Digital art harnesses advanced technology to create visually captivating and innovative pieces that transcend traditional artistic methods. Techniques range from algorithmic design and digital painting to 3D modeling, enabling unparalleled creative freedom and precision. Explore the rest of the article to discover how digital art can transform your creative expression in today's tech-driven world.
Table of Comparison
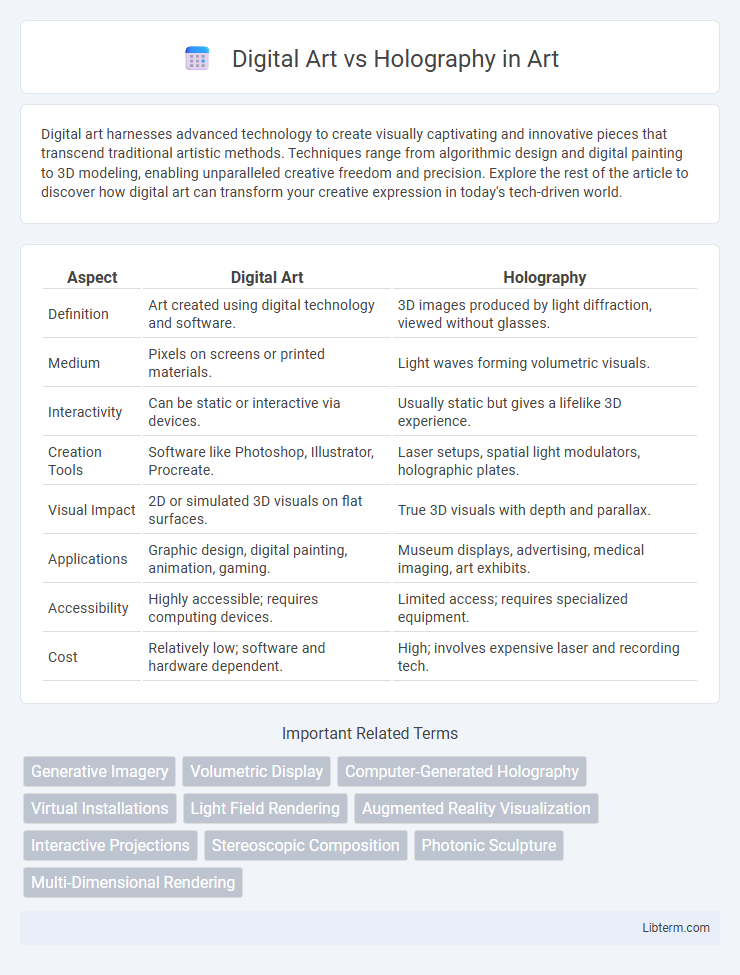
| Aspect | Digital Art | Holography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created using digital technology and software. | 3D images produced by light diffraction, viewed without glasses. |
| Medium | Pixels on screens or printed materials. | Light waves forming volumetric visuals. |
| Interactivity | Can be static or interactive via devices. | Usually static but gives a lifelike 3D experience. |
| Creation Tools | Software like Photoshop, Illustrator, Procreate. | Laser setups, spatial light modulators, holographic plates. |
| Visual Impact | 2D or simulated 3D visuals on flat surfaces. | True 3D visuals with depth and parallax. |
| Applications | Graphic design, digital painting, animation, gaming. | Museum displays, advertising, medical imaging, art exhibits. |
| Accessibility | Highly accessible; requires computing devices. | Limited access; requires specialized equipment. |
| Cost | Relatively low; software and hardware dependent. | High; involves expensive laser and recording tech. |
Understanding Digital Art: Definition and Evolution
Digital art, a form of artistic expression created through digital technology, has evolved from basic pixel-based images to complex multimedia installations utilizing software, graphics tablets, and virtual reality tools. It encompasses a wide range of styles and techniques, including 3D modeling, digital painting, and algorithmic art, reflecting the integration of technology with creative processes. The evolution of digital art parallels advancements in computer graphics, interactivity, and the internet, enabling both accessibility and global distribution.
