Use precise wording to enhance the meaning and clarity of your text while maintaining the original intent. Focus on expressing the same ideas with fresh vocabulary and sentence structures to improve engagement and comprehension. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for mastering paraphrasing techniques.
Table of Comparison
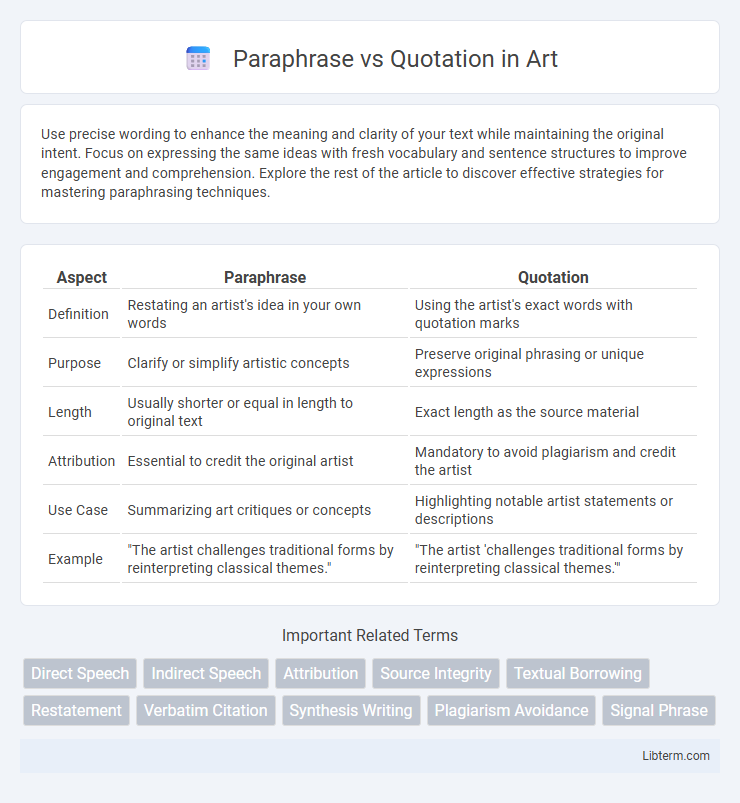
| Aspect | Paraphrase | Quotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restating an artist's idea in your own words | Using the artist's exact words with quotation marks |
| Purpose | Clarify or simplify artistic concepts | Preserve original phrasing or unique expressions |
| Length | Usually shorter or equal in length to original text | Exact length as the source material |
| Attribution | Essential to credit the original artist | Mandatory to avoid plagiarism and credit the artist |
| Use Case | Summarizing art critiques or concepts | Highlighting notable artist statements or descriptions |
| Example | "The artist challenges traditional forms by reinterpreting classical themes." | "The artist 'challenges traditional forms by reinterpreting classical themes.'" |
Introduction to Paraphrasing and Quoting
Paraphrasing involves restating a source's ideas using different words while maintaining the original meaning, enhancing clarity and integration in writing. Quoting directly uses the exact words from a source, often enclosed in quotation marks, to preserve the original phrasing and authority. Both techniques require proper citation to acknowledge the original author and avoid plagiarism.
Defining Paraphrase: Meaning and Purpose
Paraphrase involves restating someone else's ideas or information using different words and sentence structures while maintaining the original meaning, allowing for clearer understanding or simplification. Its purpose is to integrate external content seamlessly into new writing without directly copying, thus avoiding plagiarism and enhancing originality. This technique helps writers interpret and present source material in their unique voice while preserving the initial intent.
What is a Quotation? Key Features Explained
A quotation is the exact replication of someone else's words, placed within quotation marks to indicate the original source. Key features include preserving the original wording, punctuation, and meaning while providing proper attribution to the author. Quotations are essential in academic writing to support arguments, provide evidence, and maintain the integrity of the referenced material.
When to Paraphrase: Ideal Scenarios
Paraphrasing is ideal when conveying complex ideas in simpler terms to enhance clarity and audience understanding. It is useful for summarizing lengthy passages or integrating sources seamlessly into original writing without altering the intended meaning. Paraphrasing also helps avoid plagiarism while maintaining the author's voice and supporting evidence within academic or professional contexts.
When to Use Direct Quotations
Direct quotations should be used when the original wording is particularly impactful, authoritative, or precise, preserving the speaker's or author's intent and style. They are essential in academic writing to provide evidence, support arguments, or highlight unique phrases or definitions. Use direct quotations sparingly to maintain the originality of your work while enhancing credibility and clarity.
Benefits of Paraphrasing in Academic Writing
Paraphrasing in academic writing enhances originality by allowing authors to express ideas in their own words, reducing the risk of plagiarism. It helps deepen understanding and engagement with source material, fostering critical thinking and clearer communication. Paraphrasing also enables seamless integration of evidence into the author's argument, improving coherence and readability.
Advantages of Using Quotations
Quotations provide precise representation of original ideas, preserving the author's exact wording and tone, which enhances credibility and authenticity in writing. Using quotations strengthens arguments by directly referencing authoritative sources, ensuring accuracy and preventing misinterpretation. This method also allows writers to engage readers with impactful expressions and distinctive language that paraphrasing might dilute.
Paraphrasing Techniques and Best Practices
Paraphrasing techniques involve rewording original text using different vocabulary and sentence structures while maintaining the original meaning to avoid plagiarism. Effective paraphrasing includes understanding the source material thoroughly, using synonyms appropriately, and altering sentence patterns without distorting the message. Best practices recommend citing the original author to give credit, combining paraphrased content with original analysis, and ensuring clarity and coherence in the rewritten text.
Quotation Formatting Rules and Citation
Quotation formatting rules require enclosing the exact words from a source within quotation marks to indicate direct speech or text, preserving the original wording and punctuation. Citations for quotations must include precise source details such as the author's name, publication year, and page number to credit the original work and avoid plagiarism. Proper formatting also mandates block quotations for excerpts exceeding 40 words, indented without quotation marks, with the citation placed after the closing punctuation.
Paraphrase vs Quotation: Choosing the Right Approach
Paraphrasing involves rewriting the original text in your own words while retaining the core meaning, which helps integrate ideas smoothly and demonstrates understanding. Quotation uses the exact words from a source, ideal for emphasizing authority or specific phrasing, but requires accurate citation to avoid plagiarism. Choosing between paraphrase and quotation depends on the context, purpose, and the need to balance originality with the credibility of source material.
Paraphrase Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com