Performance art transcends traditional artistic boundaries by combining visual art with dramatic performance, creating an immersive experience that challenges audience perceptions. It often involves body movements, spoken word, and unconventional materials to convey complex ideas and emotions in real-time. Discover how performance art can transform your understanding of creativity and engage you on a deeper level throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
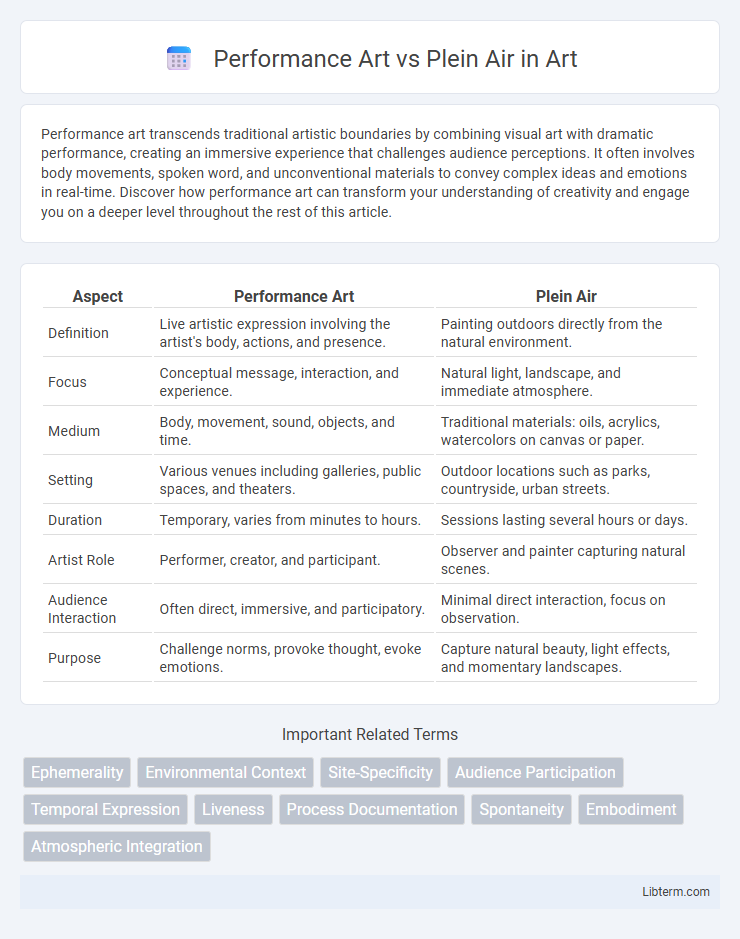
| Aspect | Performance Art | Plein Air |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Live artistic expression involving the artist's body, actions, and presence. | Painting outdoors directly from the natural environment. |
| Focus | Conceptual message, interaction, and experience. | Natural light, landscape, and immediate atmosphere. |
| Medium | Body, movement, sound, objects, and time. | Traditional materials: oils, acrylics, watercolors on canvas or paper. |
| Setting | Various venues including galleries, public spaces, and theaters. | Outdoor locations such as parks, countryside, urban streets. |
| Duration | Temporary, varies from minutes to hours. | Sessions lasting several hours or days. |
| Artist Role | Performer, creator, and participant. | Observer and painter capturing natural scenes. |
| Audience Interaction | Often direct, immersive, and participatory. | Minimal direct interaction, focus on observation. |
| Purpose | Challenge norms, provoke thought, evoke emotions. | Capture natural beauty, light effects, and momentary landscapes. |
Defining Performance Art and Plein Air
Performance art is a live, time-based artistic expression that combines visual art with dramatic performance, emphasizing the artist's physical presence and interaction with the audience. Plein air refers to the practice of painting outdoors, capturing natural landscapes and light conditions directly on-site to achieve spontaneity and authenticity. Both forms prioritize immediacy, yet performance art centers on human action and experience, while plein air focuses on environmental observation and representation.
