Irony involves a contrast between expectations and reality, often highlighting the difference through humor or criticism. This literary device can appear in various forms such as verbal, situational, or dramatic irony, each creating unique effects that enrich storytelling or communication. Discover how understanding irony can deepen your appreciation of language and narrative by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
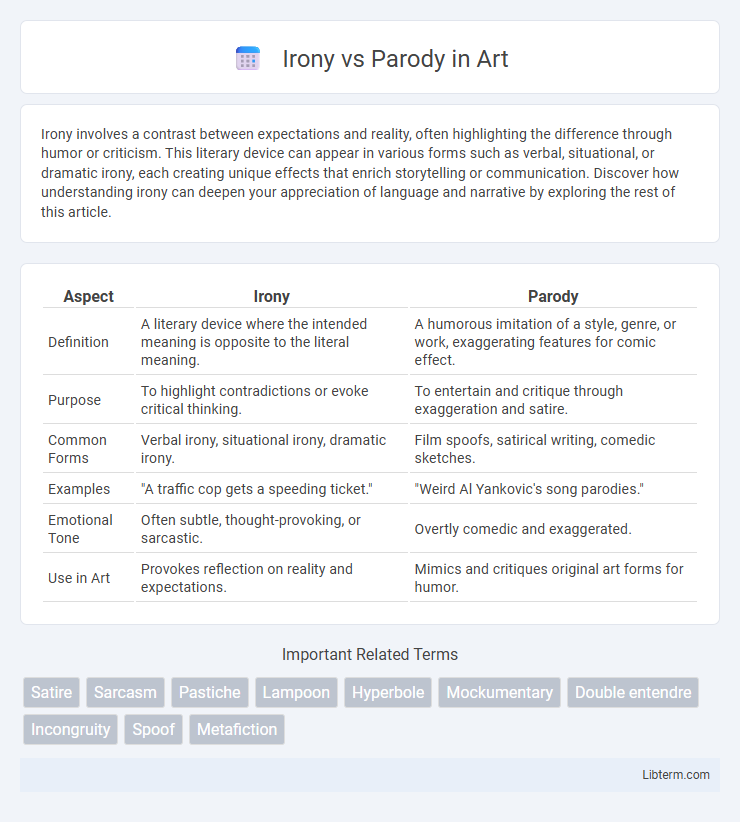
| Aspect | Irony | Parody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A literary device where the intended meaning is opposite to the literal meaning. | A humorous imitation of a style, genre, or work, exaggerating features for comic effect. |
| Purpose | To highlight contradictions or evoke critical thinking. | To entertain and critique through exaggeration and satire. |
| Common Forms | Verbal irony, situational irony, dramatic irony. | Film spoofs, satirical writing, comedic sketches. |
| Examples | "A traffic cop gets a speeding ticket." | "Weird Al Yankovic's song parodies." |
| Emotional Tone | Often subtle, thought-provoking, or sarcastic. | Overtly comedic and exaggerated. |
| Use in Art | Provokes reflection on reality and expectations. | Mimics and critiques original art forms for humor. |
Defining Irony: Key Concepts
Irony involves expressing meaning through language that signifies the opposite of what is actually said, often highlighting contrasts between appearance and reality. Key concepts include verbal irony, where spoken words differ from intended meaning, and situational irony, which occurs when outcomes defy expectations. Dramatic irony arises when the audience possesses knowledge unknown to characters, creating tension or humor.
What is Parody? An Introduction
Parody is a creative work that imitates the style or characteristics of another piece, often to produce a humorous or satirical effect. It exaggerates or distorts key elements of the original to highlight its flaws, quirks, or cultural significance. Unlike irony, which relies on contrast between expectation and reality, parody depends on recognizable mimicry to engage and entertain audiences.
Core Differences: Irony vs Parody
Irony involves expressing meaning through language that typically signifies the opposite, creating a contrast between expectation and reality, often used to highlight disparities or critique subtly. Parody imitates the style or content of a particular work, genre, or author, exaggerating distinctive features to create humor or satire. The core difference lies in irony's reliance on implicit contradiction for effect, while parody depends on explicit mimicry and exaggeration to convey its message.
Types of Irony in Literature and Media
Irony in literature and media manifests primarily as verbal, situational, and dramatic irony, each serving distinct narrative functions; verbal irony involves a contrast between spoken words and intended meaning, situational irony arises when events contradict expectations, and dramatic irony occurs when the audience knows critical information unknown to characters. Parody, by contrast, imitates and exaggerates the style of a work or genre for comedic effect, often employing irony to highlight its targets' absurdities. Understanding these types enriches the analysis of storytelling techniques across novels, films, and television shows.
Forms and Methods of Parody
Parody employs imitation and exaggeration of distinctive features from original works, using techniques such as mimicry, exaggeration, and satire to create humorous or critical effect. It often recontextualizes characters, styles, or themes to expose flaws or highlight absurdities, differing from irony which relies primarily on contrast between expectation and reality. Forms of parody range from literary and musical pastiches to visual spoofs and digital memes, utilizing methods like pastiche, caricature, and contextual inversion to engage audiences through recognizable references.
Purpose and Effect: Irony’s Role
Irony serves to highlight contradictions between appearance and reality, often provoking critical reflection or humor by revealing underlying truths. Its purpose is to create a subtle tension that encourages audiences to question or reconsider assumptions, enhancing the depth and complexity of communication. Unlike parody, which explicitly mimics and exaggerates for comedic effect, irony relies on understated contrast to produce intellectual engagement and emotional impact.
Parody’s Function in Pop Culture
Parody functions in pop culture by humorously imitating and exaggerating recognizable works, genres, or styles to critique or celebrate the original content. It engages audiences through familiar references while offering commentary on societal norms, media conventions, or artistic trends. This blend of entertainment and critique helps parody remain a powerful tool for both cultural reflection and subversion.
Recognizing Irony and Parody: Practical Examples
Recognizing irony involves identifying situations where the intended meaning contrasts sharply with the literal expression, such as saying "What a beautiful day" during a storm. Parody can be detected by noting exaggerated imitation of a particular style or genre, like a comedy sketch that mimics a superhero movie's tropes for humorous effect. Practical examples include Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal" for irony and "Weird Al" Yankovic's song parodies that highlight parody through mimicry and satire.
Common Misconceptions: Irony and Parody
Irony is often misunderstood as simply sarcasm, but it fundamentally involves expressing meaning through contrast between expectations and reality, while parody mimics a specific work or style to criticize or humorously imitate it. Many confuse parody's exaggerated imitation for irony, though parody relies on recognizable imitation combined with satire. Recognizing that irony functions through subtle incongruities helps distinguish it from parody's overt mimicry and comedic distortion.
Why Irony and Parody Matter in Communication
Irony and parody enhance communication by adding layers of meaning that engage audiences through humor and critical reflection. Irony subtly exposes contradictions between expectations and reality, fostering deeper understanding and emotional connection. Parody imitates and exaggerates styles or ideas, encouraging critical thinking and making complex topics more accessible and memorable.
Irony Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com