3D animation brings digital creations to life by adding depth, realistic movements, and immersive environments that captivate audiences across films, games, and advertisements. Mastering techniques such as modeling, rigging, and keyframing enhances the storytelling power and visual impact of your projects. Explore the full article to discover how 3D animation can elevate your creative work and engage viewers like never before.
Table of Comparison
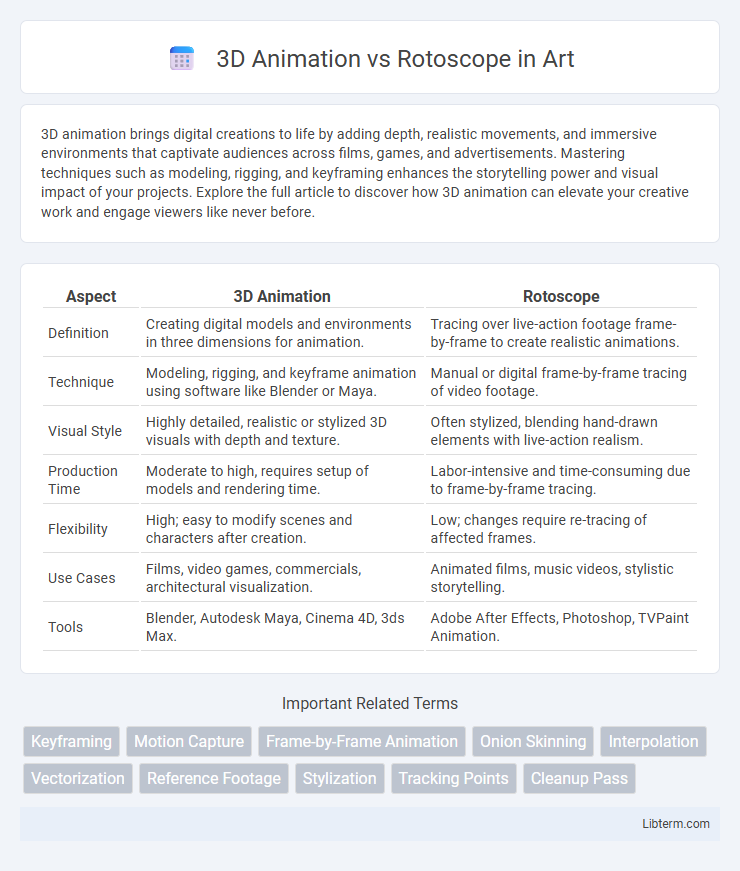
| Aspect | 3D Animation | Rotoscope |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating digital models and environments in three dimensions for animation. | Tracing over live-action footage frame-by-frame to create realistic animations. |
| Technique | Modeling, rigging, and keyframe animation using software like Blender or Maya. | Manual or digital frame-by-frame tracing of video footage. |
| Visual Style | Highly detailed, realistic or stylized 3D visuals with depth and texture. | Often stylized, blending hand-drawn elements with live-action realism. |
| Production Time | Moderate to high, requires setup of models and rendering time. | Labor-intensive and time-consuming due to frame-by-frame tracing. |
| Flexibility | High; easy to modify scenes and characters after creation. | Low; changes require re-tracing of affected frames. |
| Use Cases | Films, video games, commercials, architectural visualization. | Animated films, music videos, stylistic storytelling. |
| Tools | Blender, Autodesk Maya, Cinema 4D, 3ds Max. | Adobe After Effects, Photoshop, TVPaint Animation. |
Introduction to 3D Animation and Rotoscope
3D animation involves creating moving images in a three-dimensional digital environment using specialized software like Autodesk Maya or Blender, allowing for realistic textures, lighting, and camera movements. Rotoscope is an animation technique where animators trace over live-action footage frame-by-frame to produce lifelike motion, commonly used in traditional and hybrid animation workflows. Both methods serve distinct purposes in visual storytelling, with 3D animation emphasizing computer-generated imagery and rotoscope focusing on enhancing realism through direct reference to filmed sequences.
