Photography captures moments with precision, transforming fleeting scenes into lasting memories through skillful use of light, composition, and timing. Mastering techniques such as exposure, focus, and framing enhances your ability to tell compelling visual stories. Explore the rest of the article to unlock tips and insights that will elevate your photography skills.
Table of Comparison
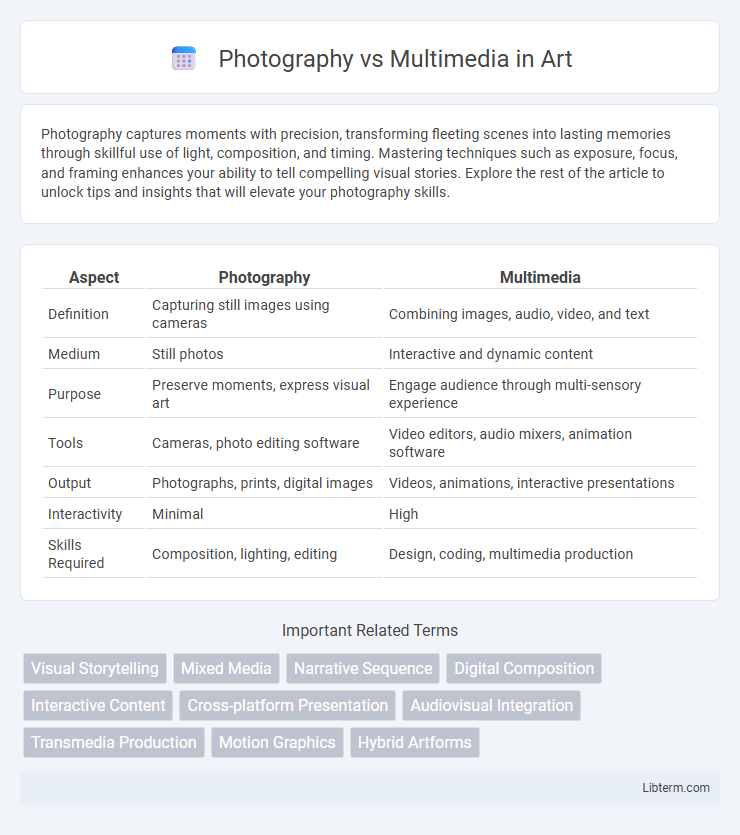
| Aspect | Photography | Multimedia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Capturing still images using cameras | Combining images, audio, video, and text |
| Medium | Still photos | Interactive and dynamic content |
| Purpose | Preserve moments, express visual art | Engage audience through multi-sensory experience |
| Tools | Cameras, photo editing software | Video editors, audio mixers, animation software |
| Output | Photographs, prints, digital images | Videos, animations, interactive presentations |
| Interactivity | Minimal | High |
| Skills Required | Composition, lighting, editing | Design, coding, multimedia production |
Understanding Photography and Multimedia
Photography captures moments through still images, emphasizing composition, lighting, and subject to convey emotion or tell a story visually. Multimedia integrates various content forms such as images, video, audio, and text to create interactive and dynamic experiences that engage multiple senses. Understanding photography involves mastering camera techniques and visual aesthetics, while multimedia requires knowledge of different media formats and tools to produce cohesive, immersive narratives.
Historical Evolution of Both Mediums
Photography originated in the early 19th century with inventions like the daguerreotype, revolutionizing visual documentation through still images. Multimedia emerged in the late 20th century, integrating photography, audio, video, and interactive elements to create dynamic experiences. The evolution from analog to digital technologies accelerated the convergence of photography and multimedia, transforming storytelling and communication across platforms.
Key Differences Between Photography and Multimedia
Photography captures still images using cameras to convey a single moment or subject with emphasis on composition, lighting, and detail. Multimedia integrates various content forms such as video, audio, graphics, and text to create dynamic and interactive experiences. The primary difference lies in photography's static visual focus versus multimedia's combination of multiple media types to engage a broader range of senses.
The Artistic Approaches in Each Field
Photography emphasizes capturing singular moments with a focus on composition, lighting, and emotion to create visually striking images. Multimedia combines various artistic elements such as video, sound, animation, and interactive features to deliver immersive and dynamic storytelling experiences. Both fields utilize creativity and technical skills but differ in their sensory engagement and narrative complexity.
Tools and Technologies Used
Photography relies heavily on digital cameras, lenses, and advanced photo editing software like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom to capture and enhance images with precision. Multimedia incorporates a broader range of technologies, including video cameras, audio recorders, animation software such as Adobe After Effects, and interactive platforms to create dynamic content that combines visuals, sound, and motion. Cutting-edge tools like drones, 360-degree cameras, and virtual reality devices further expand multimedia capabilities beyond traditional photography.
Skills Required for Photography vs Multimedia
Photography demands expertise in camera operation, lighting techniques, composition, and photo editing software such as Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom. Multimedia requires proficiency in a broader skill set including video production, graphic design, animation, sound editing, and software tools like Adobe Premiere Pro, After Effects, and Audition. Strong storytelling ability and adaptability to various digital platforms are essential skills that differentiate multimedia professionals from photographers.
Impact on Storytelling
Photography captures powerful, singular moments that evoke strong emotional responses through visual specificity and composition, creating a direct and immediate impact on storytelling. Multimedia combines images, video, audio, and interactive elements, offering a multidimensional narrative experience that enhances engagement and conveys complex stories with deeper context. The integration of diverse media types in multimedia allows for a richer, more immersive storytelling approach compared to the focused, evocative strength of individual photographic images.
Career Opportunities in Both Domains
Photography offers specialized career paths such as portrait photographer, photojournalist, and commercial photographer, emphasizing visual storytelling through still images. Multimedia careers encompass broader roles like video producer, graphic designer, and digital content creator, integrating audio, video, animation, and interactive elements to engage diverse audiences. Skills in software like Adobe Photoshop and After Effects increase employability in photography and multimedia, with multimedia roles generally offering more versatility and higher demand in digital marketing and entertainment industries.
Challenges and Limitations
Photography faces challenges such as limited storytelling scope confined to static images, dependence on lighting conditions, and constraints in conveying complex narratives. Multimedia integrates various formats like video, audio, and animation, offering enhanced engagement but encounters technical limitations, increased production costs, and the need for advanced skills in multiple domains. Both fields grapple with issues of content accessibility, copyright concerns, and balancing artistic expression with audience preferences.
Future Trends in Photography and Multimedia
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven image enhancement, 3D imaging, and immersive virtual reality are reshaping the future of photography and multimedia, enabling hyper-realistic content creation and interactive experiences. The integration of augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) in multimedia platforms is driving demand for dynamic, multimedia-rich storytelling beyond traditional photo and video formats. Advancements in computational photography and real-time rendering are crucial for seamless cross-device content delivery, highlighting the convergence between photography and multimedia industries.
Photography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com