Virtual culture shapes how people interact, communicate, and collaborate in online environments, influencing social norms and behaviors across digital platforms. Understanding virtual culture enhances your ability to navigate remote work, online communities, and global networks effectively. Discover how virtual culture impacts communication and relationships by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
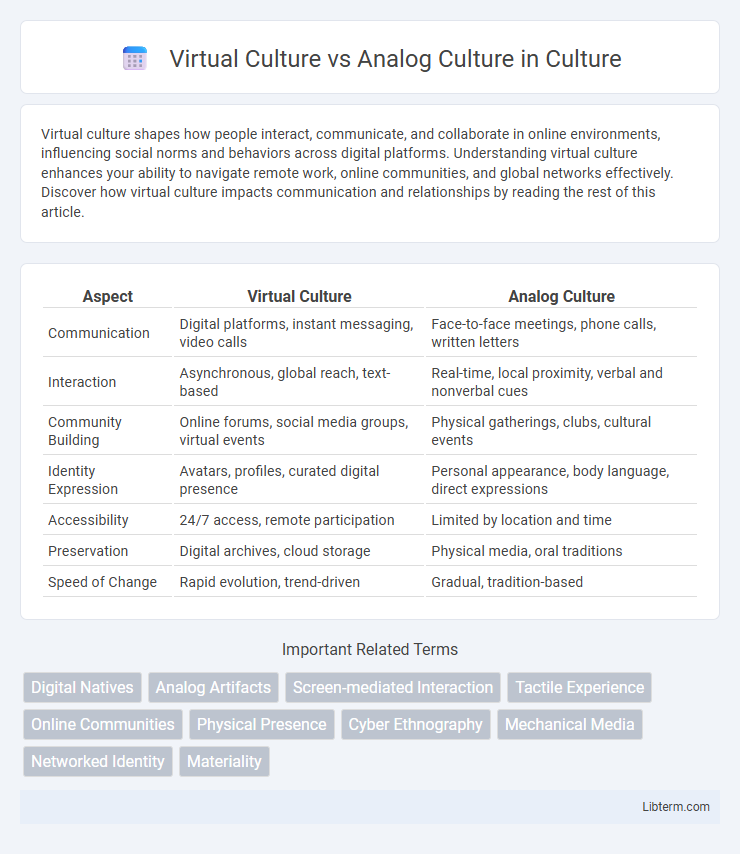
| Aspect | Virtual Culture | Analog Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Digital platforms, instant messaging, video calls | Face-to-face meetings, phone calls, written letters |
| Interaction | Asynchronous, global reach, text-based | Real-time, local proximity, verbal and nonverbal cues |
| Community Building | Online forums, social media groups, virtual events | Physical gatherings, clubs, cultural events |
| Identity Expression | Avatars, profiles, curated digital presence | Personal appearance, body language, direct expressions |
| Accessibility | 24/7 access, remote participation | Limited by location and time |
| Preservation | Digital archives, cloud storage | Physical media, oral traditions |
| Speed of Change | Rapid evolution, trend-driven | Gradual, tradition-based |
Introduction to Virtual and Analog Cultures
Virtual culture revolves around digital environments where interactions occur through online platforms, social media, and virtual communities, emphasizing connectivity, immediacy, and global reach. Analog culture pertains to traditional, physical-world interactions and communication, rooted in face-to-face exchanges, tangible artifacts, and localized social norms. Understanding these cultural frameworks highlights the shift in how societies engage, communicate, and preserve cultural values across different mediums.
Defining Virtual Culture in the Digital Age
Virtual culture in the digital age encompasses the shared practices, values, and social interactions that emerge through online platforms, digital communication, and virtual environments. It redefines community by transcending physical boundaries, enabling real-time global connectivity, and fostering new forms of identity and collaboration. Digital technologies shape this culture by influencing language, behavior, and social norms within the virtual spaces people inhabit.
Analog Culture: Traditions and Tangibility
Analog culture emphasizes the preservation of traditions and the tangible experiences embedded in physical interactions, such as handwritten letters, face-to-face conversations, and handcrafted artifacts. These practices foster a deep sense of authenticity and emotional connection, reinforcing cultural heritage through sensory engagement and shared rituals. The physicality of analog culture supports memory retention and community bonding, contrasting with the fleeting and often intangible nature of digital experiences.
Key Differences Between Virtual and Analog Experiences
Virtual culture emphasizes digital interaction, relying on online platforms, social media, and virtual environments for communication and community building, while analog culture is rooted in face-to-face interactions, physical presence, and tangible experiences. Virtual experiences offer immediate, global connectivity and immersive multimedia engagement, whereas analog experiences provide sensory richness, authenticity, and deeper emotional connections through direct human contact. The key differences lie in accessibility, sensory input, and the nature of social dynamics shaped by technology in virtual culture versus physical proximity in analog culture.
The Impact of Technology on Human Interaction
Virtual culture transforms human interaction by enabling instant communication across global networks, fostering diverse connections beyond physical boundaries. Technology-mediated interactions prioritize efficiency and accessibility but can reduce non-verbal cues critical for emotional understanding. Analog culture relies on face-to-face communication, enhancing empathy and social bonding through tangible presence and shared environments.
Cultural Preservation: Analog Media vs Digital Archives
Analog culture relies on physical artifacts like books, paintings, and tapes that offer tactile and sensory experiences crucial for cultural preservation. Digital archives enable vast, searchable databases that safeguard cultural heritage through high-resolution imaging, metadata tagging, and cloud storage, ensuring longevity and accessibility. Challenges include digital obsolescence and data degradation, contrasting with analog media's vulnerability to physical decay but enduring sensory authenticity.
Creativity and Expression in Virtual vs Analog Platforms
Virtual culture fosters creativity and expression through digital tools that enable instant sharing, multimedia integration, and global collaboration, expanding artistic possibilities beyond physical limitations. Analog culture emphasizes tactile engagement and sensory experience, where creativity is shaped by material interaction, craftsmanship, and the unique imperfections of handmade work. The contrast highlights virtual platforms' capacity for rapid innovation and diverse expression, while analog platforms preserve authenticity and intimate connection in creative processes.
Social Connectivity: Virtual Communities vs Physical Gatherings
Virtual culture enhances social connectivity through online platforms, enabling global communities to interact instantly regardless of location, fostering diverse and dynamic virtual networks. Analog culture depends on physical gatherings, promoting face-to-face interactions that strengthen local bonds and create deeper emotional connections through shared experiences. The contrast highlights digital platforms' efficiency in maintaining widespread virtual communities, while physical events nurture tangible social cohesion and trust.
Challenges and Benefits of Each Cultural Paradigm
Virtual culture offers increased accessibility and global connectivity, enabling real-time collaboration and diverse perspectives across digital platforms. Challenges include digital fatigue, reduced face-to-face interaction, and difficulties in interpreting non-verbal cues, which can hinder deep relationship-building. Analog culture provides rich, personal communication and stronger emotional bonds but faces limitations in scalability and geographical constraints.
The Future: Bridging Virtual and Analog Worlds
The future of culture lies in integrating virtual and analog experiences to create a seamless hybrid environment where digital interactions enhance physical presence. Emerging technologies like augmented reality and mixed reality enable immersive engagements, allowing users to navigate between virtual spaces and tangible settings effortlessly. This fusion drives innovation in education, entertainment, and social connectivity, redefining cultural participation in the digital age.
Virtual Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com