Appropriation involves the adoption or use of elements from one culture by another, often raising complex ethical and legal questions. Understanding the distinctions between cultural appreciation and appropriation is crucial to respecting the origins and meanings behind these elements. Explore the rest of this article to gain deeper insights into how appropriation impacts society and your role in navigating it thoughtfully.
Table of Comparison
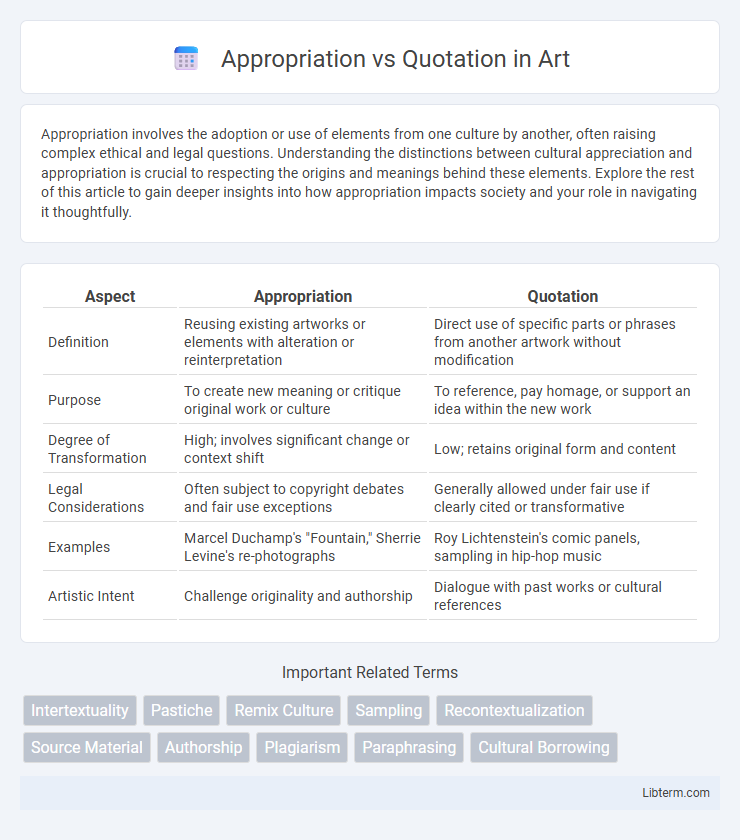
| Aspect | Appropriation | Quotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reusing existing artworks or elements with alteration or reinterpretation | Direct use of specific parts or phrases from another artwork without modification |
| Purpose | To create new meaning or critique original work or culture | To reference, pay homage, or support an idea within the new work |
| Degree of Transformation | High; involves significant change or context shift | Low; retains original form and content |
| Legal Considerations | Often subject to copyright debates and fair use exceptions | Generally allowed under fair use if clearly cited or transformative |
| Examples | Marcel Duchamp's "Fountain," Sherrie Levine's re-photographs | Roy Lichtenstein's comic panels, sampling in hip-hop music |
| Artistic Intent | Challenge originality and authorship | Dialogue with past works or cultural references |
Introduction to Appropriation and Quotation
Appropriation involves reusing existing artworks or cultural elements with minimal transformation, often raising questions about originality and intellectual property. Quotation, in contrast, explicitly references or incorporates parts of existing works within a new context to create dialogue or critique, usually acknowledged through attribution. Understanding these practices is essential for navigating contemporary art, copyright law, and cultural expression.
Defining Appropriation in Art and Culture
Appropriation in art and culture involves the intentional borrowing, recycling, or repurposing of existing images, symbols, or styles from other works to create new meanings or critiques. It challenges traditional notions of originality and authorship by recontextualizing familiar cultural elements within different frameworks or perspectives. Appropriation often engages in critical dialogue with historical, social, or political issues by transforming pre-existing cultural artifacts into contemporary statements.
Understanding Quotation in Creative Works
Quotation in creative works involves accurately reproducing a portion of another creator's content to provide evidence, critique, or commentary while respecting copyright laws. Proper quotation requires clear attribution, ensuring the original source is acknowledged and the use falls under fair use or fair dealing exceptions. Understanding the boundaries and purposes of quoting helps maintain originality and ethical standards in artistic and academic productions.
Historical Context of Appropriation
Appropriation in art often involves taking elements from historical or cultural sources and recontextualizing them, raising critical debates around originality and cultural ownership. Historically, appropriation has been used to challenge traditional narratives and power structures, particularly during movements like Dadaism and Pop Art, where artists repurposed commercial and popular imagery. This contrasts with quotation, which directly references or copies specific works to acknowledge sources without fundamentally altering their original meaning.
The Role of Quotation in Artistic Expression
Quotation in artistic expression functions as a powerful tool for creators to reference, reinterpret, and engage with existing works, enriching their own narratives and themes. It allows artists to build intertextual dialogues, fostering layers of meaning and cultural resonance that deepen audience connection. This practice contrasts with appropriation by maintaining clear acknowledgment and transformative intent, emphasizing homage rather than mere reuse.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Appropriation involves using someone else's work without permission, raising significant legal risks such as copyright infringement and potential lawsuits under intellectual property law. Quotation, when properly attributed and within fair use boundaries, is legally protected and ethically acceptable as it respects original creators' rights while contributing to discourse. Understanding the distinction is crucial for compliance with copyright statutes and maintaining ethical standards in creative and academic environments.
Appropriation vs Quotation: Key Differences
Appropriation involves adopting elements from existing works to create new content, often raising legal and ethical questions about originality and copyright infringement, while quotation refers to the direct use of excerpts from a source with proper attribution and within fair use limits. Appropriation transforms or repurposes the original material beyond mere reference, whereas quotation preserves the original context to support analysis or commentary. Key differences hinge on intent, legality, and the extent of modification applied to the source material.
Impact on Originality and Creativity
Appropriation often blurs the line between originality and replication by incorporating existing works into new contexts, which can challenge traditional notions of creativity but also foster innovation through reinterpretation. Quotation explicitly acknowledges the source material, maintaining the integrity and originality of the new work while building upon established ideas. Both practices impact creativity differently: appropriation reshapes and transforms content, potentially creating novel artistic expressions, whereas quotation preserves originality by transparently referencing and situating new creations within an existing intellectual framework.
Contemporary Examples and Case Studies
Contemporary examples of appropriation versus quotation often emerge in visual arts and music, where artists like Shepard Fairey merge existing imagery with new political messages, raising debates about originality and fair use. Case studies such as Richard Prince's re-photographing of Instagram images highlight tensions between appropriation as transformative art and copyright infringement claims. The distinction hinges on context, intent, and transformation degree, influencing legal interpretations and cultural reception in ongoing controversies.
Conclusion: Navigating Between Inspiration and Imitation
Appropriation and quotation differ fundamentally in intention and context, with appropriation often blurrier, risking imitation rather than inspiration. Understanding copyright laws and ethical guidelines helps creators balance homage with originality, fostering innovation without infringing on intellectual property. Clear differentiation ensures respect for source material while advancing creative expression.
Appropriation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com