Digital printing offers high-quality, cost-effective solutions for producing vibrant images and sharp text on various materials with quick turnaround times. This method enhances customization and flexibility, enabling you to meet specific design needs without the limitations of traditional printing techniques. Explore the rest of the article to discover how digital printing can transform your creative projects efficiently.
Table of Comparison
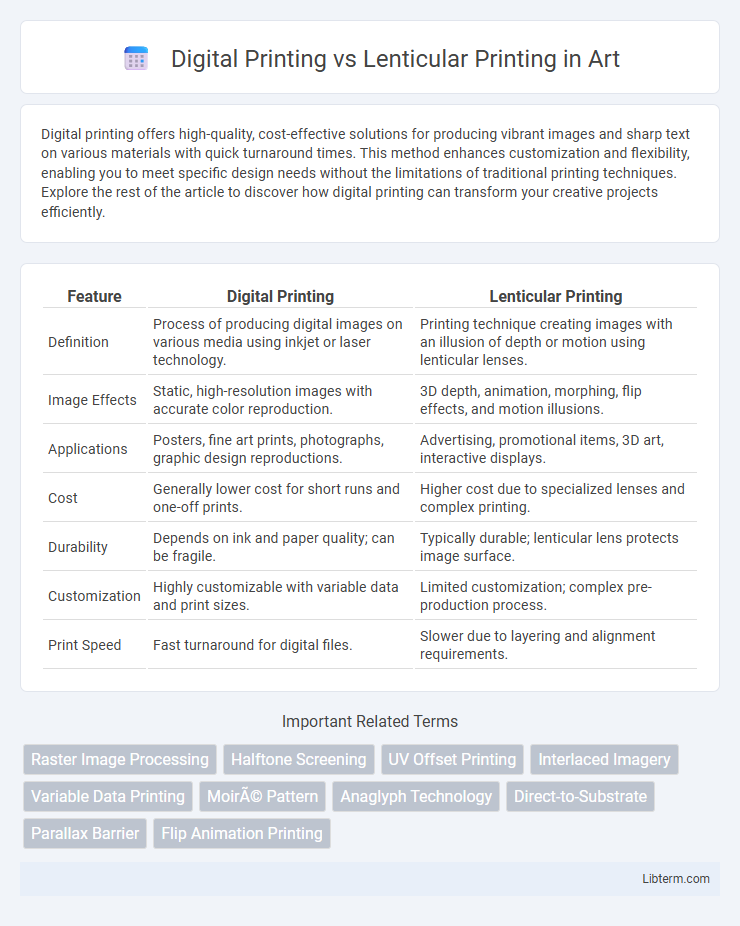
| Feature | Digital Printing | Lenticular Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of producing digital images on various media using inkjet or laser technology. | Printing technique creating images with an illusion of depth or motion using lenticular lenses. |
| Image Effects | Static, high-resolution images with accurate color reproduction. | 3D depth, animation, morphing, flip effects, and motion illusions. |
| Applications | Posters, fine art prints, photographs, graphic design reproductions. | Advertising, promotional items, 3D art, interactive displays. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for short runs and one-off prints. | Higher cost due to specialized lenses and complex printing. |
| Durability | Depends on ink and paper quality; can be fragile. | Typically durable; lenticular lens protects image surface. |
| Customization | Highly customizable with variable data and print sizes. | Limited customization; complex pre-production process. |
| Print Speed | Fast turnaround for digital files. | Slower due to layering and alignment requirements. |
Introduction to Digital and Lenticular Printing
Digital printing utilizes advanced inkjet or laser technology to produce high-resolution images directly from digital files, offering quick turnaround and cost-effective customization for various materials. Lenticular printing involves creating images that appear to change or move when viewed from different angles by embedding lenses over specially printed graphics, enhancing visual engagement in advertising and packaging. Both techniques serve distinct marketing needs, with digital printing excelling in versatility and lenticular printing specializing in dynamic visual effects.
