Medium is a popular online publishing platform that empowers writers to share their stories, ideas, and expertise with a wide audience. Its clean design and user-friendly interface make it easy for you to create engaging content while connecting with readers from diverse backgrounds. Explore the rest of this article to discover tips on maximizing your reach and impact on Medium.
Table of Comparison
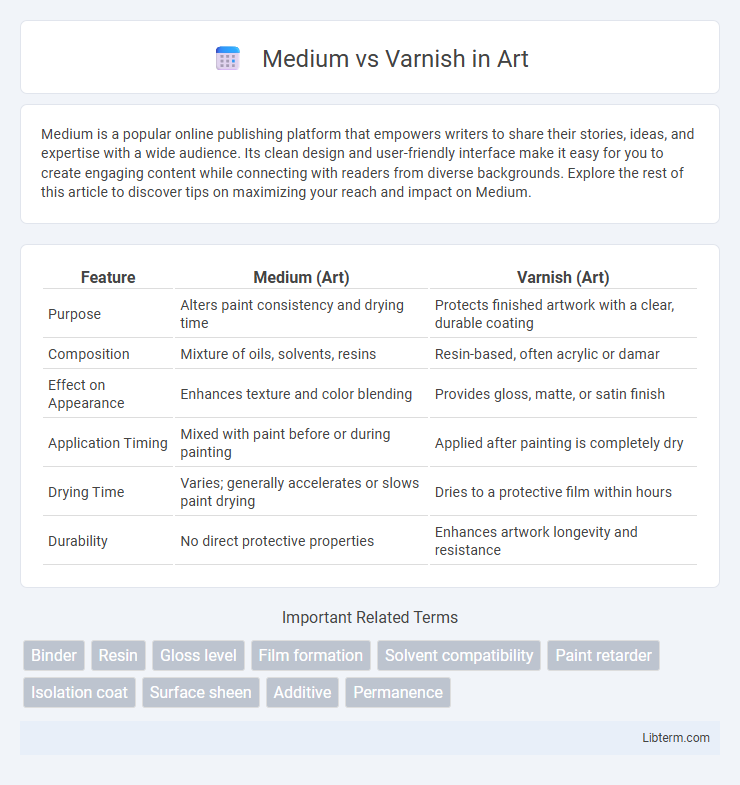
| Feature | Medium (Art) | Varnish (Art) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Alters paint consistency and drying time | Protects finished artwork with a clear, durable coating |
| Composition | Mixture of oils, solvents, resins | Resin-based, often acrylic or damar |
| Effect on Appearance | Enhances texture and color blending | Provides gloss, matte, or satin finish |
| Application Timing | Mixed with paint before or during painting | Applied after painting is completely dry |
| Drying Time | Varies; generally accelerates or slows paint drying | Dries to a protective film within hours |
| Durability | No direct protective properties | Enhances artwork longevity and resistance |
Introduction to Medium and Varnish
Medium is a popular online publishing platform designed to facilitate storytelling and knowledge sharing through clean, user-friendly interfaces that support diverse content formats. Varnish is a powerful HTTP accelerator and reverse proxy used primarily to improve web performance by caching server responses, reducing load times, and enhancing scalability. While Medium focuses on content creation and distribution, Varnish optimizes web delivery and enhances user experience through advanced caching mechanisms.
Core Differences Between Medium and Varnish
Medium is a popular online publishing platform designed for writers and readers to share articles and ideas, emphasizing content creation and community interaction. Varnish is a powerful web application accelerator and HTTP reverse proxy focused on caching and improving website performance by reducing server load and latency. The core difference lies in Medium being a content distribution service, whereas Varnish is a technical tool aimed at optimizing web content delivery and server efficiency.
Purpose and Use Cases of Medium
Medium serves as a user-friendly online publishing platform designed for writers, bloggers, and businesses to share long-form content, stories, and thought leadership articles. It prioritizes ease of content creation and audience engagement, making it ideal for personal expression, brand storytelling, and reaching diverse readerships. Unlike caching solutions like Varnish, Medium aims to foster community interaction and content discovery rather than enhancing website performance or server response times.
Purpose and Use Cases of Varnish
Varnish is a powerful HTTP accelerator designed to cache content and speed up web delivery by storing frequently accessed pages in memory. It is primarily used to improve website performance, reduce server load, and enhance user experience for high-traffic websites, content-heavy platforms, and APIs. Varnish excels in scenarios requiring fast response times and efficient content distribution, such as e-commerce sites, news portals, and streaming services.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Medium typically refers to a base substance used to modify the texture and drying time of paints, often composed of oils or solvents such as linseed oil or turpentine. Varnish consists primarily of a resin dissolved in a solvent that forms a hard, protective coating upon drying, commonly made from natural resins like damar or synthetic polymers. The chemical properties of mediums allow them to remain flexible and blendable, while varnishes chemically cure into a brittle, glossy finish that resists moisture and UV damage.
Application Techniques Compared
Medium application techniques involve using brushes, rollers, or spray equipment to ensure smooth, even coverage tailored to the material's absorbency and texture. Varnish application typically requires multiple thin coats with fine brushes or spray guns, allowing each layer to dry thoroughly to achieve a durable, glossy finish. Both mediums demand surface preparation and controlled environmental conditions for optimal adhesion and longevity.
Impact on Artwork Durability
Mediums significantly influence artwork durability by altering paint adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors, with oil mediums enhancing longevity through increased hardness and resistance to cracking. Varnish serves as a protective top layer that shields artwork from UV light, dust, and moisture, improving longevity without altering the original paint structure. Combining the right medium with a quality varnish optimizes both the mechanical stability and surface protection, prolonging the artwork's lifespan effectively.
Aesthetic Effects and Finish
Mediums enhance paint texture and luminosity by altering viscosity and drying time, allowing artists to achieve varied aesthetic effects such as glossier or matte finishes. Varnishes provide a protective, final layer that can modify the surface sheen, with options including gloss, satin, and matte, preserving the artwork's appearance while adding depth or reducing glare. Both mediums and varnishes contribute to the artwork's visual impact, with mediums influencing the foundational paint qualities and varnishes focusing on long-term finish and durability.
Common Mistakes with Medium and Varnish
Common mistakes with Medium and Varnish include misconfiguring cache settings, leading to ineffective content delivery and slower load times. Many users overlook proper cache invalidation rules in Varnish, causing outdated content to persist and degrade user experience. Additionally, inadequate understanding of Medium's content visibility options can result in unintended exposure or restricted audience reach.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Artwork
When choosing between medium and varnish for your artwork, consider the purpose: mediums modify paint consistency and drying time, enhancing texture and blending, while varnishes provide a protective, glossy or matte finish to preserve the painting. Acrylic mediums like gel or glazing medium increase transparency and flexibility, ideal for layering, whereas varnishes such as damar or synthetic acrylic protect against dust, UV damage, and yellowing. Selecting the right product depends on your artistic goals--use mediums during the painting process for creative effects and varnishes post-completion to seal and conserve the artwork.
Medium Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com