Classical art embodies the principles of harmony, proportion, and balance that defined ancient Greek and Roman aesthetics. It reflects timeless beauty through sculptures, paintings, and architecture that continue to influence modern artistic expressions. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how classical art shapes contemporary creativity and your appreciation for visual culture.
Table of Comparison
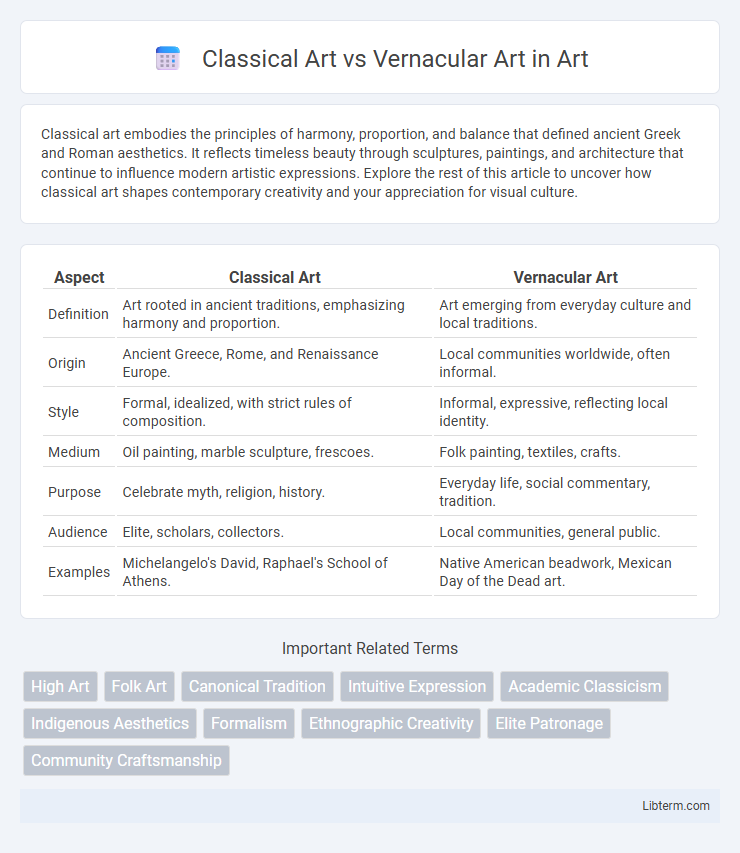
| Aspect | Classical Art | Vernacular Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art rooted in ancient traditions, emphasizing harmony and proportion. | Art emerging from everyday culture and local traditions. |
| Origin | Ancient Greece, Rome, and Renaissance Europe. | Local communities worldwide, often informal. |
| Style | Formal, idealized, with strict rules of composition. | Informal, expressive, reflecting local identity. |
| Medium | Oil painting, marble sculpture, frescoes. | Folk painting, textiles, crafts. |
| Purpose | Celebrate myth, religion, history. | Everyday life, social commentary, tradition. |
| Audience | Elite, scholars, collectors. | Local communities, general public. |
| Examples | Michelangelo's David, Raphael's School of Athens. | Native American beadwork, Mexican Day of the Dead art. |
Defining Classical Art: Origins and Characteristics
Classical art originates from ancient Greek and Roman traditions, characterized by its emphasis on harmony, proportion, and idealized beauty. It often features mythological or historical subjects rendered with precise anatomy and balanced compositions, reflecting philosophical ideals of order and symmetry. This art style prioritizes timeless aesthetics and technical mastery, influencing Western art for centuries.
What is Vernacular Art? Meaning and Context
Vernacular art refers to creative expressions rooted in the everyday lives and cultural traditions of ordinary people, often produced outside formal artistic institutions. It embodies local customs, materials, and social practices, reflecting the community's identity and historical context. Unlike classical art, which follows established academic standards and techniques, vernacular art is characterized by its spontaneous, utilitarian, and culturally specific nature.