Understanding 3D Animation Techniques
3D animation techniques involve creating digital models and environments, allowing animators to manipulate objects in a three-dimensional space for realistic movement and depth. Unlike rotoscope, which traces over live-action footage frame by frame, 3D animation relies on rigging, keyframing, and physics simulations to generate fluid and dynamic sequences. Mastery of 3D software such as Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max is essential for producing complex animations used in films, games, and virtual reality.
Fundamentals of Rotoscoping
Rotoscoping is a traditional animation technique that involves tracing over live-action footage frame by frame to create realistic motion, emphasizing accuracy in capturing human movement. Unlike 3D animation, which builds models in a digital environment, rotoscoping relies on hand-drawn or digital tracing to achieve a seamless integration of animated elements with real environments. The fundamentals of rotoscoping include meticulous frame analysis, consistent line work, and attention to detail in matching the original footage's motion and timing.
Key Differences Between 3D Animation and Rotoscope
3D animation involves creating digital models and environments that can be manipulated in a virtual space, offering dynamic camera angles, lighting, and detailed textures. Rotoscope, by contrast, is a technique where animators trace over live-action footage frame-by-frame, preserving realistic motion but limiting flexibility in altering scenes. Key differences include the degree of control over movement and style, with 3D animation allowing full creative freedom while rotoscope relies heavily on original footage for reference.
Advantages of 3D Animation
3D animation offers unparalleled flexibility in creating lifelike characters and environments that can be manipulated from any angle, enhancing visual storytelling. Its ability to generate complex simulations, such as realistic lighting, textures, and physics effects, surpasses the frame-by-frame limitations of rotoscope techniques. Furthermore, 3D animation streamlines the production process with reusable models and assets, significantly reducing time and cost compared to the labor-intensive tracing method of rotoscoping.
Benefits of Rotoscoping in Animation
Rotoscoping offers precise control over character movements by tracing live-action footage, resulting in highly realistic animations that capture subtle nuances. This technique reduces the time and effort needed to animate complex motion sequences compared to creating them entirely from scratch in 3D animation. Enhanced fluidity and naturalism in animated scenes make rotoscoping a valuable tool for producing lifelike visuals while maintaining artistic flexibility.
Visual Styles: 3D Animation vs. Rotoscope
3D animation creates highly detailed, lifelike visuals through computer-generated models and environments, offering depth, dynamic lighting, and complex textures. Rotoscope animation relies on tracing over live-action footage, resulting in a stylized, painterly effect that merges realism with artistic abstraction. The visual style of 3D animation emphasizes precision and immersion, while rotoscope evokes a more fluid, hand-crafted aesthetic with a blend of reality and fantasy.
Popular Uses in Film and Media
3D animation is widely used in blockbuster films and video games for creating immersive, lifelike environments and characters, exemplified by studios like Pixar and DreamWorks. Rotoscoping remains popular in visual effects and indie films for achieving realistic motion by tracing live-action footage, often used to blend animated elements seamlessly with live actors. Both techniques serve distinct purposes, with 3D animation excelling in creating fully virtual worlds while rotoscoping enhances visual storytelling through precise frame-by-frame animation integration.
Workflow and Production Considerations
3D animation involves creating digital models and animating them within a virtual environment, offering extensive flexibility in character movement and scene manipulation but requiring significant time for modeling, rigging, and rendering. Rotoscoping, a frame-by-frame tracing technique applied to live-action footage, demands meticulous handwork to achieve realistic motion, making it labor-intensive yet efficient for integrating real-world actions. Production considerations highlight 3D animation's advantage in scalability and reuse of assets, whereas rotoscoping excels in capturing authentic human movement with fewer post-production adjustments.
Choosing the Right Method: 3D Animation or Rotoscope
Choosing between 3D animation and rotoscope depends on project goals, budget, and desired aesthetic. 3D animation offers flexibility with dynamic camera angles, complex movements, and realistic textures ideal for immersive storytelling and product visualization. Rotoscoping excels in achieving fluid, lifelike motion by tracing live-action footage, making it suitable for stylistic animation or when blending real actors with animated elements.
3D Animation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com