Genre painting captures everyday scenes reflecting ordinary life, emphasizing naturalism and detailed representation. These artworks often portray social interactions, domestic activities, and common events, revealing cultural norms and human emotions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how genre painting continues to influence contemporary art and your appreciation of everyday moments.
Table of Comparison
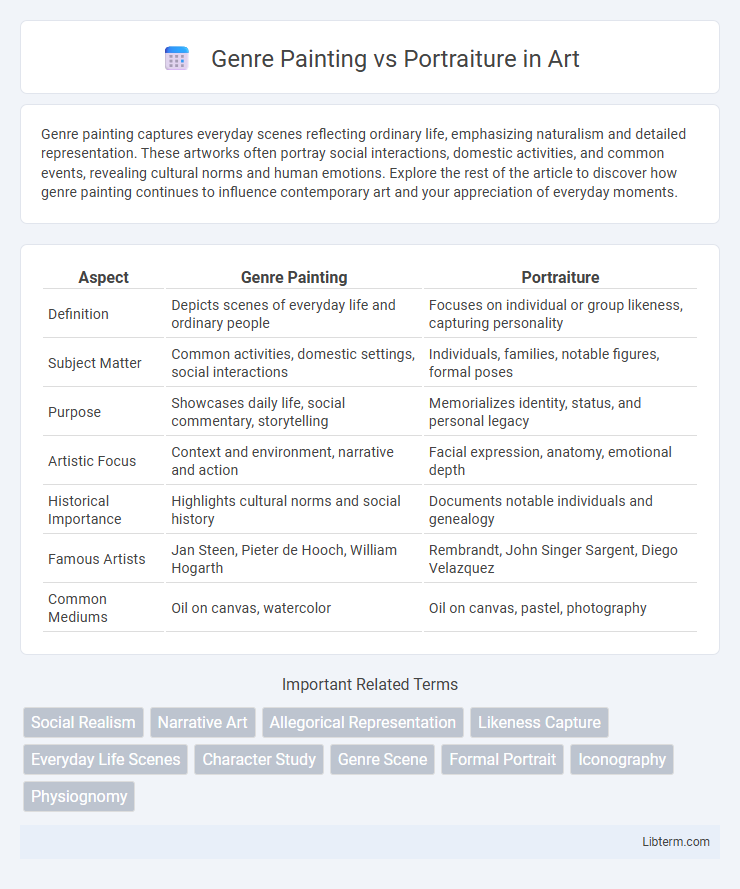
| Aspect | Genre Painting | Portraiture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Depicts scenes of everyday life and ordinary people | Focuses on individual or group likeness, capturing personality |
| Subject Matter | Common activities, domestic settings, social interactions | Individuals, families, notable figures, formal poses |
| Purpose | Showcases daily life, social commentary, storytelling | Memorializes identity, status, and personal legacy |
| Artistic Focus | Context and environment, narrative and action | Facial expression, anatomy, emotional depth |
| Historical Importance | Highlights cultural norms and social history | Documents notable individuals and genealogy |
| Famous Artists | Jan Steen, Pieter de Hooch, William Hogarth | Rembrandt, John Singer Sargent, Diego Velazquez |
| Common Mediums | Oil on canvas, watercolor | Oil on canvas, pastel, photography |
Defining Genre Painting and Portraiture
Genre painting depicts everyday scenes and ordinary people engaged in common activities, emphasizing narrative and social context rather than individual identity. Portraiture focuses on capturing the likeness, personality, and status of a specific individual or group, highlighting facial features and expressions. Both art forms reflect cultural and historical values but serve distinct purposes: genre painting portrays collective life while portraiture immortalizes individual identity.
Historical Origins and Development
Genre painting emerged in the 16th century, particularly in Dutch and Flemish art, depicting everyday life scenes that reflected social customs and domestic activities. Portraiture, dating back to ancient civilizations like Egypt and Rome, evolved as a means to document individual status, identity, and political power throughout history. Both art forms developed distinct techniques and purposes, with genre painting emphasizing narrative storytelling and portraiture focusing on precise likeness and personal representation.
Key Techniques and Artistic Approaches
Genre painting often employs narrative scenes with multiple figures engaged in everyday activities, using a balanced composition and naturalistic lighting to evoke relatable human experiences. Portraiture focuses on capturing the likeness, personality, and status of an individual through precise anatomical accuracy, detailed facial expressions, and controlled use of light and shadow to emphasize character. Both genres utilize brushwork strategically; genre paintings favor dynamic, textured strokes to enhance storytelling, while portraits demand smooth, refined techniques for realistic depiction.
Subject Matter and Thematic Focus
Genre painting captures everyday scenes and ordinary people engaged in common activities, emphasizing social interactions, domestic settings, and cultural customs. Portraiture centers on individual identity, character, and status, often highlighting facial expression, attire, and the sitter's social or professional role. While genre painting explores collective experiences and narratives, portraiture focuses on personal representation and psychological depth.
Representation of Everyday Life vs. Individual Identity
Genre painting captures scenes of everyday life, emphasizing common activities and social interactions to reflect cultural and societal norms. Portraiture focuses on individual identity by highlighting personal features, emotions, and status, often conveying the subject's unique character and social position. While genre painting offers a broader societal context, portraiture provides an intimate exploration of singular identity.
Iconic Artists and Masterpieces
Genre painting captures everyday scenes of ordinary life, with iconic artists such as Johannes Vermeer, whose masterpiece "The Milkmaid" epitomizes Dutch Golden Age genre art. Portraiture focuses on depicting individual likenesses and personalities, exemplified by artists like Rembrandt, renowned for his powerful self-portraits including "Self-Portrait with Two Circles." Both genres reveal distinct artistic intentions, with genre painting emphasizing social narratives and portraiture highlighting personal identity and status.
Social and Cultural Contexts
Genre painting captures everyday life and ordinary people, reflecting social customs, cultural norms, and class dynamics within a specific historical period. Portraiture often emphasizes individual identity, status, and power, serving as a visual record of social hierarchy and personal legacy. Both art forms provide critical insights into the societal values and cultural contexts of their respective eras, revealing shifts in social structure and cultural attitudes.
Evolution Across Art Movements
Genre painting evolved from depicting everyday life scenes in the Dutch Golden Age to embracing social realism and impressionist styles, reflecting societal changes and artistic experimentation. Portraiture shifted from rigid, formal representations in Renaissance and Baroque periods to more expressive and psychological portrayals during Romanticism and Modernism. Both genres demonstrate a dynamic evolution influenced by cultural contexts, technological advancements, and shifting artistic priorities across movements such as Realism, Impressionism, and Expressionism.
Collectors, Patrons, and Market Trends
Collectors often favor genre paintings for their narrative depth and everyday scenes, offering relatable content that attracts a broad audience, while portraiture appeals to patrons seeking status and personal legacy through bespoke representations. Market trends indicate genre paintings enjoy increasing interest for their cultural insights and emotional resonance, contrasting with the steady demand for portraiture driven by commissions from private clients and institutions. Emerging art markets also show a shift toward contemporary interpretations of genre painting, reflecting evolving tastes and expanding collector demographics.
Lasting Influence on Contemporary Art
Genre painting captures everyday scenes reflecting culture and societal norms, shaping contemporary art's emphasis on relatability and narrative depth. Portraiture, with its focus on individual identity and psychological expression, continues to influence modern artists exploring self-representation and human emotion. Both genres contribute enduring frameworks for storytelling and character study in contemporary visual arts.
Genre Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com