Dialectic logic explores the process of reasoning through dialogue and contradiction, aiming to arrive at truth by resolving opposing ideas. It emphasizes the dynamic nature of thought, contrasting with traditional static logic frameworks. Discover how dialectic logic can enhance your critical thinking by reading the rest of the article.
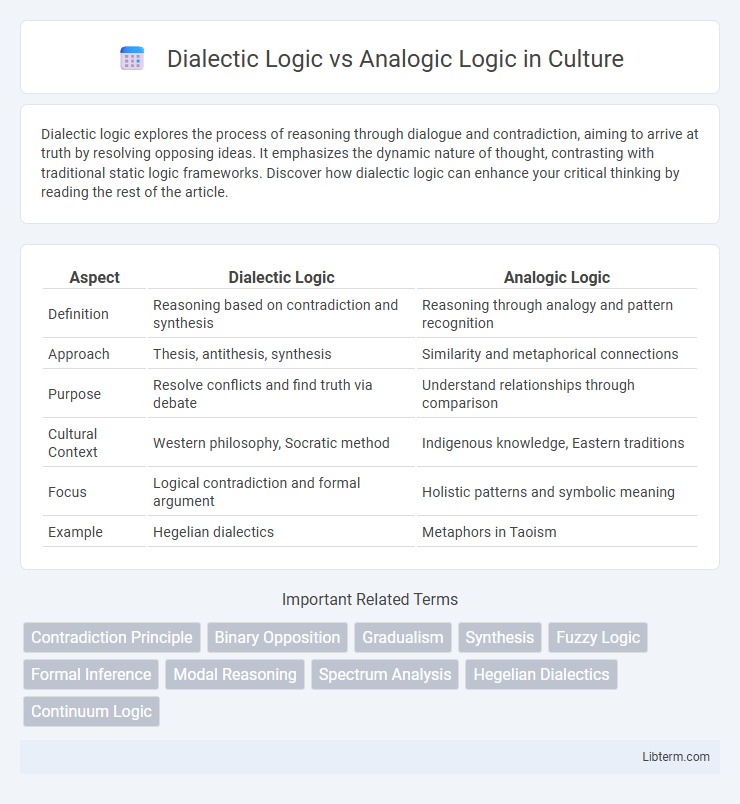
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dialectic Logic | Analogic Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reasoning based on contradiction and synthesis | Reasoning through analogy and pattern recognition |
| Approach | Thesis, antithesis, synthesis | Similarity and metaphorical connections |
| Purpose | Resolve conflicts and find truth via debate | Understand relationships through comparison |
| Cultural Context | Western philosophy, Socratic method | Indigenous knowledge, Eastern traditions |
| Focus | Logical contradiction and formal argument | Holistic patterns and symbolic meaning |
| Example | Hegelian dialectics | Metaphors in Taoism |
Introduction to Dialectic Logic and Analogic Logic
Dialectic Logic centers on the process of reasoning through contradictions and oppositions to reach higher levels of understanding, emphasizing thesis, antithesis, and synthesis. Analogic Logic relies on drawing parallels and highlighting similarities between different concepts or phenomena to foster comprehension and insight. Both frameworks serve distinct cognitive functions, with dialectic logic driving dynamic change and conflict resolution, while analogic logic facilitates pattern recognition and analogy-based reasoning.
Defining Dialectic Logic
Dialectic logic is a method of reasoning that emphasizes the resolution of contradictions through dialogue, integrating opposing ideas to arrive at higher truths or synthesis. Unlike analogic logic, which relies on comparisons and similarities between concepts to infer conclusions, dialectic logic focuses on the dynamic process of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis to reveal deeper understanding. It is foundational in philosophical discourse, particularly in Hegelian and Marxist traditions, for analyzing complex social and intellectual phenomena.
Understanding Analogic Logic
Analogic logic emphasizes reasoning through the recognition of patterns, relationships, and similarities between different entities, often relying on metaphor and analogy rather than strict formal rules. It supports problem-solving by drawing parallels from known experiences to new situations, enabling flexible and creative thinking. Understanding analogic logic involves appreciating its capacity to bridge abstract concepts and concrete examples, facilitating insight where dialectic logic's binary oppositions and contradictions may be less effective.
Historical Origins and Philosophical Roots
Dialectic logic, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, particularly in the works of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, emphasizes argumentation through thesis, antithesis, and synthesis to reveal contradictions and advance knowledge. Analogic logic, with origins tracing back to medieval scholasticism and later formalized in the 19th and 20th centuries, relies on analogies and comparative reasoning to understand relationships between disparate concepts. While dialectic logic inherently focuses on dynamic, oppositional processes, analogic logic prioritizes relational similarities, reflecting distinct philosophical commitments to change versus resemblance.
Core Principles of Dialectic Logic
Dialectic logic centers on the dynamic interplay of contradictory ideas and the synthesis that emerges from their resolution, emphasizing change and development through thesis, antithesis, and synthesis. It contrasts with analogic logic, which relies on similarity and analogy to establish reasoning based on resemblance rather than contradiction. Core principles of dialectic logic include the recognition of contradictions as driving forces, the processual nature of reality, and the unity and struggle of opposites.
Fundamental Concepts of Analogic Logic
Analogic logic is based on the principle of analogy, emphasizing relationships and similarities between different entities rather than fixed binary categories. Fundamental concepts include the use of continuous variables, interpretation of partial truths, and the recognition of context-dependent meanings that reflect real-world complexity. This logic system contrasts with dialectic logic by prioritizing fluid, nuanced connections over oppositional frameworks.
Key Differences Between Dialectic and Analogic Logic
Dialectic logic centers on reasoning through contradictions and synthesis, emphasizing thesis, antithesis, and resolution to arrive at truth, while analogic logic relies on similarity and analogy to draw conclusions by comparing comparable situations or concepts. Dialectic logic is dynamic and process-oriented, focusing on evolving ideas through debate and contradiction, whereas analogic logic is static and pattern-based, depending on identifying shared properties between entities. Key differences include dialectic's emphasis on conflict and resolution versus analogic's emphasis on resemblance and metaphorical inference.
Applications in Real-World Problem Solving
Dialectic Logic excels in real-world problem solving by facilitating the resolution of contradictions through structured debate and critical analysis, making it highly effective in conflict resolution, legal reasoning, and ethical decision-making. Analogic Logic applies comparative reasoning by drawing parallels between similar situations, proving valuable in fields like medicine, design thinking, and artificial intelligence for pattern recognition and innovation. Combining both logics enhances problem-solving strategies by leveraging dialectical synthesis with analogical inference for comprehensive and adaptive solutions.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Dialectic logic excels in resolving contradictions through structured argumentation, fostering critical thinking and synthesis of opposing ideas but can be limited by its reliance on binary oppositions and potential for endless debate. Analogic logic leverages similarity and analogy to facilitate creative problem-solving and intuitive understanding, though it may lead to oversimplifications or false equivalences when dissimilar elements are compared. The strength of dialectic logic lies in rigorous debate and clarity, while analogic logic offers flexibility and innovation, each constrained by their inherent methodological biases.
Conclusion: Integrating Dialectic and Analogic Perspectives
Integrating dialectic and analogic logic enhances critical thinking by combining the structured, oppositional reasoning of dialectics with the relational, pattern-based insights of analogies. This synthesis promotes more comprehensive problem-solving and innovation by balancing contradiction analysis with creative similarity recognition. Employing both perspectives enables a deeper understanding of complex issues and supports adaptive decision-making in diverse contexts.
Dialectic Logic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com