A primer is a preparatory coating applied before painting to ensure better adhesion of paint to the surface, increase paint durability, and provide additional protection to the material being painted. It helps to create a smooth and uniform base, covering imperfections and preventing stains from bleeding through the topcoat. Discover how choosing the right primer can enhance your painting project by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
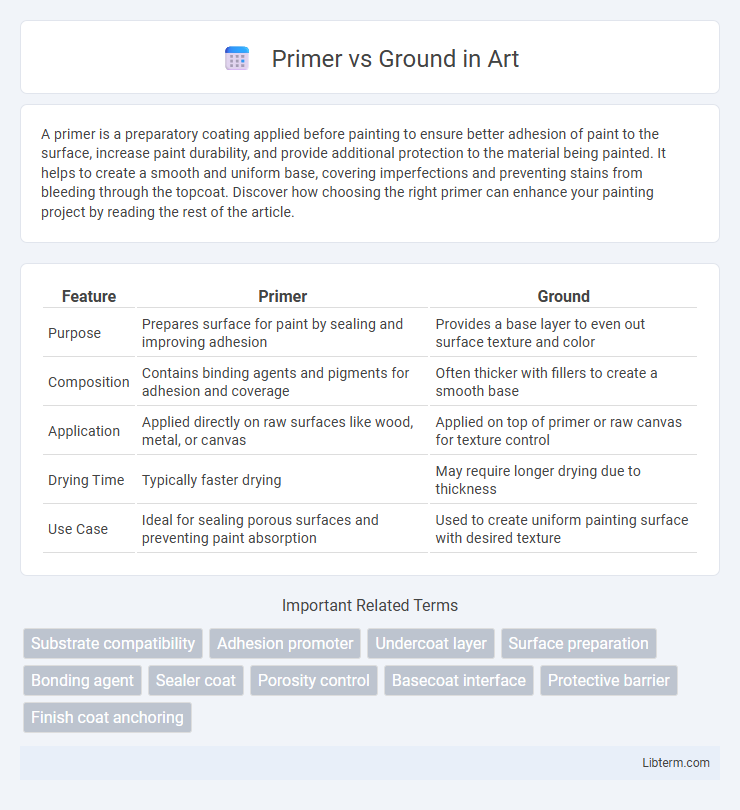
| Feature | Primer | Ground |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prepares surface for paint by sealing and improving adhesion | Provides a base layer to even out surface texture and color |
| Composition | Contains binding agents and pigments for adhesion and coverage | Often thicker with fillers to create a smooth base |
| Application | Applied directly on raw surfaces like wood, metal, or canvas | Applied on top of primer or raw canvas for texture control |
| Drying Time | Typically faster drying | May require longer drying due to thickness |
| Use Case | Ideal for sealing porous surfaces and preventing paint absorption | Used to create uniform painting surface with desired texture |
Understanding Primer and Ground: Key Differences
Primer is a preparatory coating applied to surfaces before painting, enhancing paint adhesion and durability by sealing porous materials and preventing peeling or rust. Ground, specifically in art contexts, refers to the initial layer applied to a canvas or panel, creating a uniform surface that improves paint application and longevity. The key difference lies in their purpose and composition: primer is primarily functional for protection and adhesion in construction and automotive industries, while ground is tailored for fine art, emphasizing texture and absorbency for painting techniques.
What is Primer? Definition and Function
Primer is a preparatory coating applied to surfaces before painting to enhance adhesion and durability. It seals porous materials, preventing paint from soaking in unevenly and ensuring a consistent finish. Primers also protect surfaces from moisture, rust, and other damage, extending the lifespan of the paint job.
What is Ground? Definition and Function
Ground refers to a type of paint applied to a surface to create a stable, uniform foundation for subsequent layers, enhancing adhesion and durability. It often contains fillers and binders that seal porous surfaces, preventing paint absorption and improving overall finish quality. Ground helps to protect the substrate from moisture and environmental damage, ensuring long-lasting performance of the paint system.
When to Use Primer vs Ground in Painting
Primer is essential for preparing new or bare surfaces by sealing porous materials and promoting adhesion, while ground is typically used in artistic painting to create a smooth, uniform base on canvas or panels. Use primer when dealing with surfaces like wood, metal, or drywall to enhance paint durability and prevent peeling. Choose ground when working with fine art materials to ensure even paint absorption and longevity of the artwork.
Chemical Composition: Primer vs Ground
Primer contains organic solvents, binders, and reactive chemical compounds designed to enhance adhesion and corrosion resistance on metal or wood surfaces. Ground, often composed of inert pigments like titanium dioxide combined with fillers and a neutral binder, serves primarily to create a uniform, sealed surface for paint application. The chemical composition of primer is more complex, aiming to interact chemically with substrates, whereas ground provides a physical barrier without significant chemical reactivity.
Types of Primers and Grounds
Primers include types such as bonding primers for challenging surfaces, moisture-resistant primers for damp environments, and stain-blocking primers that prevent discoloration through paint layers. Grounds commonly consist of drywall, plaster, or wood panels prepared to receive paint, with specific ground treatments like sealed gypsum board or primed MDF enhancing adhesion and durability. Selecting the correct primer type for the specific ground ensures optimal paint performance and longevity.
Application Techniques for Primer and Ground
Primer and ground serve as foundational layers in painting, each requiring distinct application techniques to optimize surface preparation. Primer is typically applied in thin, even coats using a brush, roller, or spray to seal the surface and enhance paint adhesion, while ground involves a more textured, thicker application with a palette knife or brush to create absorbency and tooth for subsequent paint layers. Mastery of these methods ensures durability and vibrancy in the final artwork by controlling moisture absorption and pigment binding effectively.
Pros and Cons: Primer vs Ground
Primer offers superior adhesion to bare surfaces, creating a strong base for paint and preventing peeling or blistering, but it can be more time-consuming to apply and requires proper drying time. Ground provides a uniform, sealed surface that enhances paint coverage and color vibrancy, though it may lack the deep bonding properties of a primer and might not block stains effectively. Choosing between primer and ground depends on the project's specific needs, such as the surface condition and desired finish durability.
Compatibility with Various Surfaces
Primer offers superior adhesion by creating a uniform base, making it compatible with diverse surfaces such as wood, metal, plastic, and drywall. Ground is typically a thicker, textured layer used mainly in painting to enhance paint grip but may not bond as effectively to non-porous substrates. Choosing the right primer ensures optimal surface compatibility, improving durability and finish quality across various materials.
Choosing the Right Base: Primer or Ground?
Choosing the right base between primer and ground depends on the surface and medium used; primers create a sealed, uniform layer ideal for non-porous surfaces and acrylics, while grounds offer textured absorption preferred for oil and traditional painting. Primer enhances adhesion and prevents paint from soaking into the surface, ensuring longevity and color vibrancy, whereas ground modifies surface texture and absorbency for optimal paint application. Evaluating the type of paint, substrate condition, and desired finish guides the decision for using primer or ground to achieve professional results.
Primer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com