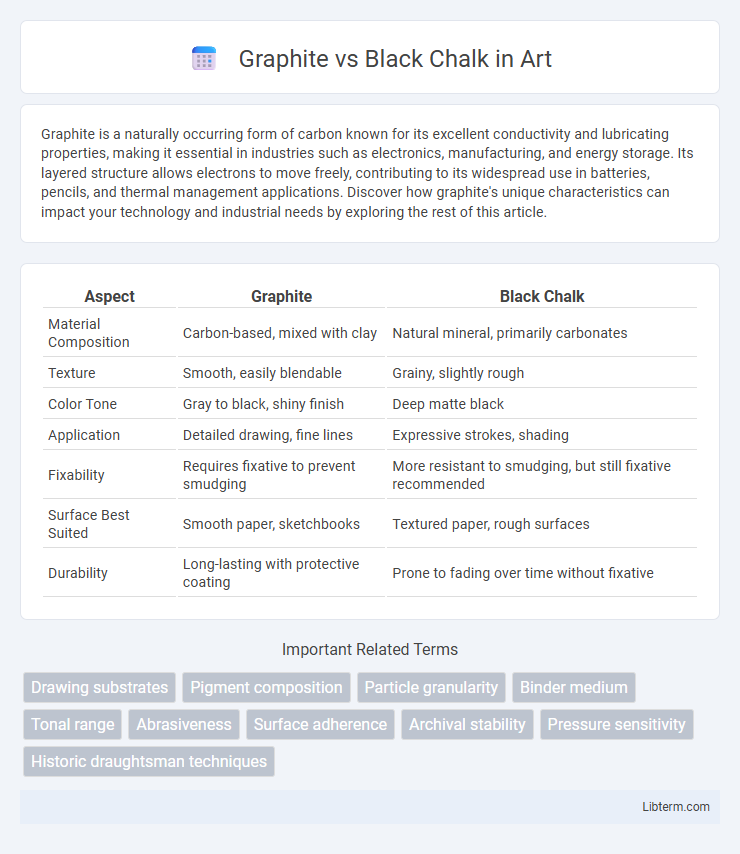
| Aspect | Graphite | Black Chalk |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based, mixed with clay | Natural mineral, primarily carbonates |
| Texture | Smooth, easily blendable | Grainy, slightly rough |
| Color Tone | Gray to black, shiny finish | Deep matte black |
| Application | Detailed drawing, fine lines | Expressive strokes, shading |
| Fixability | Requires fixative to prevent smudging | More resistant to smudging, but still fixative recommended |
| Surface Best Suited | Smooth paper, sketchbooks | Textured paper, rough surfaces |
| Durability | Long-lasting with protective coating | Prone to fading over time without fixative |
Introduction to Graphite and Black Chalk
Graphite, a crystalline form of carbon, is widely valued for its smooth texture and versatility in drawing and writing applications. Black chalk, composed primarily of natural clay and carbonaceous materials, offers a matte finish with a slightly grainy texture preferred for expressive sketching and shading. Both mediums have distinct chemical compositions and physical properties that influence their use in fine art and technical drawing.
Historical Use and Evolution
Graphite has been used since the 16th century for writing and drawing, initially discovered in England and prized for its smooth texture and erasability. Black chalk, made from hardened clay mixed with carbon, dates back to the Renaissance, favored by artists for its rich, velvety lines and ability to create subtle shading. Over time, graphite evolved with improved manufacturing techniques, becoming a staple in both art and technical drawing, while black chalk remained a specialized medium for fine art and portraiture.
Material Composition and Sources
Graphite consists primarily of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice structure, obtained mainly from natural deposits or synthesized through high-temperature processes. Black chalk, made from a mixture of clay and natural carbonaceous materials such as pulverized coal or charcoal, derives from sedimentary deposits rich in organic matter. The distinct material compositions influence their texture and application, with graphite providing smooth, consistent marks and black chalk offering a more granular, matte finish.
Physical Properties Comparison
Graphite exhibits a metallic luster with a slippery feel due to its layered atomic structure, enabling easy cleavage and electrical conductivity, whereas black chalk has a matte appearance, is brittle, and lacks conductivity. The hardness of graphite on the Mohs scale ranges from 1 to 2, making it softer compared to black chalk, which typically measures around 3 to 4 and has a chalky texture. Graphite's density is approximately 2.2 g/cm3, significantly lower than black chalk's density of about 2.7 g/cm3, reflecting differences in mineral composition and crystal arrangement.
Drawing Techniques with Graphite
Graphite offers versatile drawing techniques such as blending, layering, and shading, enabling artists to achieve smooth gradients and fine details. Its wide range of hardness grades allows for varied textures and depths, from light sketch lines to rich, dark tones. Unlike black chalk, which has a more powdery texture suited for loose, expressive marks, graphite excels in precision and control, making it ideal for detailed renderings and realistic illustrations.
Artistic Applications of Black Chalk
Black chalk offers unique artistic applications by providing rich, deep tones and a textured, matte finish ideal for expressive shading and detailed line work. Artists favor black chalk for life drawing and portraiture due to its ability to create soft gradients and subtle contrasts without the sheen often seen in graphite. Its versatility on various paper textures enhances the dimensionality and depth of sketches, making it a preferred medium over graphite for dynamic, emotive artwork.
Differences in Texture and Line Quality
Graphite produces smooth, consistent lines with a shiny, reflective surface, offering a broad tonal range from light gray to deep black, ideal for detailed shading and fine textures. Black chalk yields a matte finish with a softer, grainier texture that creates rich, velvety lines and expressive marks, making it perfect for dynamic, textured drawings. The granular composition of black chalk allows for easier blending and smudging, while graphite's harder core maintains sharper edges and precise line work.
Preservation and Longevity of Artworks
Graphite offers superior preservation qualities due to its chemical stability and resistance to smudging, making artworks more durable over time. Black chalk, while providing rich texture and depth, is more prone to fading and smearing without protective measures like fixatives. Museums and conservators often prefer graphite for long-term longevity, whereas black chalk pieces require careful handling and environmental controls to maintain their integrity.
Famous Artists and Iconic Works
Graphite, favored by artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Albrecht Durer, enables precise, detailed sketches exemplified in da Vinci's "Vitruvian Man." In contrast, black chalk was popular among Renaissance and Baroque masters such as Peter Paul Rubens, whose dynamic figure studies highlight the medium's rich texture and depth. Both media contributed uniquely to iconic works, with graphite excelling in fine line work and black chalk offering expressive softness.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Art
Selecting between graphite and black chalk depends on the desired texture and depth in your artwork; graphite offers smooth, precise lines ideal for detailed sketches, while black chalk provides rich, matte tones perfect for expressive, bold strokes. Consider the paper surface as graphite works best on smooth paper to showcase its reflective qualities, whereas black chalk excels on textured paper, enhancing its natural grain. Your choice should align with your artistic style and the visual effect you intend to achieve, balancing control with expressive freedom.
Graphite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com