Oil painting offers rich textures and vibrant colors that can bring any artistic vision to life. Mastering the blend of pigments and drying times allows you to create depth and intricate details in your work. Discover techniques and tips in the rest of the article to enhance your oil painting skills.
Table of Comparison
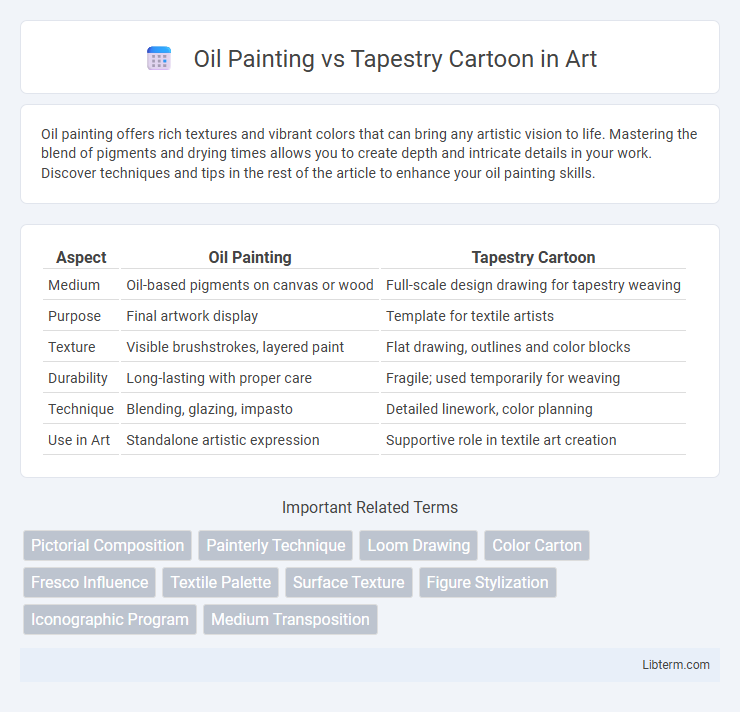
| Aspect | Oil Painting | Tapestry Cartoon |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Oil-based pigments on canvas or wood | Full-scale design drawing for tapestry weaving |
| Purpose | Final artwork display | Template for textile artists |
| Texture | Visible brushstrokes, layered paint | Flat drawing, outlines and color blocks |
| Durability | Long-lasting with proper care | Fragile; used temporarily for weaving |
| Technique | Blending, glazing, impasto | Detailed linework, color planning |
| Use in Art | Standalone artistic expression | Supportive role in textile art creation |
Introduction to Oil Painting and Tapestry Cartoon
Oil painting utilizes pigment suspended in drying oils to create rich textures and vibrant colors, offering flexibility in blending and layering. Tapestry cartoons are full-scale preparatory drawings that guide the weaving of intricate textile artworks, serving as detailed blueprints for tapestry production. Both mediums play crucial roles in art history, with oil paintings emphasizing painterly techniques and tapestry cartoons ensuring precise translation of designs into woven form.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Oil painting originated in the early 15th century, attributed to artists like Jan van Eyck who perfected the use of oil-based pigments for rich color and durability. Tapestry cartoons date back to the medieval period, serving as full-scale preparatory drawings for weaving large decorative tapestries, primarily used in European castles and churches. Over time, oil painting evolved into a primary medium for fine art expression during the Renaissance, while tapestry cartoons transitioned into detailed templates that guided intricate textile production and storytelling.
Artistic Techniques Compared
Oil painting utilizes layered brushstrokes, glazing, and blending techniques to create depth, texture, and rich color variations, enabling precise control over light and shadow. Tapestry cartoons serve as full-scale preparatory designs that guide weaving, relying on line drawing and color blocking without direct modulation, as the weaver translates the image into textile form. The oil painting process emphasizes painterly detail and subtle gradients, while tapestry cartoons prioritize clear composition and contrast to accommodate the weaving medium's constraints.
Materials and Tools Overview
Oil painting utilizes pigments suspended in oil, typically linseed, applied with brushes or palette knives on primed canvas or wood panels, allowing rich texture and vibrant color blending. Tapestry cartoons employ durable materials such as charcoal, chalk, or ink on large sheets of paper or linen to create detailed designs that guide weavers during tapestry production. The primary tools for tapestry cartoons include drawing implements and measuring grids, contrasting with the wide range of brushes and solvents essential in oil painting techniques.
Visual Aesthetics: Color, Texture, and Depth
Oil painting offers rich, vibrant colors with a luminous quality achieved through layering and glazing techniques, creating a dynamic interplay of light and shadow that enhances depth perception. Tapestry cartoons translate designs into woven textiles, where color is expressed through interlaced threads, resulting in a textured surface with a more muted, matte palette that emphasizes tactile dimension over luminous brilliance. The visual depth in oil paintings emerges from nuanced brushwork and tonal gradients, whereas tapestries rely on the physical relief and weave density to evoke spatial complexity and material richness.
Prominent Masters and Notable Works
Oil painting, exemplified by masters like Rembrandt with "The Night Watch" and Johannes Vermeer's "Girl with a Pearl Earring," showcases intricate brushwork and vibrant color blending, creating lifelike textures and depth. Tapestry cartoons, designed by artists such as Raphael for the Vatican tapestries and William Morris for the Arts and Crafts Movement, serve as detailed preparatory drawings that guide the weaving process, emphasizing compositional clarity and decorative motifs. Both mediums highlight the technical skill and artistic vision of their creators, with paintings focusing on direct pigment application and cartoons on translating designs into woven narratives.
Cultural and Symbolic Significance
Oil painting embodies a rich cultural legacy, symbolizing artistic innovation and individual expression since the Renaissance, with its vivid colors and texture reflecting societal values and historical narratives. Tapestry cartoons, as detailed preparatory drawings, hold symbolic significance in medieval and Renaissance art, representing the meticulous planning behind grand tapestries that conveyed power, religious themes, and social order. Both mediums serve as cultural artifacts, illustrating different methods of storytelling and preservation of heritage through visual art.
Preservation and Longevity
Oil paintings, composed of layered pigments on canvas, offer significant durability when properly maintained, resisting fading and environmental damage for centuries. Tapestry cartoons, created as detailed full-scale designs for woven tapestries, often suffer durability challenges due to their paper or cloth materials, making them more susceptible to deterioration from light exposure and humidity. Preservation efforts for oil paintings typically involve climate-controlled environments and protective varnishes, whereas tapestry cartoons require specialized conservation techniques to prevent fragility and preserve intricate details over time.
Modern Adaptations and Innovations
Modern adaptations of oil painting incorporate digital techniques and mixed media to enhance texture and depth, pushing traditional boundaries. Tapestry cartoons have evolved with technological innovations such as digital printing and laser cutting, allowing for more precise and diverse designs. Both art forms increasingly blend classic craftsmanship with contemporary tools to create innovative visual experiences.
Choosing Between Oil Painting and Tapestry Cartoon
Choosing between oil painting and tapestry cartoon depends on the desired medium and artistic effect. Oil paintings offer rich textures, vibrant colors, and greater detail, ideal for standalone art pieces, while tapestry cartoons serve as detailed templates for weaving intricate designs into fabric, emphasizing durability and decorative function. Consider whether the focus is on visual depth and brushwork or on translating a design into textile form when making a decision.
Oil Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com