Surrealism revolutionized art and literature by blending dreamlike imagery with reality, challenging traditional perceptions and unlocking the subconscious mind. This movement inspired artists to explore irrational compositions, unexpected juxtapositions, and symbolic meanings that continue to influence contemporary creativity. Discover how surrealism shapes your understanding of imagination and reality in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
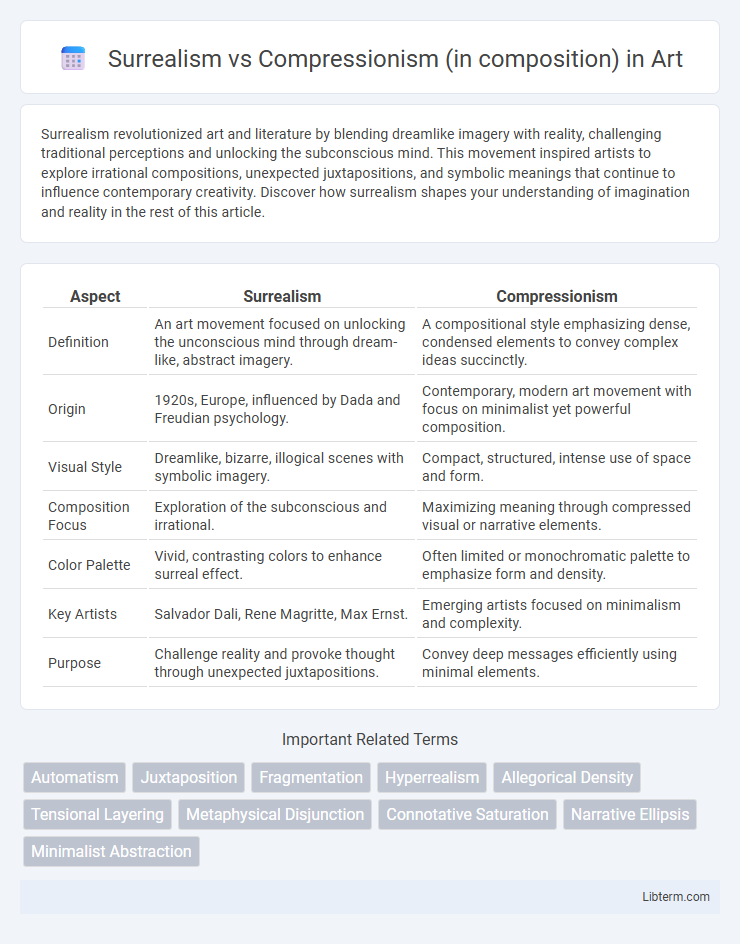
| Aspect | Surrealism | Compressionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An art movement focused on unlocking the unconscious mind through dream-like, abstract imagery. | A compositional style emphasizing dense, condensed elements to convey complex ideas succinctly. |
| Origin | 1920s, Europe, influenced by Dada and Freudian psychology. | Contemporary, modern art movement with focus on minimalist yet powerful composition. |
| Visual Style | Dreamlike, bizarre, illogical scenes with symbolic imagery. | Compact, structured, intense use of space and form. |
| Composition Focus | Exploration of the subconscious and irrational. | Maximizing meaning through compressed visual or narrative elements. |
| Color Palette | Vivid, contrasting colors to enhance surreal effect. | Often limited or monochromatic palette to emphasize form and density. |
| Key Artists | Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst. | Emerging artists focused on minimalism and complexity. |
| Purpose | Challenge reality and provoke thought through unexpected juxtapositions. | Convey deep messages efficiently using minimal elements. |
Understanding Surrealism in Composition
Surrealism in composition emphasizes the exploration of the unconscious mind through unexpected juxtapositions, dream-like scenarios, and non-linear narratives. It challenges traditional structures by incorporating irrational elements and free association techniques to evoke deeper emotional and psychological responses. Key composers such as Erik Satie and early 20th-century avant-garde artists used surrealism to defy conventions and create innovative soundscapes that blur reality and imagination.