Key Differences Between Digital and Lenticular Printing
Digital printing utilizes inkjet or laser technology to produce high-resolution images directly on various surfaces, offering quick turnaround and cost-effectiveness for short runs. Lenticular printing, on the other hand, involves creating images with lenticular lenses to produce 3D effects, motion, or depth perception, which requires precise alignment and specialized materials. Key differences include the visual output--flat images versus dynamic effects--and the complexity and cost, with lenticular printing demanding more intricate setup and higher production expenses.
How Digital Printing Works
Digital printing works by transferring digital images directly onto various substrates using inkjet or laser technology, allowing for high-resolution, full-color prints with minimal setup time. The process involves precise control of ink droplets or toner particles to produce detailed and vibrant images, making it ideal for short runs and custom designs. Unlike lenticular printing, which requires specialized lenses to create 3D or animated effects, digital printing emphasizes speed, flexibility, and cost-efficiency in producing flat images.
How Lenticular Printing Works
Lenticular printing creates images that change or move as the viewing angle shifts by using a series of interlaced images combined with a lenticular lens sheet made of tiny cylindrical lenses. These lenses direct light from different images into each eye, producing effects like 3D depth, flip, or animation without special glasses. The precise alignment of the interlaced images with the lens array is crucial for achieving smooth lenticular effects, distinguishing it from standard digital printing techniques.
Print Quality Comparison: Digital vs Lenticular
Digital printing offers high-resolution, vibrant color accuracy ideal for detailed images and small text, producing consistent results on various substrates. Lenticular printing, however, excels in creating dynamic visual effects such as 3D depth and motion by using specialized lenticular lenses, although it may have lower resolution and visible interlacing lines compared to digital prints. For print quality, digital delivers sharper clarity and fine detail, while lenticular prioritizes visual interaction and novelty effects over image precision.
Cost and Production Considerations
Digital printing offers lower setup costs and faster turnaround times, making it ideal for short runs and customized prints with high-resolution color fidelity. Lenticular printing involves higher initial investment due to the specialized lenses and complex image preparation, suitable for creating 3D or animated effects in medium to large print runs. Production for lenticular requires precise alignment and skilled labor, increasing overall expenses compared to the streamlined, automated processes of digital printing.
Applications and Use Cases
Digital printing excels in producing high-quality images on various materials, making it ideal for customized marketing materials, packaging, and short-run production. Lenticular printing is primarily used for creating visual effects such as 3D depth or motion, often applied in promotional displays, product packaging, and novelty items. Both printing methods serve distinct purposes: digital printing for versatility and speed, lenticular for eye-catching, interactive visual engagement.
Advantages of Digital Printing
Digital printing offers high-speed production and cost-efficiency for short runs, making it ideal for customized and on-demand projects. It delivers sharp, vibrant colors with precise detail and supports a wide variety of substrates and finishes. Unlike lenticular printing, digital printing provides greater flexibility and faster turnaround without the need for specialized materials or complex alignment processes.
Advantages of Lenticular Printing
Lenticular printing offers distinct advantages such as producing eye-catching 3D effects and motion illusions that digital printing cannot replicate, enhancing user engagement and product appeal. It provides a unique tactile experience and durability suited for marketing materials requiring visual impact and longevity. This printing technique excels in applications like packaging, promotional displays, and signage where visual interaction drives consumer attention and brand differentiation.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Project
Digital printing offers fast turnaround and high-resolution images, ideal for short runs and detailed graphics, while lenticular printing delivers eye-catching 3D effects or animations, perfect for promotional materials requiring visual impact. Evaluate your project goals, budget, and desired viewer experience to determine the best method; choose digital printing for cost-effective, precise color reproduction or lenticular printing for dynamic, interactive displays. Consider production volume and durability requirements to ensure the selected printing technique aligns with your marketing objectives and target audience engagement.
Digital Printing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com