Historical Development of Classical and Vernacular Art
Classical art, rooted in ancient Greek and Roman traditions, evolved through the Renaissance by emphasizing idealized forms, symmetry, and adherence to established canons of beauty, reflecting the cultural values of the elite and scholarly classes. Vernacular art developed alongside local customs and everyday life, often created by anonymous artists, embracing regional materials, traditional techniques, and themes relevant to specific communities. The historical development of classical art centralized in academic institutions influenced Western art standards, while vernacular art preserved and expressed diverse cultural identities through folk art, crafts, and popular visual culture.
Techniques and Materials: Classical vs Vernacular Approaches
Classical art techniques emphasize precision, symmetry, and the use of traditional materials such as marble, bronze, and tempera, reflecting meticulous craftsmanship rooted in historical methods. Vernacular art employs locally sourced, everyday materials like wood, fabric, and natural pigments, showcasing spontaneous, culturally specific techniques passed through generations. The contrast highlights classical art's formalized training and vernacular art's organic, community-driven processes.
The Role of Tradition in Classical Art
Classical art relies heavily on established traditions, maintaining strict adherence to historical techniques, subject matter, and aesthetic principles developed during ancient Greek and Roman periods. This emphasis on tradition ensures continuity and preservation of cultural values, reinforcing ideals such as harmony, balance, and proportion in its compositions. The role of tradition in classical art acts as a foundation for artistic mastery and cultural identity, distinguishing it from vernacular art's more flexible, community-based expressions.
Local Culture and Everyday Life in Vernacular Art
Vernacular art captures the essence of local culture and everyday life by reflecting the traditions, customs, and daily experiences of ordinary people, often using familiar motifs and materials accessible to the community. Unlike classical art, which emphasizes idealized forms and universal themes, vernacular art serves as a living record of regional identity and social practices, preserving cultural heritage in its authentic, unfiltered expression. This art form plays a crucial role in sustaining community memory and fostering a sense of belonging through its rootedness in place and lived experience.
Aesthetic Principles: Comparisons and Contrasts
Classical art emphasizes harmony, balance, and idealized forms rooted in Greco-Roman traditions, prioritizing symmetry and proportion to evoke timeless beauty. Vernacular art reflects local culture, customs, and everyday life, often prioritizing function and community meaning over strict aesthetic rules. The contrast lies in classical art's universal aesthetic ideals versus vernacular art's contextual and organic expressions shaped by regional identity.
Social and Cultural Impact of Both Art Forms
Classical art, rooted in formal traditions and academic standards, often reflects the dominant cultural narratives and social hierarchies, reinforcing elite values and historical continuity. Vernacular art, emerging from local customs and everyday life, serves as a vibrant expression of community identity and social resistance, preserving marginalized voices and folk heritage. Both art forms significantly influence societal cohesion and cultural memory by shaping collective identity and enabling dialogue between mainstream and grassroots experiences.
Preservation and Recognition in Contemporary Times
Classical art, characterized by established techniques and historical significance, benefits from widespread preservation efforts supported by museums and academic institutions worldwide. Vernacular art, rooted in local traditions and everyday culture, faces challenges in preservation due to its often transient materials and underrepresentation in formal art discourse. Recognition of vernacular art is increasing through digital platforms and community-driven initiatives, bridging gaps between traditional academic appreciation and contemporary cultural relevance.
The Future of Classical and Vernacular Art Traditions
Classical art, rooted in established historical techniques and themes, continues to influence contemporary artists seeking to preserve traditional aesthetics, while vernacular art thrives by embracing cultural specificity and evolving local narratives. The future of classical art traditions depends on integrating modern technologies with time-honored craftsmanship to maintain relevance in global art markets. Vernacular art's trajectory is shaped by digital platforms that amplify localized expressions, fostering cross-cultural dialogue and expanding its audience beyond indigenous communities.
Classical Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com