Internet culture shapes how communities connect, share ideas, and express creativity across digital platforms worldwide. Memes, social media trends, and online slang evolve rapidly, influencing both virtual and real-life interactions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your online behaviors impact this dynamic culture.
Table of Comparison
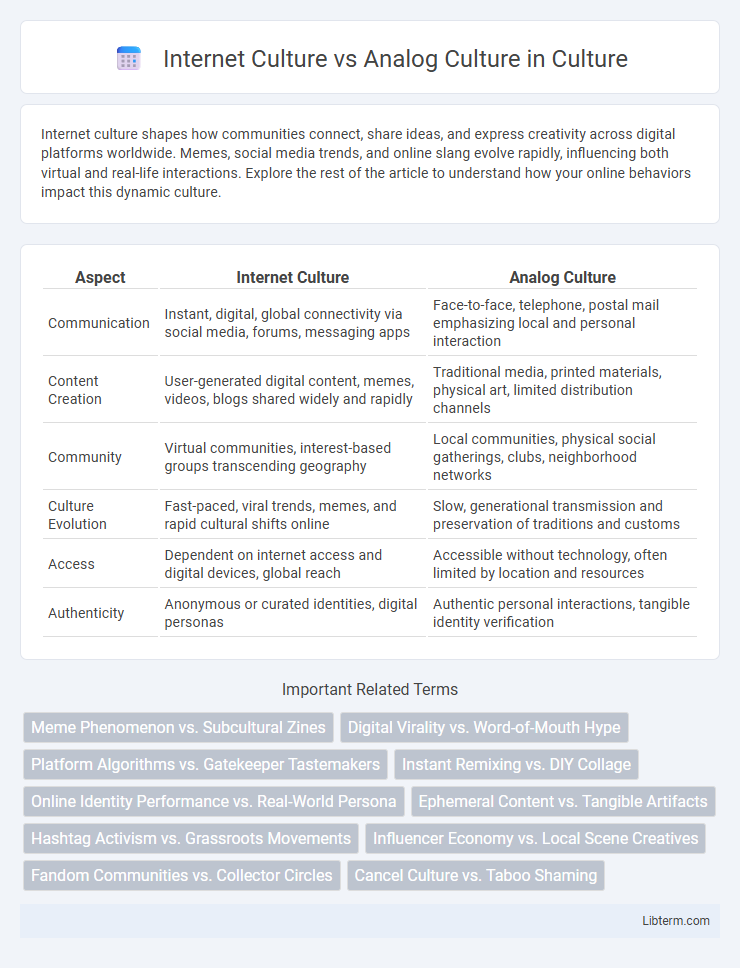
| Aspect | Internet Culture | Analog Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Instant, digital, global connectivity via social media, forums, messaging apps | Face-to-face, telephone, postal mail emphasizing local and personal interaction |
| Content Creation | User-generated digital content, memes, videos, blogs shared widely and rapidly | Traditional media, printed materials, physical art, limited distribution channels |
| Community | Virtual communities, interest-based groups transcending geography | Local communities, physical social gatherings, clubs, neighborhood networks |
| Culture Evolution | Fast-paced, viral trends, memes, and rapid cultural shifts online | Slow, generational transmission and preservation of traditions and customs |
| Access | Dependent on internet access and digital devices, global reach | Accessible without technology, often limited by location and resources |
| Authenticity | Anonymous or curated identities, digital personas | Authentic personal interactions, tangible identity verification |
Defining Internet Culture and Analog Culture
Internet culture centers around digital communication, social media trends, memes, and virtual communities shaping modern interactions globally. Analog culture emphasizes physical, face-to-face experiences, traditional media, and tangible artifacts that define pre-digital social and cultural exchanges. Both cultures influence identity formation, communication styles, and information dissemination but differ fundamentally in mediums and immediacy.
