Futurism envisions a dynamic world driven by technological innovation, transforming industries and societies at an unprecedented pace. This movement shapes your understanding of emerging trends and inspires forward-thinking strategies for adapting to rapid change. Explore the full article to uncover how futurism will impact your future and the steps you can take to stay ahead.
Table of Comparison
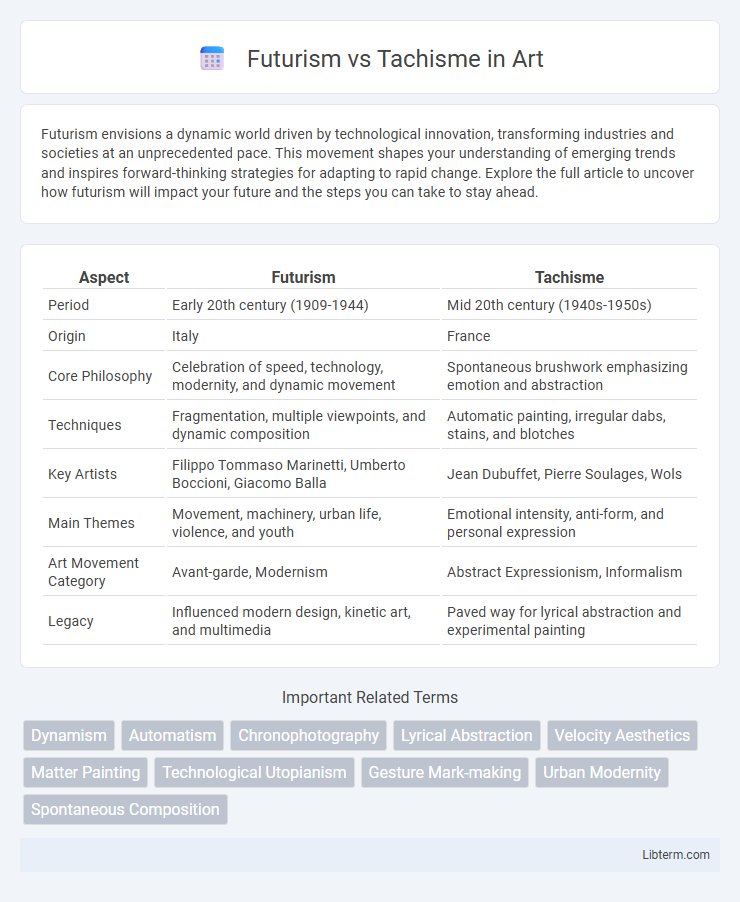
| Aspect | Futurism | Tachisme |
|---|---|---|
| Period | Early 20th century (1909-1944) | Mid 20th century (1940s-1950s) |
| Origin | Italy | France |
| Core Philosophy | Celebration of speed, technology, modernity, and dynamic movement | Spontaneous brushwork emphasizing emotion and abstraction |
| Techniques | Fragmentation, multiple viewpoints, and dynamic composition | Automatic painting, irregular dabs, stains, and blotches |
| Key Artists | Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Umberto Boccioni, Giacomo Balla | Jean Dubuffet, Pierre Soulages, Wols |
| Main Themes | Movement, machinery, urban life, violence, and youth | Emotional intensity, anti-form, and personal expression |
| Art Movement Category | Avant-garde, Modernism | Abstract Expressionism, Informalism |
| Legacy | Influenced modern design, kinetic art, and multimedia | Paved way for lyrical abstraction and experimental painting |
Introduction to Futurism and Tachisme
Futurism, emerging in early 20th-century Italy, emphasized dynamic movement, technology, and modernity, often showcasing speed and industrial power through vibrant, angular forms. Tachisme, a post-World War II European art movement, focused on spontaneous brushwork and abstract expression, highlighting emotional intensity with uncontrolled, gestural marks. Both movements reflect distinct reactions to their contemporary cultural environments, with Futurism embracing mechanization and Tachisme exploring artistic freedom and subjectivity.
