Static proportion refers to the fixed ratio or relationship between elements within a design or system that remains constant regardless of external changes. Maintaining static proportions ensures visual harmony and balance, which is crucial in fields like architecture, graphic design, and engineering. Discover how understanding static proportion can enhance your projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
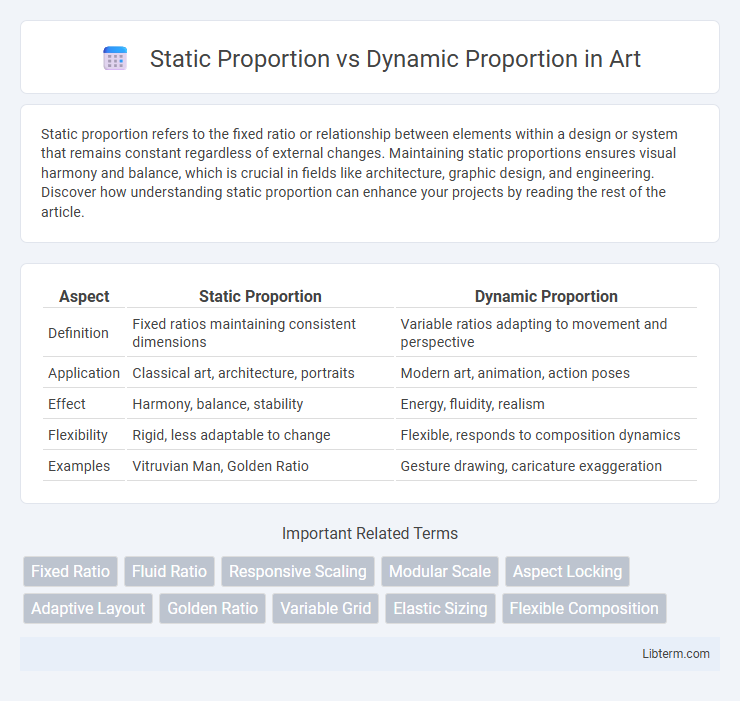
| Aspect | Static Proportion | Dynamic Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed ratios maintaining consistent dimensions | Variable ratios adapting to movement and perspective |
| Application | Classical art, architecture, portraits | Modern art, animation, action poses |
| Effect | Harmony, balance, stability | Energy, fluidity, realism |
| Flexibility | Rigid, less adaptable to change | Flexible, responds to composition dynamics |
| Examples | Vitruvian Man, Golden Ratio | Gesture drawing, caricature exaggeration |
Introduction to Static and Dynamic Proportion
Static proportion refers to fixed, unchanging ratios in design or composition, providing stability and balance across elements. Dynamic proportion involves varying ratios that create movement and visual interest by adapting sizes and scales contextually. Understanding these concepts is essential for architects, artists, and designers to manipulate space, form, and aesthetics effectively.
Defining Static Proportion
Static proportion refers to fixed or unchanging ratios within a system or design, where elements maintain a constant size or relationship regardless of external variables. This concept is essential in fields like architecture and graphic design, ensuring stability and consistency in visual or structural composition. Static proportion contrasts with dynamic proportion, which adjusts according to context, scale, or interaction.
Defining Dynamic Proportion
Dynamic proportion refers to the adaptable relationship between elements in a design or composition that changes based on context, function, or user interaction, contrasting with static proportion's fixed ratios. This concept is crucial in responsive web design, architecture, and product development, where elements must resize or reposition to accommodate different environments or user needs. Emphasizing fluidity and flexibility, dynamic proportion enhances user experience by ensuring visual harmony and functionality across varying conditions.
Key Differences Between Static and Dynamic Proportion
Static proportion refers to fixed ratios that remain constant regardless of context, commonly used in design and architecture to maintain balanced and harmonious structures. Dynamic proportion varies according to the environment or user interaction, adapting sizes and relationships to optimize functionality and aesthetics in real time. Key differences include stability versus adaptability, predictability in static proportions, and flexibility and responsiveness characterizing dynamic proportions.
Applications of Static Proportion
Static proportion finds extensive applications in architecture and graphic design, where maintaining fixed ratios ensures visual harmony and structural stability in building layouts and logo compositions. In manufacturing, static proportional analysis aids in quality control by keeping component dimensions consistent to meet precise engineering specifications. Additionally, static proportions are crucial in data visualization, enabling balanced chart elements that enhance readability and accurate interpretation of information.
Applications of Dynamic Proportion
Dynamic proportion adapts to changing conditions, making it ideal for applications like responsive web design, where layout elements resize fluidly across devices. In digital advertising, dynamic proportion enables ad creatives to maintain visual balance on various screen sizes, improving user engagement. This adaptability is crucial in interactive interfaces and real-time data visualization, providing optimal user experience regardless of screen resolution or device orientation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Static Proportion
Static proportion ensures consistent layout and design across different screen sizes, simplifying the development process and maintaining visual harmony. It may, however, lead to poor user experience on devices with varied resolutions since fixed dimensions can cause elements to appear too small or too large. This rigidity limits flexibility, making static proportions less ideal for responsive web design compared to dynamic proportions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dynamic Proportion
Dynamic proportion offers the advantage of flexibility, allowing systems or algorithms to adjust resource allocation based on real-time demand and usage patterns, leading to improved efficiency and responsiveness. This adaptability can enhance performance in environments with fluctuating workloads, such as cloud computing or network bandwidth management. However, the complexity of implementing dynamic proportion mechanisms may result in higher computational overhead and potential instability if the adjustments are not carefully controlled.
Choosing the Right Proportion Method
Selecting the appropriate proportion method depends on the context and data variability, with static proportion relying on fixed ratios ideal for stable datasets and dynamic proportion adjusting based on real-time changes to capture fluctuating trends accurately. Static proportion offers simplicity and consistency, making it suitable for long-term planning, while dynamic proportion provides flexibility necessary in environments with unpredictable patterns, such as marketing analytics or resource allocation during peak demand. Evaluating data stability, desired responsiveness, and computational resources ensures the right balance between precision and practicality in choosing between static and dynamic proportions.
Future Trends in Proportion Techniques
Future trends in proportion techniques emphasize adaptive dynamic proportion methods leveraging AI and machine learning to personalize sizing in fashion and design industries. Static proportion models are evolving towards hybrid systems that integrate real-time biometric data for enhanced fit accuracy. Advancements in 3D scanning and virtual reality further propel dynamic proportion applications, enabling immersive customization and predictive adjustments.
Static Proportion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com