Institutions play a critical role in shaping social, economic, and political frameworks by establishing rules and norms that guide individual and collective behavior. Effective institutions foster stability, promote trust, and drive sustainable development within communities and nations. Explore the article to understand how institutions impact your daily life and contribute to broader societal progress.
Table of Comparison
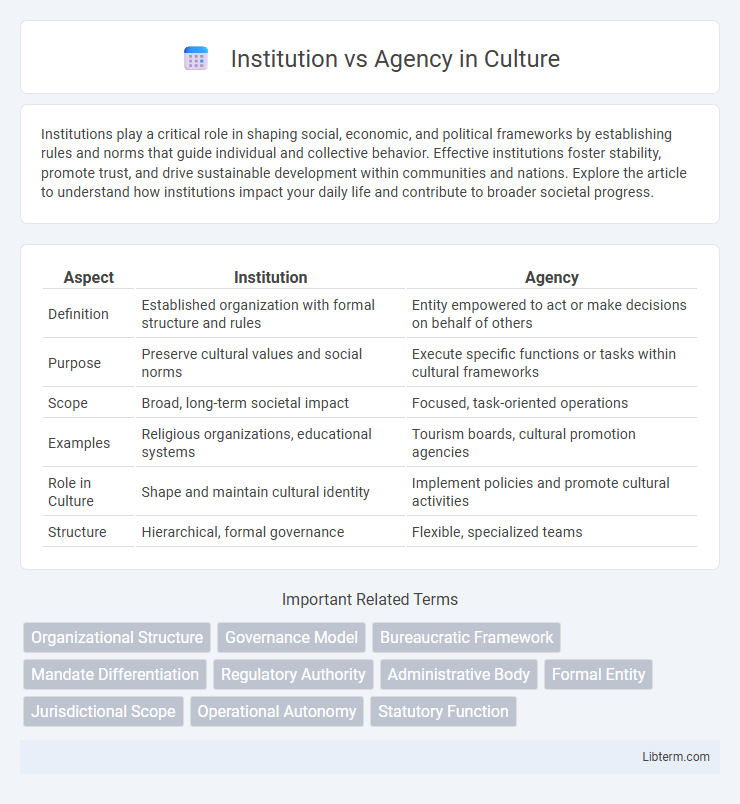
| Aspect | Institution | Agency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Established organization with formal structure and rules | Entity empowered to act or make decisions on behalf of others |
| Purpose | Preserve cultural values and social norms | Execute specific functions or tasks within cultural frameworks |
| Scope | Broad, long-term societal impact | Focused, task-oriented operations |
| Examples | Religious organizations, educational systems | Tourism boards, cultural promotion agencies |
| Role in Culture | Shape and maintain cultural identity | Implement policies and promote cultural activities |
| Structure | Hierarchical, formal governance | Flexible, specialized teams |
Understanding Institutions and Agencies
Institutions are established systems or structures that govern social behavior, such as legal, educational, or governmental frameworks, whereas agencies refer to organizations or entities that execute specific functions within these systems. Understanding institutions involves analyzing their roles, rules, and norms that shape societal interactions, while understanding agencies focuses on their operational capacities and decision-making processes within institutional contexts. This distinction highlights how institutions provide the overarching rules, and agencies act as the actors implementing policies and actions.
Key Definitions: Institution vs Agency
Institutions refer to established systems or structures governing behavior, such as laws, norms, and organizations that shape societal functions and interactions. Agencies denote the capacity of individuals or groups to act independently and make choices within or outside these institutional frameworks. Understanding the key definitions highlights institutions as the overarching frameworks, while agencies represent the actors exercising autonomy within or against these structures.
Historical Evolution of Institutions and Agencies
Institutions have evolved over centuries as foundational structures shaping social, political, and economic order, originating from early tribal governance and religious organizations to modern legal and educational systems. Agencies developed later as specialized bodies or entities designed to implement policies and manage specific functions within or on behalf of institutions, often emerging alongside the rise of complex bureaucratic states in the 19th and 20th centuries. The historical evolution reflects institutions as enduring frameworks with broad societal roles, while agencies serve as dynamic, operative extensions facilitating institutional goals.
Core Functions and Roles
Institutions establish foundational rules, norms, and frameworks that shape political, economic, and social interactions within a society, serving as stable reference points for behavior and governance. Agencies operate within these institutional frameworks, executing specific tasks, policies, and programs to achieve targeted objectives, often functioning as administrative or operational arms of the government or organizations. The core function of institutions lies in creating continuity and legitimacy, whereas agencies focus on implementation, enforcement, and service delivery.
Structural Differences
Institutions are formal organizations with established rules, roles, and procedures designed to govern behavior within societies, often embodying long-term societal norms and values. Agencies, in contrast, refer to the capacity of individuals or entities to act independently and make choices within the constraints of institutional structures, emphasizing dynamic decision-making and action. Structural differences highlight that institutions provide stable frameworks for social order, while agency represents the ability to navigate, influence, or change these frameworks through individual or collective action.
Impact on Governance and Society
Institutions shape governance by establishing enduring norms, laws, and frameworks that guide political and social behavior, ensuring stability and predictability in societal interactions. Agencies operate within these institutional structures to implement policies, deliver public services, and respond to specific societal needs, directly influencing daily governance outcomes. The dynamic interplay between institutions and agencies determines the effectiveness, accountability, and adaptability of governance systems, ultimately affecting social trust and public welfare.
Examples of Institutions and Agencies
Examples of institutions include universities, banks, and courts, which serve foundational roles in education, finance, and legal systems. Agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), and Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) operate as specialized governmental bodies enforcing regulations and managing specific public functions. Institutions are often broad entities shaping societal norms, while agencies execute targeted administrative or regulatory tasks within governmental frameworks.
Comparative Analysis: Strengths and Weaknesses
Institutions possess long-term structural stability and established norms that foster consistent policy implementation, while agencies offer flexibility and specialization, enabling rapid response to specific issues. Institutions may suffer from rigidity and slower adaptation due to bureaucratic layers, whereas agencies risk narrow focus and potential fragmentation without overarching coordination. Effective governance often requires balancing the institutional depth and legitimacy with the operational agility and expertise of agencies.
Influence on Policy-Making
Institutions establish formal rules and frameworks that shape policy-making processes by defining roles, responsibilities, and procedural norms, thereby ensuring stability and consistency in governance. Agencies act as operational arms within these institutions, applying policies through implementation, enforcement, and specialized expertise, directly influencing policy outcomes on the ground. The dynamic interaction between institutions' structural authority and agencies' practical execution determines the effectiveness and adaptability of policy decisions.
Future Trends and Challenges
Institutions and agencies are evolving rapidly due to advancements in technology and increasing demands for transparency and accountability. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence for decision-making and enhanced data analytics to improve policy outcomes. Future challenges involve addressing cybersecurity threats, adapting to regulatory changes, and managing the ethical implications of automated governance systems.
Institution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com