Performance art pushes the boundaries of traditional art forms by combining visual art with live actions, creating immersive and often provocative experiences. This dynamic medium challenges audiences to engage with concepts of identity, time, and space in real-time, emphasizing the ephemeral nature of artistic expression. Explore this article to uncover how performance art transforms the relationship between artist, audience, and environment.
Table of Comparison
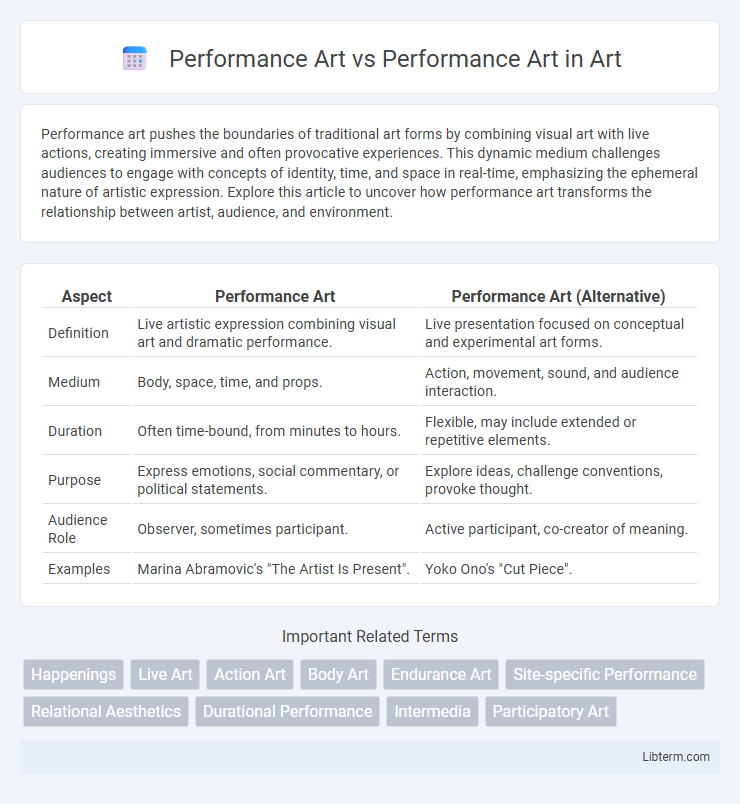
| Aspect | Performance Art | Performance Art (Alternative) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Live artistic expression combining visual art and dramatic performance. | Live presentation focused on conceptual and experimental art forms. |
| Medium | Body, space, time, and props. | Action, movement, sound, and audience interaction. |
| Duration | Often time-bound, from minutes to hours. | Flexible, may include extended or repetitive elements. |
| Purpose | Express emotions, social commentary, or political statements. | Explore ideas, challenge conventions, provoke thought. |
| Audience Role | Observer, sometimes participant. | Active participant, co-creator of meaning. |
| Examples | Marina Abramovic's "The Artist Is Present". | Yoko Ono's "Cut Piece". |
Defining Performance Art: Concepts and Evolution
Performance Art is an interdisciplinary form blending visual art with live actions to convey conceptual narratives or critique societal norms. Emerging in the 1960s and 1970s, it challenges traditional art boundaries by emphasizing process, temporality, and audience interaction over static objects. Key figures such as Marina Abramovic and Yoko Ono have shaped its evolution, integrating elements from theater, dance, and music to expand the medium's expressive potential.
Historical Context: Performance Art Origins
Performance Art originated in the early 20th century as a radical departure from traditional visual arts, drawing influence from Dadaism, Futurism, and Fluxus movements. It emphasizes live, ephemeral experiences where the artist's body and actions are central, challenging conventional art forms like theater and painting. Key pioneers such as Marina Abramovic and Allan Kaprow shaped its development through experimental, boundary-breaking performances that reflect socio-political contexts and personal narratives.
Key Figures in Performance Art
Performance art features key figures such as Marina Abramovic, whose endurance-based works challenge the limits of physical and mental boundaries. Chris Burden's daring and provocative performances, like "Shoot" (1971), critically explore themes of risk and societal control. Yoko Ono's pioneering contributions combine conceptual art and audience interaction, pushing the boundaries of traditional performance conventions.
Distinguishing Features of Performance Art
Performance Art distinguishes itself through its emphasis on live, ephemeral experiences that merge visual art with dramatic presentation, often prioritizing process over a finished product. It challenges traditional boundaries by incorporating audience interaction, multimedia elements, and non-linear narratives to evoke emotional and intellectual responses. Unlike conventional theater or dance, Performance Art frequently utilizes unconventional spaces and incorporates elements of chance, improvisation, and personal expression as core components.
Performance Art vs. Traditional Art Forms
Performance art challenges traditional art forms by emphasizing live, ephemeral experiences rather than static, collectible objects. It integrates multiple disciplines such as theater, dance, and visual art, creating a dynamic interaction between artist and audience that traditional art often lacks. This art form prioritizes process and presence over permanence, redefining artistic expression beyond conventional mediums like painting or sculpture.
Cultural Impact of Performance Art
Performance Art has significantly influenced contemporary culture by challenging traditional boundaries of art and engaging audiences in participatory experiences. Its emphasis on ephemeral, live actions fosters critical dialogue around social, political, and identity issues, reflecting and shaping cultural narratives. This dynamic medium continues to inspire interdisciplinary collaboration, expanding the definition and impact of art within global societies.
Live Performance vs. Documented Performance
Live performance in performance art emphasizes the ephemeral, immediate interaction between artist and audience, creating a unique, unrepeatable experience often shaped by real-time spontaneity and site-specific context. Documented performance preserves the artwork through video, photographs, or written records, allowing wider accessibility and analysis but risks losing the original event's dynamic presence and sensory impact. The debate hinges on the authenticity and experiential value of live acts versus the archival benefits and broader reach of documentation.
Audience Participation in Performance Art
Performance art distinguishes itself through active audience participation, transforming viewers from passive observers into integral collaborators who influence the unfolding event. This interactive engagement enhances the immediacy and unpredictability of the artwork, often blurring boundaries between performer and spectator. Audience involvement is essential in shaping the performance's meaning, creating a dynamic experience unique to each encounter.
Contemporary Trends in Performance Art
Contemporary trends in performance art emphasize interdisciplinary approaches, blending technology, digital media, and interactive elements to create immersive experiences. Artists increasingly address social issues, utilizing performance as a platform for activism and community engagement, challenging traditional boundaries between audience and performer. The integration of virtual reality and live-streaming expands accessibility and redefines temporality and space within the performance art landscape.
The Future of Performance Art
The future of performance art is increasingly shaped by immersive technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality, enabling artists to create interactive and multisensory experiences that transcend traditional stage boundaries. Integration of digital platforms and live streaming expands global accessibility, allowing diverse audiences to engage with performances in real-time or asynchronously. Collaboration between performance artists and technologists will likely drive innovative narratives, blending human expression with artificial intelligence to redefine artistic boundaries and audience participation.
Performance Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com