Chisels are essential tools for carving and shaping wood, stone, or metal with precision and control. Their sharp, beveled edge allows you to remove small amounts of material for fine detailing or rough shaping. Discover how to select the right chisel and master techniques by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
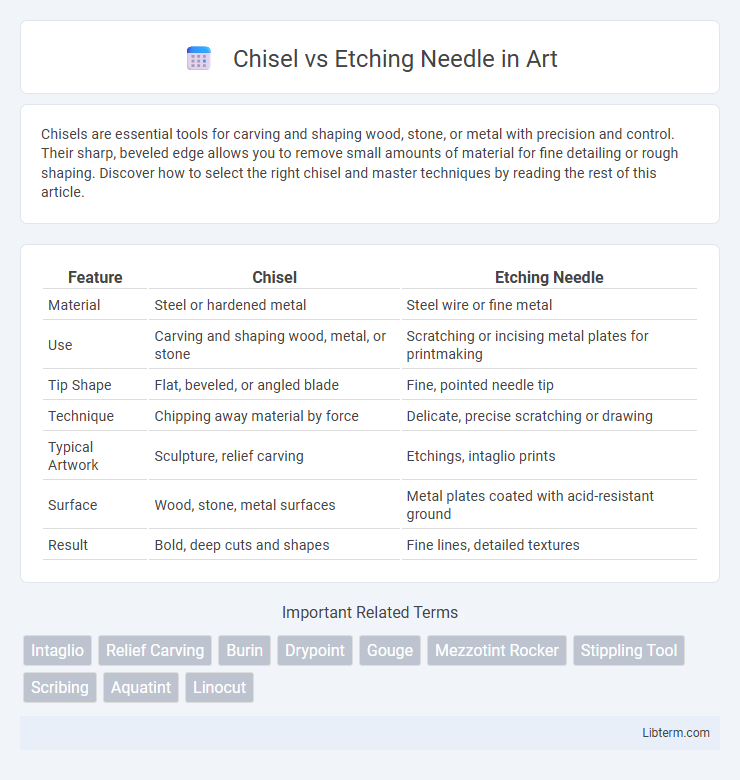
| Feature | Chisel | Etching Needle |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel or hardened metal | Steel wire or fine metal |
| Use | Carving and shaping wood, metal, or stone | Scratching or incising metal plates for printmaking |
| Tip Shape | Flat, beveled, or angled blade | Fine, pointed needle tip |
| Technique | Chipping away material by force | Delicate, precise scratching or drawing |
| Typical Artwork | Sculpture, relief carving | Etchings, intaglio prints |
| Surface | Wood, stone, metal surfaces | Metal plates coated with acid-resistant ground |
| Result | Bold, deep cuts and shapes | Fine lines, detailed textures |
Introduction to Chisels and Etching Needles
Chisels are precision tools featuring a sharp, wedge-shaped blade designed for carving and shaping materials such as wood, metal, or stone during engraving or sculpting. Etching needles are fine, pointed instruments primarily used in intaglio printmaking to scratch detailed lines into a metal plate coated with a resist. Both tools serve distinct purposes in artistic and industrial processes, with chisels suited for broader carving and etching needles ideal for intricate line work.
What is a Chisel?
A chisel is a tool with a sharp, beveled edge used for carving or cutting hard materials like wood, stone, or metal. Unlike an etching needle, which is fine and pointed for detailed engraving on surfaces, a chisel applies force to remove larger material sections. Its sturdy design and versatility make it essential in woodworking, sculpture, and masonry for shaping and detailing.
What is an Etching Needle?
An etching needle is a fine, sharp tool used in intaglio printmaking to incise precise lines directly onto a metal plate coated with an acid-resistant ground. Unlike a chisel, which removes material by cutting or carving, the etching needle scratches through the protective layer without gouging the plate, allowing acid to bite into the exposed metal during the etching process. This enables artists to create intricate, delicate designs essential for high-detail printmaking techniques.
Key Differences Between Chisels and Etching Needles
Chisels feature a flat, wedge-shaped blade designed for carving and shaping materials like wood or stone, offering broad, controlled cuts, while etching needles have a sharp, pointed tip used primarily for precise incisions on metal, glass, or other hard surfaces. The durability and varied blade sizes of chisels enable removal of larger material sections, whereas etching needles focus on fine detail and surface design work. Material composition also differs, with chisels typically forged from hardened steel for heavy-duty use, and etching needles crafted from fine, high-carbon steel for sharpness and precision.
Primary Uses of Chisels
Chisels are primarily used for shaping, carving, and cutting hard materials like wood, stone, and metal, making them essential tools in woodworking, masonry, and metalworking. Unlike etching needles, which are designed for fine, detailed engraving on metal plates or glass, chisels provide broader, more forceful cuts necessary for creating precise joints or removing large sections of material. Their versatility in smoothing surfaces and creating intricate designs highlights their significance in various craft and industrial applications.
Primary Uses of Etching Needles
Etching needles are primarily used in printmaking for creating detailed lines and textures on metal plates, enabling artists to achieve fine, precise designs before acid is applied. Unlike chisels, which remove larger areas of material through carving, etching needles gently scratch the surface to form intricate patterns essential for intaglio techniques. Their precision makes them indispensable for artists focusing on delicate line work and detailed etching processes.
Material Compatibility: Chisel vs Etching Needle
Chisels are generally compatible with harder materials such as wood, stone, and metal due to their robust, sharp edges designed for carving and shaping. Etching needles, on the other hand, are primarily suited for softer surfaces like glass, metal plates, and coated materials, enabling precise engraving without excessive material removal. Material compatibility dictates tool selection, with chisels excelling in bulk material removal and etching needles favored for fine, detailed surface work.
Pros and Cons of Using Chisels
Chisels provide precise control and efficient material removal, making them ideal for shaping wood, stone, and metal in detailed carving projects, with their sharp edges facilitating clean cuts. However, chisels require significant skill and strength, as improper use can cause splintering or uneven surfaces. The durability of chisels is a benefit, but they need regular sharpening to maintain performance, and their rigid design limits flexibility compared to finer tools like etching needles.
Pros and Cons of Using Etching Needles
Etching needles offer precise control and fine detail work, making them ideal for delicate line engraving on metal plates and glass. They provide a cost-effective and straightforward tool for artists and printmakers, but they can be time-consuming and require steady hands to avoid unintentional scratches. Unlike chisels, etching needles lack the power for deep cuts, limiting their use to surface-level incisions and finer textures.
Choosing the Right Tool: Chisel or Etching Needle
Choosing between a chisel and an etching needle depends on the desired line quality and material being engraved. Chisels are ideal for creating deep, broad cuts on harder surfaces like wood or stone, offering precision and durability. Etching needles excel at fine, detailed lines on metal plates, allowing artists to achieve intricate designs with greater control and subtlety.
Chisel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com