Formalism focuses on analyzing the structure, style, and techniques used in literary works, emphasizing how form shapes meaning. It prioritizes close reading of the text itself rather than external context such as author intention or historical background. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how formalist theory unveils the intricate craftsmanship behind literature.
Table of Comparison
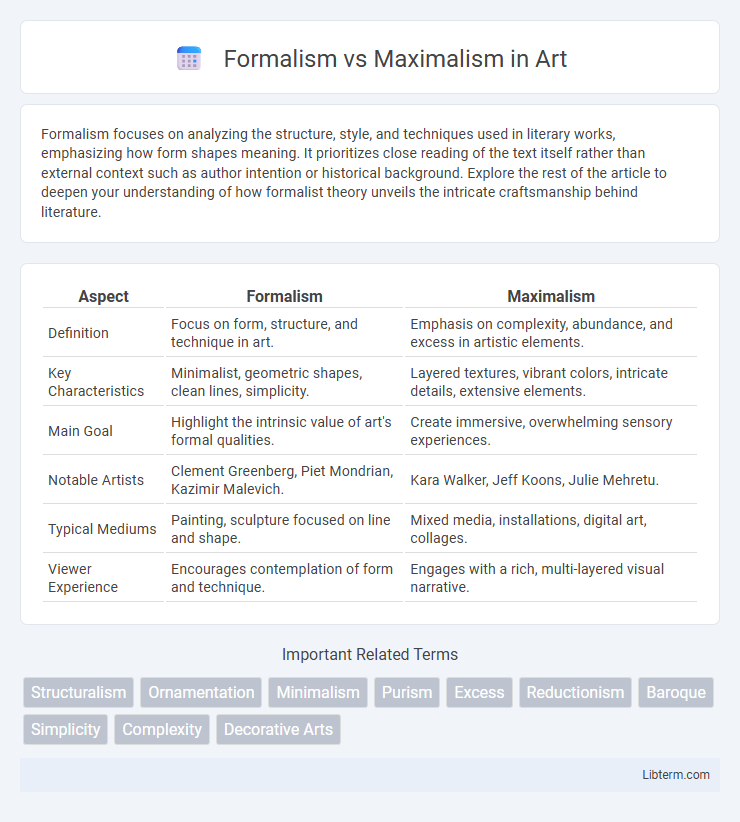
| Aspect | Formalism | Maximalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on form, structure, and technique in art. | Emphasis on complexity, abundance, and excess in artistic elements. |
| Key Characteristics | Minimalist, geometric shapes, clean lines, simplicity. | Layered textures, vibrant colors, intricate details, extensive elements. |
| Main Goal | Highlight the intrinsic value of art's formal qualities. | Create immersive, overwhelming sensory experiences. |
| Notable Artists | Clement Greenberg, Piet Mondrian, Kazimir Malevich. | Kara Walker, Jeff Koons, Julie Mehretu. |
| Typical Mediums | Painting, sculpture focused on line and shape. | Mixed media, installations, digital art, collages. |
| Viewer Experience | Encourages contemplation of form and technique. | Engages with a rich, multi-layered visual narrative. |
Understanding Formalism: Definition and Principles
Formalism in art and literature emphasizes the importance of form, structure, and stylistic elements over content or context, prioritizing composition, technique, and linguistic features. Key principles include focusing on the intrinsic features of the work itself, such as narrative devices, meter, and symbolism, to derive meaning without external references. This approach allows for a concentrated analysis of how artistic elements function to create aesthetic experience and meaning within the boundaries of the work.
Exploring Maximalism: Key Characteristics
Maximalism embraces complexity, rich detail, and layered meanings, contrasting with Formalism's emphasis on structure and form. This artistic approach prioritizes vibrant colors, diverse textures, and elaborate compositions to create immersive, sensory experiences. Maximalism encourages bold expression and eclectic combinations, reflecting cultural diversity and emotional depth in its aesthetic.
