Oil paint offers vibrant colors and exceptional durability, making it a favorite medium for artists seeking rich texture and depth in their work. Its slow drying time allows for intricate blending and layering, enhancing the creative process and final result. Explore the rest of this article to discover tips, techniques, and the best materials to elevate your oil painting skills.
Table of Comparison
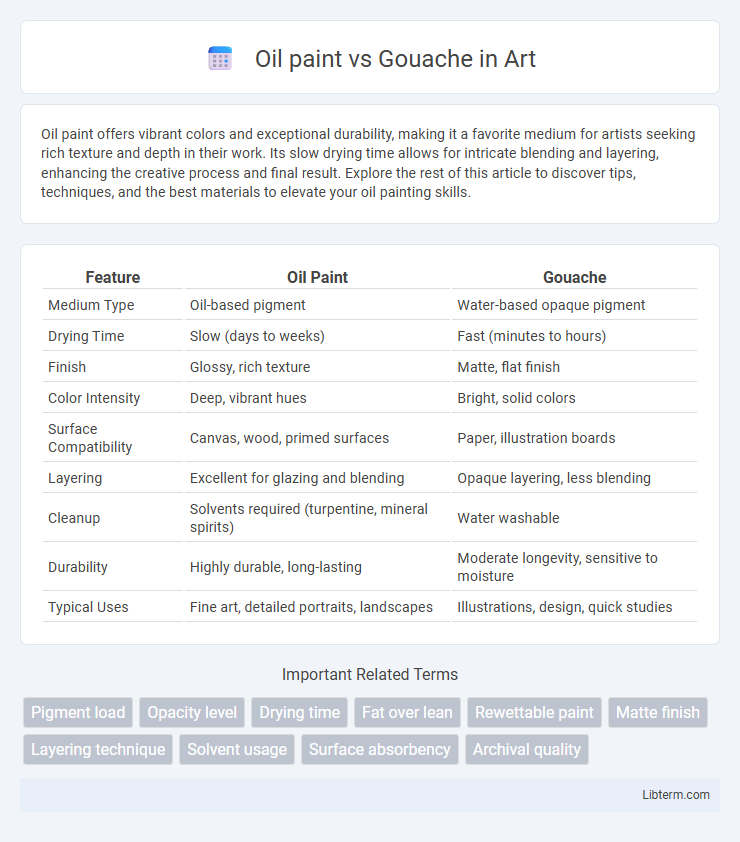
| Feature | Oil Paint | Gouache |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Type | Oil-based pigment | Water-based opaque pigment |
| Drying Time | Slow (days to weeks) | Fast (minutes to hours) |
| Finish | Glossy, rich texture | Matte, flat finish |
| Color Intensity | Deep, vibrant hues | Bright, solid colors |
| Surface Compatibility | Canvas, wood, primed surfaces | Paper, illustration boards |
| Layering | Excellent for glazing and blending | Opaque layering, less blending |
| Cleanup | Solvents required (turpentine, mineral spirits) | Water washable |
| Durability | Highly durable, long-lasting | Moderate longevity, sensitive to moisture |
| Typical Uses | Fine art, detailed portraits, landscapes | Illustrations, design, quick studies |
Introduction to Oil Paint and Gouache
Oil paint, composed of pigments suspended in drying oils like linseed, offers rich color depth and a slow drying time ideal for blending and detailed layering. Gouache, a water-based paint with opaque qualities due to added chalk or white pigment, provides vibrant, matte finishes and quick drying suitable for illustrations and graphic work. Both mediums serve distinct artistic purposes, with oil favored for texture and longevity, and gouache prized for its versatility and ease of use.
Composition and Material Differences
Oil paint consists of pigments suspended in drying oils such as linseed or walnut oil, resulting in a thick, slow-drying medium that offers rich texture and depth. Gouache is composed of pigment mixed with water and a binding agent like gum arabic, producing an opaque, matte finish that dries quickly and can be reactivated with water. The fundamental difference lies in oil's oil-based binder enabling longer manipulation and blending, while gouache's water-soluble composition allows for lighter layering and rapid drying.
Color Vibrancy and Pigmentation
Oil paint offers superior color vibrancy and rich pigmentation due to its slow drying time and oil binder, allowing pigments to refract light more effectively. Gouache, while providing matte, opaque finishes with strong pigmentation, tends to appear less luminous compared to oil paint because of its water-based binder and quicker drying characteristics. Artists seeking intense, glowing colors typically prefer oil paint, whereas gouache is favored for its flat, even color coverage and ease of layering.
Drying Time and Layering Techniques
Oil paint typically requires several days to weeks to dry, allowing extensive blending and smooth transitions between layers, which can be reworked multiple times before fully curing. Gouache dries rapidly, usually within 15 to 30 minutes, enabling fast layering but demanding precision as reworking can disturb underlying layers and cause lifting. The slow drying of oil paint benefits techniques such as glazing and wet-on-wet, while gouache's quick drying suits opaque layering and flat color applications.
Surface Compatibility and Preparation
Oil paint requires a primed surface, typically canvas or wood, to prevent absorption and ensure proper adhesion, often using gesso as a preparatory layer. Gouache performs well on paper or board and demands minimal surface preparation, as its opaque, water-based formula adheres directly without priming. Understanding these differences optimizes texture, durability, and color vibrancy for each medium's unique characteristics.
Finish and Texture Comparison
Oil paint produces a rich, glossy finish with a smooth, buttery texture that allows for intricate blending and layering, resulting in depth and luminosity. Gouache, by contrast, dries to a matte, opaque finish with a velvety surface, offering a flat texture ideal for bold, solid coverage and quick drying times. The finish and texture differences make oil paint suitable for detailed, textured artworks, while gouache excels in graphic, vibrant designs with uniform color consistency.
Flexibility and Reworking Capabilities
Oil paint offers superior flexibility due to its slow drying time, allowing artists to blend colors seamlessly and rework areas multiple times without compromising the texture or finish. Gouache, while fast-drying and opaque, has limited reworking capabilities once dry, often requiring scraping or overpainting to make adjustments. The choice between oil paint and gouache heavily depends on the artist's need for extended manipulation and layering possibilities during the painting process.
Archival Quality and Longevity
Oil paint offers exceptional archival quality and longevity due to its slow drying process and durable oil-based binder, which resists fading and cracking over centuries when properly maintained. Gouache, while vibrant and opaque, typically contains water-soluble ingredients that make it more vulnerable to moisture damage and fading over time unless sealed carefully. Artists seeking long-term preservation often prefer oil paint for its proven stability in archival collections and historical artworks.
Common Artistic Uses and Styles
Oil paint is favored for its rich texture and slow drying time, allowing artists to create detailed, layered works often seen in classical realism and portraiture. Gouache is prized for its vibrant opacity and quick drying, making it ideal for graphic design, illustration, and watercolor-style paintings with bold, flat areas of color. Both mediums serve distinctive artistic styles, with oil excelling in depth and blending, while gouache suits precision and matte finishes.
Choosing Between Oil Paint and Gouache
Choosing between oil paint and gouache depends on desired texture, drying time, and finish; oil paint offers rich, glossy textures with slow drying suitable for blending, while gouache provides matte, opaque results with quick drying ideal for detailed, layered work. Artists prioritizing durability and vibrant color depth often prefer oil paint, whereas those seeking portability and ease of correction gravitate toward gouache. Understanding the medium's chemical properties and application methods ensures the best choice for specific artistic goals.
Oil paint Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com