Evolution from Analog to Digital Societies
The evolution from analog to digital societies marks a profound shift in communication, creativity, and social interaction, driven by the rise of Internet culture characterized by immediacy, global connectivity, and information abundance. Analog culture relied heavily on physical media, face-to-face interactions, and localized communities, whereas Internet culture enables decentralized digital networks, user-generated content, and real-time collaboration transcending geographic boundaries. This transition reshapes identity formation, collective memory, and cultural production by merging traditional narratives with digital innovation and virtual environments.
Communication Styles: Online vs Offline
Internet culture favors rapid, concise communication through text, emojis, and multimedia, enabling instant global connectivity and asynchronous interactions. Analog culture emphasizes face-to-face conversations, non-verbal cues, and vocal tone, enhancing emotional depth and immediate feedback. These contrasting communication styles highlight the shift from personal, context-rich exchanges to fast, text-based interactions shaped by digital platforms.
Community Building in Virtual and Physical Spaces
Internet culture fosters global community building through digital platforms like social media, forums, and multiplayer games, enabling instant communication and shared experiences across diverse geographic locations. Analog culture emphasizes local, face-to-face interactions in physical spaces such as community centers, clubs, and neighborhoods, promoting deeper interpersonal connections and social cohesion. The contrast lies in virtual spaces offering scalability and inclusivity, while physical spaces provide tangible presence and nonverbal communication essential for strong social bonds.
Impact on Creativity and Content Creation
Internet culture accelerates creativity and content creation by enabling instant global collaboration, diverse multimedia formats, and rapid dissemination through social media platforms like TikTok and YouTube. Analog culture relies on slower, more tactile processes such as handwritten manuscripts and physical art, which often results in lengthier creative development and limited audience reach. This digital shift democratizes content production, fostering innovative styles and interactive experiences that were not feasible in traditional analog environments.
Identity and Self-Expression in Both Worlds
Internet culture amplifies identity fluidity through digital avatars, social media profiles, and online communities, enabling users to experiment with self-expression beyond geographic and social constraints. Analog culture grounds identity in physical presence, tangible interactions, and localized social norms, fostering self-expression through real-world artifacts like fashion, art, and interpersonal communication. The contrast highlights digital platforms as spaces for curated, performative identities, while analog environments emphasize authentic, embodied expressions shaped by immediate cultural and social contexts.
Memory, Preservation, and Cultural Heritage
Internet culture revolutionizes memory and preservation through digital archives, cloud storage, and instant access, enabling dynamic and participatory cultural heritage experiences. Analog culture relies on physical media such as printed books, photographs, and artifacts that preserve tangible, fixed memories requiring careful maintenance and limited accessibility. The shift from analog to internet culture transforms cultural heritage stewardship, emphasizing digitization, global connectivity, and evolving narratives over static, localized traditions.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Behaviors
Technology drives a fundamental shift in behavior, with internet culture emphasizing instant communication, digital multitasking, and global connectivity, while analog culture values face-to-face interactions, slower information exchange, and physical presence. Online platforms foster new social norms, influence identity expression, and reshape attention spans, promoting rapid information consumption and viral content sharing. Analog culture's reliance on tangible experiences encourages deeper reflection, sustained focus, and community rituals rooted in physical settings, highlighting contrasting impacts on cognitive and social behaviors.
Challenges and Benefits of Each Culture
Internet culture accelerates communication and global connectivity, fostering rapid information exchange and diverse collaboration, but it also faces challenges like digital misinformation, privacy concerns, and decreased face-to-face interaction. Analog culture emphasizes tangible experiences, deep personal connections, and reinforced community bonds, yet struggles with slower information dissemination and limited accessibility across distances. Balancing the dynamic benefits of digital innovation against the authenticity and reliability of analog interactions remains a key challenge in modern cultural evolution.
The Future: Merging Digital and Analog Realms
The future envisions a seamless integration of Internet culture with analog culture, where digital technologies enhance traditional experiences without replacing them. Augmented reality and smart devices enable users to interact with physical environments enriched by digital information, fostering a hybrid cultural landscape. This convergence drives innovation in art, communication, and social interaction, creating immersive experiences that blend the tactile with the virtual.
Internet Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com