Historical Roots: Origins of Formalism and Maximalism
Formalism originated in the early 20th century, primarily through the work of Russian Formalists like Viktor Shklovsky and Roman Jakobson, who emphasized the intrinsic features of literary texts such as structure, language, and literary devices. Maximalism emerged as a response to Modernist minimalism during the late 20th century, characterized by expansive narratives, detailed descriptions, and complexity seen in authors like David Foster Wallace and Thomas Pynchon. The historical roots of Formalism center on analytically dissecting texts to uncover universal literary principles, while Maximalism's origins are tied to pushing narrative boundaries and embracing the chaotic breadth of contemporary experience.
Formalism in Art, Literature, and Design
Formalism in art, literature, and design emphasizes the intrinsic elements such as composition, form, color, and structure over contextual or thematic content. In visual art, formalism prioritizes line, shape, and texture, while literary formalism centers on narrative techniques, syntax, and diction without external influences. Design that follows formalist principles focuses on the balance, contrast, and symmetry of visual components, valuing aesthetics and form over function or symbolism.
Maximalism Across Creative Disciplines
Maximalism across creative disciplines emphasizes complexity, boldness, and an abundance of elements, contrasting sharply with the restrained and structured approach of Formalism. This style thrives in visual arts, literature, and design by embracing a rich palette of colors, intricate patterns, and layered narratives that challenge minimalistic conventions. Maximalism encourages creative freedom and emotional intensity, fostering works that invite immersive and multifaceted interpretation.
Comparing Aesthetic Philosophies: Formalism vs Maximalism
Formalism emphasizes simplicity, order, and the intrinsic qualities of form, valuing clean lines and minimal ornamentation that highlight structure and composition. Maximalism, in contrast, embraces complexity, layering, and abundant detail to create rich, vibrant, and often eclectic visual experiences. Comparing these aesthetic philosophies reveals a fundamental tension between restraint and excess, where Formalism seeks clarity and purity, while Maximalism prioritizes intensity and exuberance.
Case Studies: Iconic Works of Formalism and Maximalism
Formalism is exemplified by works like Piet Mondrian's "Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow," emphasizing simplicity, geometric forms, and harmony, while Maximalism is represented by Gustav Klimt's "The Kiss," showcasing ornate detail, rich textures, and vibrant patterns. Case studies reveal Formalism's focus on structure, purity of form, and minimal color palettes, creating clarity and order, contrasting Maximalism's dynamic layering, extravagant decoration, and complex compositions. Iconic works in both movements highlight distinct approaches to visual storytelling, with Formalism prioritizing abstraction and essentialism, whereas Maximalism embraces exuberance and sensory richness.
Cultural Impact and Contemporary Relevance
Formalism, emphasizing structured techniques and aesthetic principles, has deeply influenced modern artistic disciplines, shaping cultural standards in architecture, literature, and visual arts by reinforcing clarity and order. Maximalism, characterized by bold complexity and rich ornamentation, has catalyzed diverse cultural movements, reflecting contemporary society's embrace of diversity, abundance, and eclectic expression. Both approaches continue to impact contemporary culture by offering contrasting frameworks that challenge creators and audiences to rethink tradition and innovation in creative practices.
Critical Debates: Strengths and Criticisms
Formalism emphasizes structure, style, and technical mastery in art and literature, praised for its clarity and discipline but criticized for neglecting content and context. Maximalism prioritizes complexity, abundance, and emotional intensity, lauded for its richness and depth yet often reproached for excess and lack of coherence. Critical debates highlight Formalism's risk of sterility versus Maximalism's potential for overwhelming chaos.
Choosing Between Formalism and Maximalism in Creative Practice
Choosing between Formalism and Maximalism in creative practice hinges on the desired impact and audience engagement; Formalism emphasizes disciplined structure, precise form, and minimalistic clarity, making it ideal for works valuing order and subtlety. Maximalism embraces complexity, layering, and sensory-rich detail, appealing to creators who seek to evoke strong emotional responses and showcase abundance. Evaluating project goals, medium constraints, and artistic intent guides the decision to adopt either the refined restraint of Formalism or the exuberant expression of Maximalism.
Formalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com