Abstract Expressionism revolutionized art by emphasizing spontaneous, automatic, or subconscious creation, breaking away from traditional representational forms. This movement embraced bold colors, dynamic brushstrokes, and emotional intensity to convey the artist's inner experience rather than depicting the external world. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how Abstract Expressionism transformed modern art and influenced contemporary creative practices.
Table of Comparison
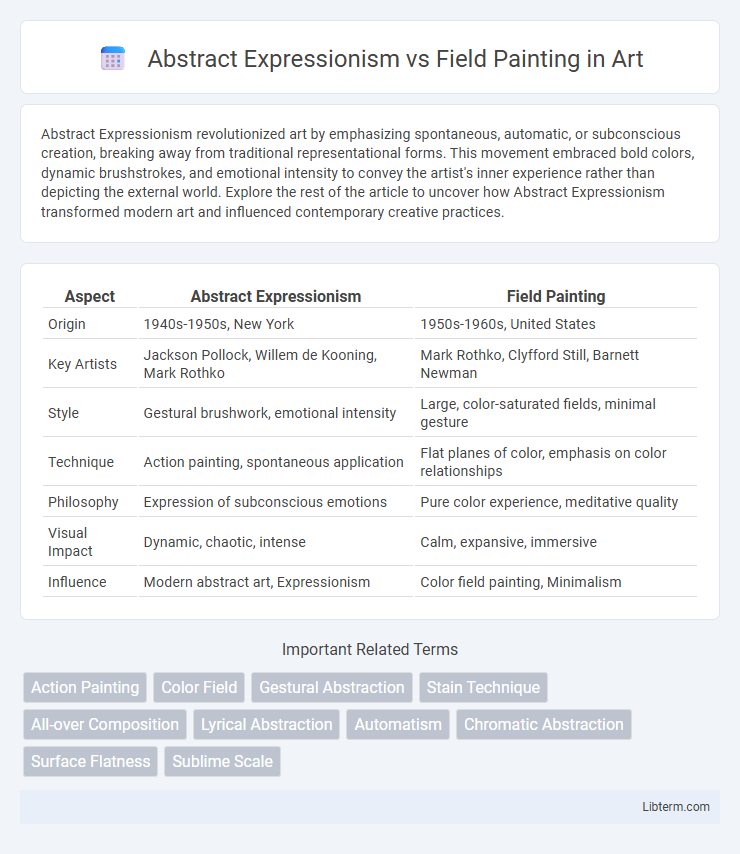
| Aspect | Abstract Expressionism | Field Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 1940s-1950s, New York | 1950s-1960s, United States |
| Key Artists | Jackson Pollock, Willem de Kooning, Mark Rothko | Mark Rothko, Clyfford Still, Barnett Newman |
| Style | Gestural brushwork, emotional intensity | Large, color-saturated fields, minimal gesture |
| Technique | Action painting, spontaneous application | Flat planes of color, emphasis on color relationships |
| Philosophy | Expression of subconscious emotions | Pure color experience, meditative quality |
| Visual Impact | Dynamic, chaotic, intense | Calm, expansive, immersive |
| Influence | Modern abstract art, Expressionism | Color field painting, Minimalism |
Introduction to Abstract Expressionism and Field Painting
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the 1940s as a post-World War II art movement centered in New York, emphasizing spontaneous, automatic, or subconscious creation with artists like Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning pushing emotional intensity. Field Painting, a subset of Abstract Expressionism pioneered by artists such as Mark Rothko and Barnett Newman, emphasizes large color fields and a focus on surface simplicity to evoke contemplative responses rather than dynamic brushwork. Both movements revolutionized modern art by shifting focus from figurative representation to emotional depth and experiential color use.
Historical Context and Emergence
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the late 1940s in New York City as a response to the post-World War II cultural climate, emphasizing emotional intensity and individual expression through spontaneous, gestural brushstrokes. Field Painting, evolving concurrently within the Abstract Expressionist movement, focused on large fields of flat, solid color to evoke mood and spatial depth, moving away from overt emotionalism toward a more contemplative visual experience. Both styles reflected a shift in the art world's center from Europe to America, highlighting a historical transformation in artistic priorities and techniques during the mid-20th century.
