Classicism emphasizes harmony, clarity, and proportion, drawing inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman art and literature. It values order, balance, and restraint, often reflecting ideals of beauty and reason. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how Classicism influences modern culture and artistic expression.
Table of Comparison
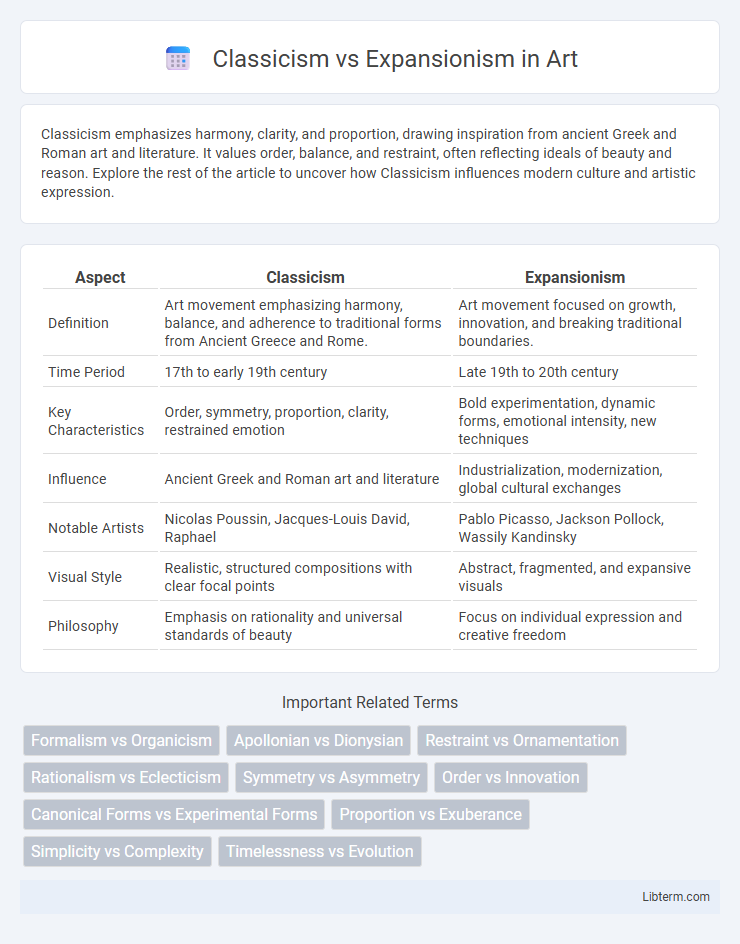
| Aspect | Classicism | Expansionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement emphasizing harmony, balance, and adherence to traditional forms from Ancient Greece and Rome. | Art movement focused on growth, innovation, and breaking traditional boundaries. |
| Time Period | 17th to early 19th century | Late 19th to 20th century |
| Key Characteristics | Order, symmetry, proportion, clarity, restrained emotion | Bold experimentation, dynamic forms, emotional intensity, new techniques |
| Influence | Ancient Greek and Roman art and literature | Industrialization, modernization, global cultural exchanges |
| Notable Artists | Nicolas Poussin, Jacques-Louis David, Raphael | Pablo Picasso, Jackson Pollock, Wassily Kandinsky |
| Visual Style | Realistic, structured compositions with clear focal points | Abstract, fragmented, and expansive visuals |
| Philosophy | Emphasis on rationality and universal standards of beauty | Focus on individual expression and creative freedom |
Defining Classicism and Expansionism
Classicism emphasizes order, balance, and adherence to traditional forms derived from ancient Greek and Roman principles, valuing harmony and rationality in art, literature, and architecture. Expansionism advocates for the growth of territories, influence, or power, often through trade, colonization, or military conquest, aiming to extend a nation's economic and political reach. Defining these concepts highlights Classicism's focus on preserving established cultural ideals versus Expansionism's drive for geographic and strategic enlargement.
