Geographic curation involves organizing and presenting information based on specific locations to enhance relevance and user engagement. This approach helps You discover content tailored to your area, improving the overall experience. Explore the rest of this article to learn how geographic curation can benefit your information consumption.
Table of Comparison
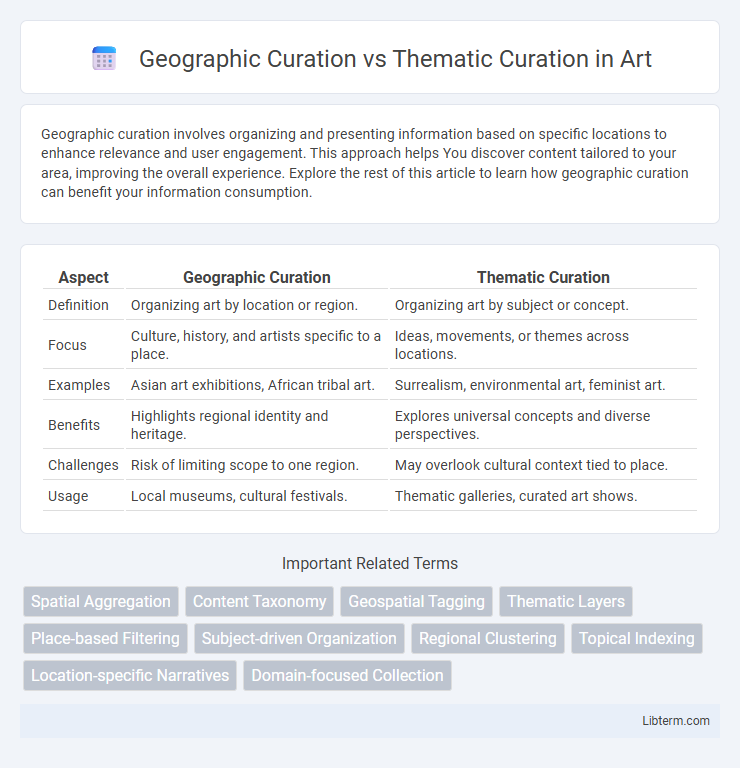
| Aspect | Geographic Curation | Thematic Curation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organizing art by location or region. | Organizing art by subject or concept. |
| Focus | Culture, history, and artists specific to a place. | Ideas, movements, or themes across locations. |
| Examples | Asian art exhibitions, African tribal art. | Surrealism, environmental art, feminist art. |
| Benefits | Highlights regional identity and heritage. | Explores universal concepts and diverse perspectives. |
| Challenges | Risk of limiting scope to one region. | May overlook cultural context tied to place. |
| Usage | Local museums, cultural festivals. | Thematic galleries, curated art shows. |
Introduction to Content Curation
Geographic curation organizes content based on location-specific relevance, enabling targeted audience engagement through regional trends and insights. Thematic curation focuses on unifying content around specific topics or themes, fostering deeper understanding within a subject area. Effective content curation combines both methods to maximize relevance and audience connection across diverse contexts.
Defining Geographic Curation
Geographic curation involves organizing content based on specific locations, such as countries, cities, or regions, enabling targeted regional insights and local relevance. This approach enhances user engagement by delivering content tailored to geographic preferences, trends, and cultural nuances. Geographic curation optimizes content discovery through localized data aggregation and contextual mapping.
Understanding Thematic Curation
Thematic curation organizes content based on shared topics, concepts, or ideas rather than physical locations, enhancing audience engagement by aligning with specific interests or narratives. It leverages semantic tags and metadata to create a coherent and meaningful collection that highlights relationships between different pieces of content. This approach provides deeper insights and richer user experiences by focusing on thematic connections rather than geographic boundaries.
Key Differences Between Geographic and Thematic Curation
Geographic curation organizes content based on specific locations or regions, emphasizing spatial relationships and local context. Thematic curation groups information according to topics, themes, or categories, highlighting conceptual connections and shared subject matter. Key differences include geographic curation's focus on place-based relevance versus thematic curation's focus on subject-driven relevance, affecting how audiences engage with curated materials.
Advantages of Geographic Curation
Geographic curation enhances content relevance by focusing on location-specific data, which improves user engagement through personalized experiences tailored to regional interests and cultural nuances. This approach enables businesses to efficiently target local markets, optimize resource allocation, and increase conversion rates by delivering highly contextualized information. Geographic curation also supports better analytics and decision-making by mapping trends and consumer behavior within defined geographic boundaries.
Benefits of Thematic Curation
Thematic curation enhances user engagement by organizing content around specific topics or themes, making information more relevant and easily accessible. It improves content discoverability and encourages deeper exploration by connecting related materials across diverse geographic locations. This approach supports targeted marketing strategies and personalized user experiences, driving higher retention and satisfaction rates.
Challenges of Geographic and Thematic Approaches
Geographic curation faces challenges in accurately representing diverse regional contexts and maintaining up-to-date spatial data, often hindered by varying local data quality and availability. Thematic curation struggles with defining clear boundaries for subject categories and managing overlapping or evolving themes, leading to potential inconsistencies in content organization. Both approaches require balancing specificity with scalability while ensuring relevance and coherence in curated collections.
Use Cases for Geographic Curation
Geographic curation excels in use cases requiring localized content delivery, such as regional marketing campaigns, local news aggregation, and targeted event promotions. By organizing information based on geographic relevance, businesses can enhance customer engagement and improve user experience through location-specific insights. This approach is critical for sectors like tourism, retail, and real estate, where geographic context directly influences decision-making.
Use Cases for Thematic Curation
Thematic curation excels in organizing content around specific topics, enabling targeted audiences to engage deeply with relevant material such as industry trends, educational resources, or specialized research. Use cases for thematic curation include creating focused knowledge hubs for marketing campaigns, developing comprehensive content collections for e-learning platforms, and aggregating expert insights within niche professional communities. This method enhances user experience by delivering coherent narratives and fostering expertise within a defined thematic scope.
Choosing the Right Curation Strategy
Geographic curation emphasizes organizing content based on specific locations, ideal for travel, local culture, or regional trends, while thematic curation groups information by common subjects or themes, perfect for industry-focused or interest-driven audiences. Choosing the right curation strategy depends on the target audience's needs and the content's purpose; geographic curation suits businesses targeting local markets, whereas thematic curation excels in delivering specialized knowledge or niche topics. Effective curation enhances user engagement by aligning the content structure with audience preferences, boosting relevance and discoverability.
Geographic Curation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com