Historical Origins and Development
Performance art emerged in the 20th century as an experimental medium blending visual art with live action, rooted in Dada and Futurist movements that challenged traditional art forms. Plein air painting, originating in the early 19th century with artists like the Barbizon School and Impressionists, emphasized capturing natural light and scenery outdoors. The development of performance art reflects a shift towards conceptual and ephemeral experiences, while plein air remains grounded in the representation of real-world environments.
Core Principles and Intentions
Performance Art emphasizes live, spontaneous expression where the artist's body and actions become the medium, prioritizing temporality and audience interaction. Plein Air centers on painting outdoors to capture natural light and atmosphere authentically, valuing observation and environmental immersion. The core principle of Performance Art is ephemeral experience, whereas Plein Air focuses on realistic representation of nature's immediate visual effects.
Mediums and Materials Used
Performance art utilizes time-based mediums such as the artist's body, movement, sound, and props to create ephemeral experiences often recorded via video or photography, emphasizing concept over permanence. Plein air painting employs traditional materials like oil, acrylic, or watercolor paints applied on canvases or paper, capturing natural light and outdoor scenes directly from the environment. The contrasting use of transient, experiential elements in performance art versus tangible, physical art objects in plein air highlights fundamental differences in medium and material selection.
Interaction with Audience and Environment
Performance art emphasizes direct interaction with the audience, transforming spectators into participants through live, often spontaneous, actions that challenge traditional boundaries. Plein air painting involves artists engaging with natural light and environmental conditions in real-time, capturing landscapes authentically while maintaining a physical, yet less interactive, presence with viewers. Both forms prioritize immediacy and environment, but performance art foregrounds human connection while plein air centers on sensory observation.
Temporality and Preservation
Performance art emphasizes temporality through live, ephemeral experiences that unfold in real-time, highlighting the transient nature of human interaction and presence. Plein air painting captures a specific moment within nature, embedding the temporality of natural light and weather directly onto a physical canvas, which allows for preservation beyond the immediate experience. While performance art relies on documentation and memory for preservation, plein air works offer tangible artifacts that maintain the temporal essence of the environment at a fixed point in time.
Artistic Expression and Technique
Performance Art emphasizes live, ephemeral expression where the artist's body and actions convey concepts and emotions directly to an audience, often incorporating improvisation and multimedia elements. Plein Air painting prioritizes capturing natural light and atmospheric conditions through direct observation, showcasing technical skills in brushwork, color mixing, and composition to represent landscapes with immediacy and detail. Both forms challenge traditional art boundaries but differ fundamentally in technique--Performance Art relies on temporal, experiential methods, whereas Plein Air focuses on visual realism and environmental immersion.
Influential Artists and Landmark Works
Performance art pioneers such as Marina Abramovic and Laurie Anderson reshaped contemporary art with immersive, time-based experiences that challenge the audience's perception and interaction. In contrast, plein air painting is epitomized by artists like Claude Monet and Camille Pissarro, who captured natural light and landscapes directly from outdoor settings, influencing Impressionism and landscape art profoundly. Landmark works like Abramovic's "The Artist Is Present" and Monet's "Impression, Sunrise" exemplify the distinct approaches and enduring impact of each art form.
Contemporary Trends and Innovations
Performance art embraces dynamic, often interactive expressions that challenge traditional boundaries, incorporating multimedia, technology, and live audience engagement to create immersive experiences. Plein air painting remains vital, evolving through modern materials, portable digital tools, and augmented reality to capture fleeting moments with enhanced precision and creative flexibility. Contemporary trends highlight a fusion of disciplines where performance artists integrate plein air techniques and plein air artists adopt performative gestures, reflecting a growing interdisciplinary innovation.
Impact on the Broader Art World
Performance Art challenges traditional art boundaries by emphasizing live, ephemeral experiences that engage audiences directly, reshaping perceptions of art's role in society. Plein Air painting revitalizes classical techniques through direct interaction with natural landscapes, influencing contemporary approaches to light and color within art communities. Together, these movements expand the art world's scope, fostering innovation and diverse expressions in artistic practice.
Performance Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com