Painting enhances your living space by adding color, texture, and personality to walls and surfaces. Choosing the right paint type and application technique ensures durability and a beautiful finish that reflects your style. Explore the rest of this article to discover expert tips and techniques for mastering the art of painting.
Table of Comparison
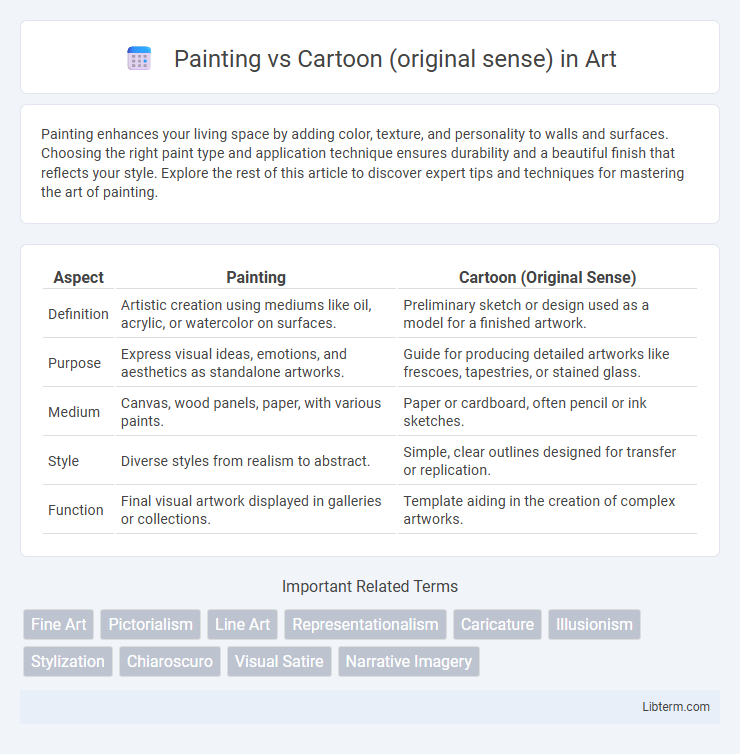
| Aspect | Painting | Cartoon (Original Sense) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic creation using mediums like oil, acrylic, or watercolor on surfaces. | Preliminary sketch or design used as a model for a finished artwork. |
| Purpose | Express visual ideas, emotions, and aesthetics as standalone artworks. | Guide for producing detailed artworks like frescoes, tapestries, or stained glass. |
| Medium | Canvas, wood panels, paper, with various paints. | Paper or cardboard, often pencil or ink sketches. |
| Style | Diverse styles from realism to abstract. | Simple, clear outlines designed for transfer or replication. |
| Function | Final visual artwork displayed in galleries or collections. | Template aiding in the creation of complex artworks. |
Introduction: Defining Painting and Original Cartoons
Painting is a visual art form that involves applying pigments to a surface, such as canvas or paper, to create expressive or representational images with depth and texture. Original cartoons refer to preliminary drawings or designs made by artists as blueprints for large-scale works like frescoes or stained glass, characterized by clear outlines and simplified shapes. The key distinction lies in paintings being finished artworks intended for display, while cartoons serve as preparatory sketches essential to the creative process.
Historical Evolution of Painting and Cartoons
Painting originated as a form of visual storytelling and ritual expression during prehistoric times, evolving through classical antiquity with developments in techniques and materials that emphasized realism and perspective. Cartoons, initially derived from the Italian word "cartone" meaning a preparatory drawing for paintings or tapestries, transformed in the late 19th century into satirical and humorous illustrations used in print media. The historical evolution of both art forms reflects shifting cultural functions: paintings maintained traditional narrative and aesthetic roles, while cartoons emerged as a popular medium for social commentary and mass communication.
Techniques and Materials Used
Painting traditionally involves applying pigments mixed with mediums like oil, acrylic, or watercolor onto surfaces such as canvas or paper, utilizing techniques that emphasize texture, layering, and brushwork to create depth and realism. Cartoons, in their original sense, are preliminary full-scale sketches drawn on paper or cardboard to serve as templates for frescoes or tapestries, created using charcoal or ink with precise, linear outlines to guide the final artwork. While painting relies on color blending and shading for visual impact, cartoons prioritize clear contours and composition planning to facilitate accurate transfer onto larger surfaces.
Artistic Intent and Communication
Painting traditionally serves as a medium for complex visual narratives and emotional expression, often emphasizing depth, texture, and subtle color variations to convey the artist's intent. Cartoons prioritize simplified, exaggerated imagery and humor or satire to communicate messages quickly and accessibly, relying on bold lines and vibrant colors. The artistic intent in paintings often aims for profound reflection and aesthetic appreciation, whereas cartoons focus on direct social commentary and entertainment.
Visual Styles and Aesthetics
Painting typically emphasizes rich textures, brushstrokes, and color blending to evoke depth and realism, showcasing diverse styles from impressionism to realism. Cartoons prioritize bold outlines, exaggerated features, and flat colors aimed at simple, clear visual storytelling and expressive characters. Both forms use distinct aesthetics: paintings highlight intricate detail and emotional nuance, while cartoons focus on clarity, humor, and immediacy in visual communication.
Role of Narrative in Painting vs Cartoon
Narrative in paintings traditionally conveys complex emotions, historical events, or symbolic meanings through visual composition and subtle details, allowing viewers to interpret stories at their own pace. Cartoons utilize concise, exaggerated storytelling with clear sequences and dialogue to deliver immediate humor, social commentary, or moral lessons. The role of narrative in painting emphasizes depth and ambiguity, while cartoons prioritize clarity and accessibility for rapid audience engagement.
Cultural Impact and Societal Perception
Painting, as a traditional fine art form, has long been revered for its role in shaping cultural heritage and expressing complex societal ideals through detailed, symbolic imagery. Cartoons, originating as humorous illustrations or satirical commentary, significantly influenced mass media and popular culture by making social critique accessible and engaging to broader audiences. Both mediums reflect and shape societal values, but painting often commands greater cultural prestige, while cartoons drive contemporary social discourse and popular representation.
Key Artists and Influential Works
Painting, epitomized by masters like Leonardo da Vinci with "Mona Lisa" and Vincent van Gogh's "Starry Night," emphasizes realism and intricate detail to evoke emotion and narrative depth. In contrast, cartoons, pioneered by artists such as Walt Disney with "Steamboat Willie" and Winsor McCay's "Gertie the Dinosaur," focus on simplified, exaggerated characters to convey humor, satire, and storytelling through sequential art. Both mediums have profoundly shaped visual culture, with painting rooted in fine art traditions and cartoons evolving as a dynamic form of popular entertainment.
Contemporary Trends and Cross-Influences
Contemporary trends reveal a growing fusion between painting and cartoon, as artists increasingly blend traditional brush techniques with animated aesthetics to challenge narrative forms and visual perception. Cross-influences are evident in the use of bold colors, simplified shapes, and exaggerated expressions characteristic of cartoons, enriching contemporary paintings with dynamic storytelling elements. This interdisciplinary approach fosters innovation, blurring boundaries and expanding the expressive potential of both mediums in modern art.
Conclusion: Distinguishing and Bridging the Two Art Forms
Painting captures intricate textures and emotions through traditional techniques and rich color palettes, embodying fine art's depth and realism. Cartoons utilize simplified lines and exaggerated features to convey humor, satire, or narratives with immediacy and accessibility. Understanding their distinct purposes enriches appreciation while recognizing their shared creative essence bridges the gap between classical artistry and popular visual storytelling.
Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com