Defining Compressionism: A Modern Approach
Compressionism in composition emphasizes dense, concentrated expression by distilling complex ideas into minimalistic, impactful elements. Unlike Surrealism, which explores dreamlike, irrational landscapes through associative imagery, Compressionism seeks clarity and precision in conveying thematic depth. This modern approach prioritizes succinctness and intensity, merging brevity with profound emotional or conceptual resonance.
Historical Origins of Surrealism and Compressionism
Surrealism, originating in the early 1920s, emerged as a revolutionary art and literary movement influenced by the Dada movement and Freudian psychoanalysis, aiming to unlock the unconscious mind through dreamlike and illogical imagery. Compressionism, a less widely recognized compositional approach, developed in the mid-20th century and emphasizes condensed and highly structured forms to convey complex meanings with minimal elements. While Surrealism seeks to explore the depths of irrational creativity, Compressionism focuses on precision and economy in artistic expression.
Key Principles of Surrealist Composition
Surrealist composition emphasizes dreamlike imagery, unexpected juxtapositions, and the liberation of the subconscious mind through automatic writing or spontaneous creation. It prioritizes irrationality and the exploration of unconscious desires to disrupt traditional narrative structures and logical coherence. This approach contrasts sharply with Compressionism, which values brevity, clarity, and condensed expression to evoke meaning succinctly.
Core Techniques in Compressionist Art
Compressionist art prioritizes condensation and intensity by reducing shapes to essential forms and emphasizing bold contrasts in color and texture. Techniques involve compact layering of brushstrokes to create dense, dynamic surfaces that evoke emotional depth within minimal spatial boundaries. This contrasts with Surrealism's fluid dreamlike imagery, as Compressionism seeks to convey powerful statements through concentrated visual elements and structural rigor.
Visual Impact: Surrealism vs Compressionism
Surrealism in composition emphasizes dreamlike, fantastical imagery that challenges perception and evokes strong emotional and cognitive responses through unexpected juxtapositions. Compressionism focuses on distilling visual elements into minimalistic, condensed forms that amplify intensity and clarity by stripping away extraneous detail. The visual impact of Surrealism lies in its imaginative complexity, while Compressionism creates power through concentrated simplicity.
Influential Artists in Both Movements
Surrealism in composition was shaped by artists like Erik Satie and John Cage, who embraced chance operations and dream-like structures to challenge conventional musical narratives. Compressionism, a lesser-known movement, found its voice through composers such as Heinrich Strobel and Gyorgy Ligeti, emphasizing condensed, intense sonic textures and intricate rhythmic patterns. Both movements revolutionized 20th-century music by expanding the boundaries of composition through distinct philosophical and technical approaches.
Emotional Narrative in Surrealist and Compressionist Works
Surrealist compositions utilize dream-like imagery and unexpected juxtapositions to evoke deep, often subconscious emotions, creating a nonlinear emotional narrative that challenges traditional storytelling. Compressionist works, by contrast, focus on distilling emotional experiences into concise, potent fragments that intensify feelings through minimalistic and precise expression. Both styles manipulate emotional narrative to engage listeners, with Surrealism expanding emotional complexity and Compressionism amplifying emotional impact through succinctness.
Contemporary Adaptations and Experiments
Contemporary adaptations of Surrealism in composition emphasize dream-like, non-linear structures and unexpected juxtapositions, pushing boundaries of perception and emotional depth. Compressionism experiments involve condensing musical ideas into minimalistic, dense forms, challenging traditional narrative and temporal flow. Both movements explore new sonic textures in digital and electroacoustic media, expanding the palette of modern compositional techniques.
Choosing Between Surrealism and Compressionism in Creative Practice
Choosing between Surrealism and Compressionism in composition depends on the desired artistic effect and conceptual focus. Surrealism emphasizes dreamlike, subconscious imagery and free association to evoke emotional and symbolic depth, ideal for exploring abstract or psychological themes. Compressionism, characterized by condensed, minimalistic expression and layered meanings, suits creators seeking clarity, precision, and impactful brevity in their work.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com