Historical Origins of Classicism
Classicism originated in the Renaissance as a revival of Ancient Greek and Roman principles, emphasizing harmony, proportion, and rationality in art, literature, and architecture. Rooted in the works of Vitruvius and Horace, Classicism sought to restore balance and order against the medieval Gothic style. This historical foundation shaped European cultural and intellectual movements, influencing the Enlightenment and Neoclassicism.
The Rise of Expansionism
The rise of Expansionism marked a significant shift from Classicism's emphasis on tradition and restraint to an aggressive pursuit of territorial and economic growth, driven by imperial ambitions and emerging industrial powers. Expansionist policies fueled global conflicts and shaped international relations by prioritizing strategic dominance and resource acquisition over cultural or philosophical ideals. This transformation redefined national priorities and accelerated the development of modern geopolitics during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Core Principles of Classicism
Classicism centers on the principles of harmony, balance, and adherence to established traditions inspired by ancient Greek and Roman art and literature. It emphasizes reason, order, and proportion as fundamental elements in artistic and intellectual expression. Core principles include clarity, restraint, and universal themes that reflect human nature and moral virtues.
Key Elements of Expansionism
Expansionism emphasizes territorial growth driven by economic interests, military conquest, and political dominance, leveraging strategic resources and infrastructure to extend influence. It prioritizes establishing new markets, expanding trade routes, and enforcing control over foreign lands to enhance national power. Unlike Classicism's focus on cultural ideals and balance, Expansionism centers on aggressive acquisition and pragmatic governance to shape geopolitical landscapes.
Classicism vs Expansionism: Main Differences
Classicism emphasizes strict adherence to traditional forms, order, and harmony rooted in ancient Greek and Roman principles, while Expansionism prioritizes growth, territorial acquisition, and the extension of influence. Classicism values balance, proportion, and restrained expression, contrasting with Expansionism's focus on aggressive policies, economic development, and geopolitical dominance. The core difference lies in Classicism's cultural and aesthetic ideals versus Expansionism's strategic and political objectives.
Impact on Society and Culture
Classicism emphasized order, harmony, and restraint, fostering a culture rooted in tradition, intellectual rigor, and artistic discipline that shaped education, literature, and architecture in European societies. Expansionism promoted cultural exchange, economic growth, and social mobility through colonialism and trade, significantly transforming societies by spreading technology, ideas, and diverse cultural influences globally. The contrasting impacts influenced societal values: Classicism preserved established norms and elite cultural practices, while Expansionism accelerated globalization and cultural hybridization.
Examples in Art, Architecture, and Literature
Classicism in art, architecture, and literature emphasizes harmony, proportion, and adherence to ancient Greek and Roman models, as seen in the works of Renaissance masters like Leonardo da Vinci, the Palladian villas in architecture, and the structured sonnets of Shakespeare. Expansionism reflects a different cultural approach, often linked to imperial or colonial ambitions that influenced Romantic and Realist art, such as the landscape paintings of Caspar David Friedrich, grandiose public buildings like the British Empire's Victorian Gothic revival structures, and literary works exploring themes of exploration and nationalism, exemplified by authors like Rudyard Kipling. These contrasting movements highlight a tension between reverence for classical ideals and the dynamic, often nationalistic drive to extend cultural and political boundaries.
Modern Relevance and Debates
Classicism emphasizes restraint, harmony, and adherence to traditional forms, influencing contemporary architectural and artistic debates on preserving cultural heritage versus innovation. Expansionism, driven by growth and adaptation, shapes modern economic and geopolitical strategies that prioritize resource acquisition and strategic influence. Current discussions often revolve around balancing classical ideals of stability with expansionist imperatives of progress and competitiveness in a globalized world.
Conclusion: Balancing Tradition and Innovation
Classicism emphasizes the preservation of established cultural and artistic traditions, valuing order, harmony, and disciplined form, while expansionism advocates for innovation, growth, and the exploration of new ideas beyond conventional boundaries. Balancing tradition and innovation requires integrating the timeless principles of classicism with the dynamic progress driven by expansionism to foster sustainable cultural and intellectual development. Achieving this balance ensures respect for historical foundations while encouraging creativity and adaptation in a constantly evolving world.
Classicism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com