Historical Contexts of Futurism and Tachisme
Futurism emerged in early 20th-century Italy, reflecting the era's fascination with technology, speed, and modernity, aiming to break away from traditional art forms through dynamic movement and industrial themes. Tachisme, developing in post-World War II France, reacted against structured abstraction, emphasizing spontaneous brushwork and emotional expression as a response to the trauma and existential uncertainty of the time. Both movements reflect their distinct historical contexts, with Futurism tied to pre-war optimism and mechanization, while Tachisme embodies post-war introspection and rebellion against conventional aesthetics.
Core Philosophies: Progress vs Spontaneity
Futurism centers on the embrace of progress, speed, and technological advancement, advocating for dynamic movement and the celebration of modernity as fundamental principles. Tachisme champions spontaneity and emotional expression, prioritizing intuitive and unplanned brushwork that captures the raw and immediate experience of the artist. These contrasting core philosophies highlight Futurism's structured vision of the future against Tachisme's emphasis on organic, moment-to-moment creativity.
Visual Characteristics and Artistic Techniques
Futurism emphasizes dynamic movement, speed, and technology, often using sharp lines, geometric shapes, and a fragmented composition to convey energy and progress. Tachisme, a European abstract art movement, features spontaneous brushwork, drips, and blobs of paint, emphasizing texture, color, and emotional expression over precise form. While Futurism relies on structured, rhythmic repetition and overlapping planes to depict motion, Tachisme embraces randomness and improvisation, creating a sense of immediacy and rawness in the visual experience.
Influential Artists in Futurism and Tachisme
Influential artists in Futurism include Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Umberto Boccioni, and Giacomo Balla, who emphasized dynamism, speed, and technological progress in their works. Key figures in Tachisme, also known as Art Informel, are Jean Dubuffet, Pierre Soulages, and Nicolas de Stael, known for their spontaneous brushwork and abstract forms focusing on texture and color. Both movements significantly shaped modern art by challenging traditional aesthetics and exploring new expressive techniques.
Impact on Modern and Contemporary Art
Futurism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing dynamic movement, technology, and the energy of the industrial age, influencing numerous avant-garde movements and reshaping visual language in the early 20th century. Tachisme, as a key post-war European abstract style, contributed to contemporary art through spontaneous brushwork and intuitive expression, paralleling American Abstract Expressionism and deeply impacting later abstraction and lyrical painting. Together, these movements expanded artistic freedom and paved the way for experimental approaches in both modern and contemporary art spheres.
Key Works: Futurist vs Tachiste Masterpieces
Key works in Futurism, such as Umberto Boccioni's "Unique Forms of Continuity in Space" and Giacomo Balla's "Dynamism of a Dog on a Leash," emphasize movement, speed, and industrial progress through dynamic forms and fragmented shapes. Tachisme masterpieces like Jean Dubuffet's "Texturologies" and Wols' "Untitled" highlight spontaneous brushstrokes, abstract textures, and emotional intensity, reflecting post-war existentialism. The contrast between Futurism's mechanistic precision and Tachisme's lyrical abstraction defines their distinct contributions to modern art.
Reception and Critique Over Time
Futurism, celebrated for its dynamic representation of speed and technology, initially received acclaim for capturing modernity but faced criticism for its aggressive nationalism and mechanistic aesthetics. Tachisme, emerging post-World War II as an abstract expressionist movement, gained appreciation for its spontaneity and emotional intensity, though some critics dismissed it as lacking structure or coherence. Over time, both movements have seen reevaluations, with Futurism recognized for its influence on avant-garde art and Tachisme appreciated for pioneering lyrical abstraction.
Global Influence and Legacy
Futurism revolutionized modern art by emphasizing dynamism, technology, and movement, profoundly influencing global avant-garde movements and shaping the visual language of the early 20th century. Tachisme, as a European counterpart to Abstract Expressionism, impacted post-war art with its emphasis on spontaneity and abstract forms, contributing to the broader acceptance of non-representational painting worldwide. Both movements left enduring legacies, with Futurism inspiring design and architecture and Tachisme advancing the development of expressive abstraction in contemporary art.
Conclusion: Contrasts and Connections
Futurism emphasizes dynamic movement, technology, and industrial progress, while Tachisme focuses on spontaneous, abstract expression through texture and color. Contrasts emerge in Futurism's precise geometric forms versus Tachisme's irregular, emotive brushstrokes. Both movements challenge traditional representation, influencing modern art by pushing boundaries of perception and creativity.
Futurism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com