Abstract art transcends traditional representation by emphasizing shapes, colors, and forms to evoke emotions and ideas. This artistic style encourages personal interpretation, allowing Your imagination to connect with the artwork uniquely. Explore the rest of the article to discover how abstract art can transform your perception of creativity.
Table of Comparison
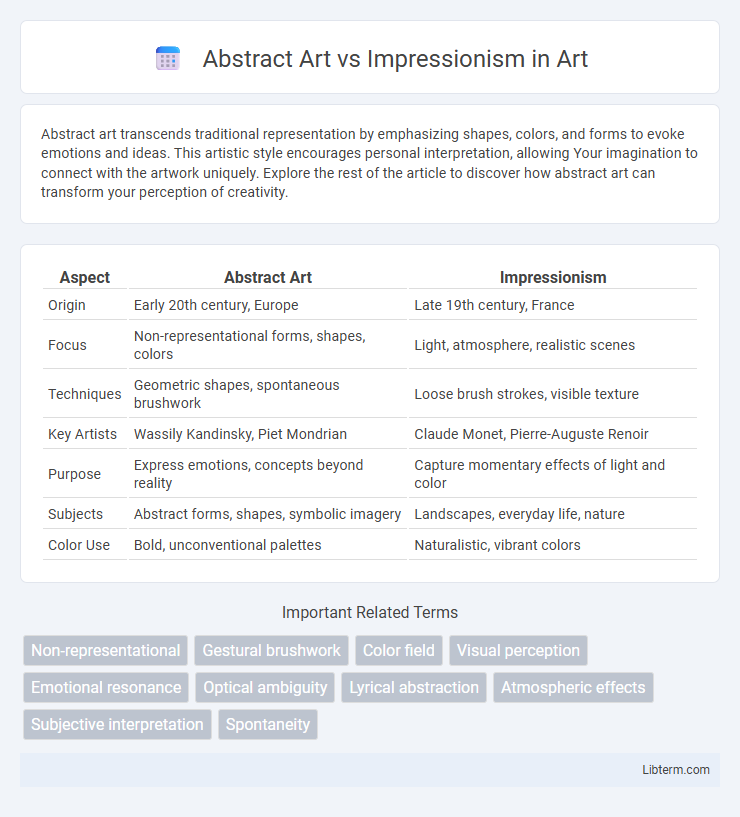
| Aspect | Abstract Art | Impressionism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Early 20th century, Europe | Late 19th century, France |
| Focus | Non-representational forms, shapes, colors | Light, atmosphere, realistic scenes |
| Techniques | Geometric shapes, spontaneous brushwork | Loose brush strokes, visible texture |
| Key Artists | Wassily Kandinsky, Piet Mondrian | Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir |
| Purpose | Express emotions, concepts beyond reality | Capture momentary effects of light and color |
| Subjects | Abstract forms, shapes, symbolic imagery | Landscapes, everyday life, nature |
| Color Use | Bold, unconventional palettes | Naturalistic, vibrant colors |
Introduction to Abstract Art and Impressionism
Abstract art emphasizes non-representational forms, using shapes, colors, and lines to convey emotions and ideas beyond visual reality. Impressionism captures fleeting moments and light effects through loose brushwork and vibrant colors, focusing on everyday scenes. Both movements revolutionized art by challenging traditional techniques and perspectives in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Historical Background of Both Movements
Impressionism emerged in the late 19th century in France, characterized by artists like Claude Monet and Pierre-Auguste Renoir who sought to capture light and everyday scenes with loose brushwork and vibrant colors. Abstract art developed in the early 20th century, pioneered by figures such as Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian, emphasizing non-representational forms and exploring color, shape, and line independently of real-world references. Both movements arose as reactions to traditional artistic conventions, with Impressionism challenging academic realism and Abstract Art breaking further away into pure abstraction.
Key Characteristics of Abstract Art
Abstract art emphasizes non-representational forms, using shapes, colors, and textures to evoke emotions without depicting recognizable objects. It relies on techniques like geometric patterns, bold color contrasts, and dynamic compositions to create a visual experience beyond literal interpretation. This contrasts with Impressionism's focus on capturing light and natural scenes through visible brushstrokes and realistic subjects.
Key Features of Impressionism
Impressionism is characterized by visible brush strokes, vibrant colors, and an emphasis on capturing light and natural scenes in a momentary feel. This movement focuses on everyday subjects and outdoor settings, often depicting fleeting effects of light and atmosphere. Unlike Abstract Art, which prioritizes non-representational forms and conceptual expression, Impressionism maintains recognizable objects and scenes with an innovative approach to perception and color.
Notable Artists: Abstract vs Impressionism
Notable artists in Abstract Art include Wassily Kandinsky, Piet Mondrian, and Jackson Pollock, who emphasized non-representational forms and emotional expression through color and shape. Impressionism features iconic figures such as Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, and Pierre-Auguste Renoir, renowned for their focus on light, natural scenes, and brushstroke techniques that capture fleeting moments. The contrast lies in Abstract artists prioritizing inner experience and conceptual interpretation, while Impressionists capture observable reality and atmospheric effects.
Techniques and Materials Used
Abstract art utilizes non-representational forms, emphasizing bold colors, dynamic shapes, and innovative use of mixed media such as acrylics, collage, and digital materials to evoke emotions rather than depict reality. Impressionism employs loose, visible brushstrokes, natural light effects, and a vibrant palette, primarily using oil paints on canvas to capture fleeting moments and the nuances of outdoor scenes. Both movements prioritize texture and layering, but abstract artists explore experimental techniques like dripping and scraping, while Impressionists focus on capturing atmospheric conditions through optical color blending.
Artistic Goals and Philosophies
Abstract Art emphasizes non-representational forms, aiming to evoke emotions and ideas through color, shape, and texture without depicting reality explicitly. Impressionism focuses on capturing the transient effects of light and atmosphere, emphasizing natural scenes and everyday moments with loose brushwork and vibrant palettes. Both movements challenge traditional artistic conventions but diverge in intent: Impressionism seeks to represent sensory experiences, while Abstract Art explores inner concepts and pure visual expression.
Influence on Modern and Contemporary Art
Abstract Art revolutionized modern and contemporary art by emphasizing non-representational forms and emotional expression, influencing movements such as Minimalism and Abstract Expressionism. Impressionism, with its focus on light, color, and momentary perception, laid the groundwork for modern visual techniques and inspired subsequent explorations in plein air painting and color theory. Both movements challenged traditional artistic conventions, shaping the trajectory of 20th and 21st-century art innovation.
Visual Impact and Emotional Response
Abstract Art uses bold colors, shapes, and forms to evoke strong emotional reactions through non-representational visuals, emphasizing personal interpretation and subjective experience. Impressionism captures fleeting moments with loose brushwork and light play, creating a softer, more naturalistic visual impact that conveys the transient beauty of everyday scenes. Both styles engage viewers emotionally, but Abstract Art pushes boundaries of perception while Impressionism invites contemplation of reality's subtle nuances.
Legacy and Cultural Significance
Abstract Art revolutionized visual expression by breaking free from representational forms, influencing modern and contemporary art movements worldwide. Impressionism's legacy lies in its pioneering use of light and color to capture fleeting moments, profoundly shaping the development of modern art in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Both movements significantly altered cultural perspectives on creativity, inspiring new artistic freedoms and continuing to impact art education and appreciation globally.
Abstract Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com