Key Philosophies and Artistic Intent
Abstract Expressionism emphasizes spontaneous, emotional intensity and the artist's individual gesture as a direct expression of subconscious creativity. Field Painting prioritizes large, flat expanses of color to evoke contemplative experiences and universal emotional responses, focusing on balance and color relationships rather than personal narrative. The key philosophical divergence lies in action and expression in Abstract Expressionism versus meditative presence and color harmony in Field Painting.
Major Artists and Influencers
Abstract Expressionism was pioneered by major artists such as Jackson Pollock, Willem de Kooning, and Mark Rothko, who emphasized spontaneous, dynamic brushwork and emotional intensity. Field Painting, a subset often associated with Color Field painters like Helen Frankenthaler and Barnett Newman, focused on large areas of color and flat spatial depth to evoke contemplative experiences. Both movements influenced each other while maintaining distinctive approaches to form and color, shaping postwar American art.
Techniques and Visual Characteristics
Abstract Expressionism employs dynamic brushstrokes, gestural marks, and spontaneous application of paint to convey intense emotion and individual expression, often featuring varied textures and layered compositions. Field Painting, a subset of Color Field painting, emphasizes large areas of solid color spread uniformly across the canvas, creating a flat, immersive visual experience with minimal brushwork or visible gestures. While Abstract Expressionism showcases energetic movement and complex surfaces, Field Painting relies on simplicity, color harmony, and expansive spatial effects to evoke mood.
Color Use and Composition
Abstract Expressionism emphasizes dynamic, gestural brushstrokes and intense color contrasts to evoke emotional intensity, frequently featuring complex, layered compositions. Field Painting prioritizes large, flat expanses of uniform color, creating immersive, meditative spaces through minimalistic composition with subtle variations in hue and tone. Both movements revolutionized color use and composition by shifting focus from representational forms to pure visual experience and emotional resonance.
Emotional Impact vs Intellectual Approach
Abstract Expressionism emphasizes raw emotional intensity through dynamic brushstrokes and vivid color contrasts, creating a visceral connection with the viewer. Field Painting, a subset of Color Field painting, prioritizes large expanses of color and subtle tonal variations to evoke a meditative and contemplative experience, engaging the viewer's intellect more than emotional turbulence. The emotional impact of Abstract Expressionism contrasts with the intellectual approach of Field Painting, highlighting different modes of artistic expression within mid-20th century American art.
Reception and Critical Debates
Abstract Expressionism, celebrated for its dynamic brushwork and emotional intensity, received widespread acclaim in the mid-20th century, with critics like Harold Rosenberg championing the movement's emphasis on spontaneity and individual expression. Field Painting, characterized by large expanses of color and minimal gesture, sparked debates among art critics regarding its perceived austerity and the reduction of emotional content, prompting figures such as Clement Greenberg to advocate for its purity and formal innovation. The critical discourse highlighted tensions between action-driven creativity in Abstract Expressionism and the contemplative serenity in Field Painting, shaping the trajectory of postwar American art criticism.
Influence on Contemporary Art
Abstract Expressionism revolutionized contemporary art by emphasizing spontaneous, emotional expression and large-scale works that conveyed inner psychological states. Field Painting, characterized by expansive color fields and minimalistic compositions, influenced the shift toward color theory and spatial perception in modern art. Both movements shaped contemporary practices, inspiring artists to explore abstraction, emotional depth, and the sensory impact of color and form.
Conclusion: Lasting Legacy and Differences
Abstract Expressionism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing spontaneous, emotive brushwork and individual expression, while Field Painting prioritized expansive color fields and flat surfaces to evoke mood and spatial depth. The lasting legacy of Abstract Expressionism lies in its influence on contemporary art movements and its role in shifting art towards personal, psychological exploration. In contrast, Field Painting's impact remains significant in its contribution to minimalism and color theory, highlighting the power of simplicity and scale in visual experience.
Abstract Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com