Holography Explained: Technology and Applications
Holography uses coherent light sources like lasers to record and reconstruct three-dimensional images by capturing the light field's amplitude and phase information. Applications of holography include data storage, security features in banknotes, medical imaging, and advanced display technologies for augmented and virtual reality. Its ability to create realistic, multidimensional visuals distinguishes it from digital art, which primarily relies on two-dimensional rendering and software-based effects.
Key Differences Between Digital Art and Holography
Digital art utilizes computer software to create two-dimensional or three-dimensional images displayed on screens or printed media, emphasizing pixel-based or vector graphics. Holography, by contrast, produces three-dimensional images by recording and reconstructing light fields, enabling viewers to perceive depth and spatial relationships without special glasses. While digital art primarily exists in virtual or flat physical forms, holography offers a more immersive visual experience that interacts with light and perspective in real space.
Creative Processes: Digital Tools vs. Holographic Methods
Digital art leverages software like Adobe Photoshop, Procreate, and 3D modeling tools to enable artists to manipulate pixels, layers, and vectors for intricate designs and easy editing. Holographic methods involve capturing light interference patterns using lasers and optical setups to create three-dimensional images that can be viewed from multiple angles without special glasses. While digital tools emphasize flexibility and versatility in creating and modifying artworks, holography requires precise physical processes and equipment to produce immersive, spatial visual experiences.
Immersive Experiences: 2D vs. 3D Visual Impact
Digital art primarily offers 2D visual experiences using screens and projections, engaging viewers through intricate designs and interactive elements. Holography generates true 3D images that occupy physical space, allowing observers to experience depth and movement from multiple angles. The immersive impact of holography surpasses digital art by creating a tangible presence that enhances spatial perception and realism.
Accessibility and Distribution: Digital Files vs. Holograms
Digital art offers unparalleled accessibility through its distribution as easily shareable files compatible with various devices and platforms, enabling instant global dissemination. In contrast, holography involves physical or specialized display equipment, limiting widespread access and requiring specific environments for viewing. The scalability of digital files reduces barriers to entry for artists and audiences, whereas holograms demand higher production costs and technical expertise, impacting their distribution and accessibility.
Artistic Expression and Constraints in Both Mediums
Digital art offers boundless creative freedom through versatile software tools, enabling artists to manipulate colors, shapes, and textures with precision and endless iteration. Holography presents unique constraints due to its reliance on light diffraction and three-dimensional projection, demanding advanced technical knowledge and limiting spontaneous modifications once created. Artistic expression in holography combines visual depth with spatial presence, creating immersive experiences that contrast with the flat, highly editable nature of digital art.
Preservation and Longevity: Durability of Digital Art vs. Holography
Digital art relies on digital storage mediums such as hard drives and cloud servers, which are susceptible to data corruption, hardware failure, and format obsolescence, posing challenges for long-term preservation. Holography, on the other hand, uses physical holographic plates or films that can last for decades if stored in controlled environments, offering greater durability against digital degradation. Preservation strategies for digital art often involve regular data migration and backups, while holography benefits from its tangible form that is less reliant on evolving technology.
Market Trends: Collecting Digital Art versus Holographic Artworks
The market for digital art continues to expand rapidly, driven by the rise of NFTs and blockchain technology, which facilitate secure ownership and provenance tracking. Holographic artworks, while niche, are gaining traction in luxury and experiential markets due to their immersive and three-dimensional qualities, commanding higher prices at specialized auctions. Collectors of digital art prioritize liquidity and global accessibility, whereas holographic art collectors focus on rarity and the physicality of holograms, reflecting distinct market demand dynamics.
Future Innovations: Merging Digital Art with Holography
Future innovations in merging digital art with holography promise immersive, three-dimensional experiences where interactive, dynamic visuals transcend traditional screens. Advancements in light-field technology and AI-driven rendering will enable artists to create holograms that respond to viewer movements and environmental cues in real time. This fusion is set to redefine creative expression across entertainment, education, and virtual collaboration, blending digital creativity with spatial reality.
Digital Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com