Scientific discoveries continuously reshape our understanding of the universe, driving innovation and improving everyday life. Breakthroughs in fields like biotechnology, physics, and environmental science offer solutions to global challenges and unlock new possibilities. Dive into this article to explore how science impacts your world and future.
Table of Comparison
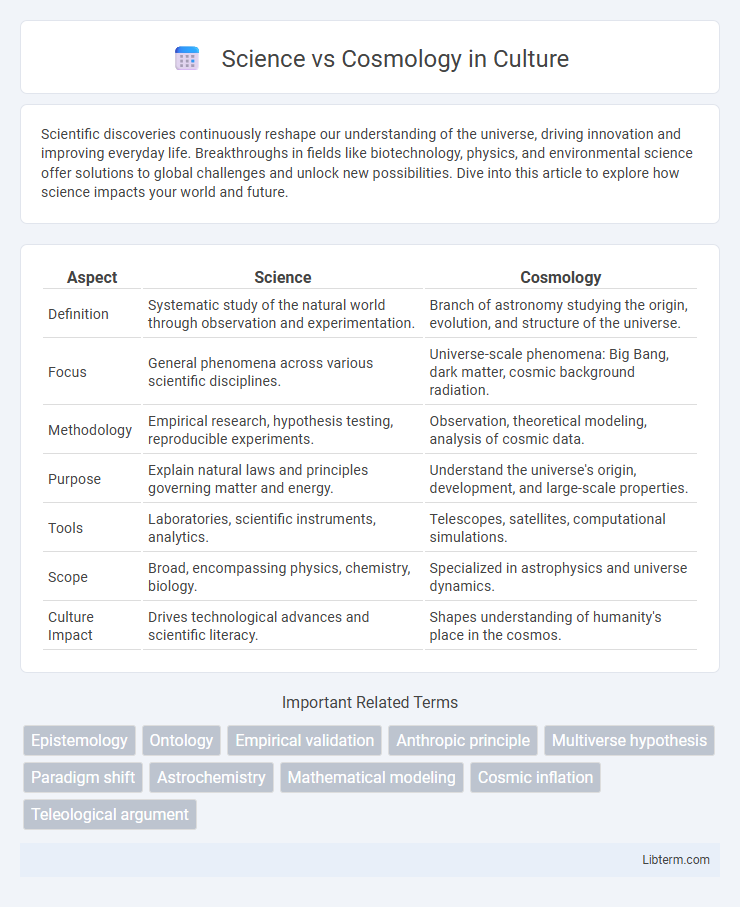
| Aspect | Science | Cosmology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic study of the natural world through observation and experimentation. | Branch of astronomy studying the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe. |
| Focus | General phenomena across various scientific disciplines. | Universe-scale phenomena: Big Bang, dark matter, cosmic background radiation. |
| Methodology | Empirical research, hypothesis testing, reproducible experiments. | Observation, theoretical modeling, analysis of cosmic data. |
| Purpose | Explain natural laws and principles governing matter and energy. | Understand the universe's origin, development, and large-scale properties. |
| Tools | Laboratories, scientific instruments, analytics. | Telescopes, satellites, computational simulations. |
| Scope | Broad, encompassing physics, chemistry, biology. | Specialized in astrophysics and universe dynamics. |
| Culture Impact | Drives technological advances and scientific literacy. | Shapes understanding of humanity's place in the cosmos. |
Introduction to Science and Cosmology
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge through testable explanations and predictions about the natural world. Cosmology, a specialized branch of science, studies the origin, evolution, and eventual fate of the universe based on astronomical observations and theoretical physics. Understanding fundamental concepts in physics and astronomy is essential to grasp cosmological theories such as the Big Bang, dark matter, and cosmic microwave background radiation.
Defining Science: Methods and Purpose
Science employs systematic observation, experimentation, and empirical evidence to understand natural phenomena, emphasizing testable hypotheses and reproducibility. Its purpose centers on developing reliable knowledge through the scientific method, which includes observation, formulation of hypotheses, experimentation, and analysis. In contrast, cosmology applies scientific principles specifically to study the universe's origin, structure, evolution, and fundamental laws.
Understanding Cosmology: Scope and Goals
Cosmology, a branch of science, focuses on studying the universe's origin, structure, evolution, and eventual fate by applying physics and astronomy principles. It aims to understand phenomena such as the Big Bang, cosmic microwave background radiation, dark matter, and dark energy, using observational data from telescopes and satellite missions. The scope of cosmology extends from the largest cosmic scales to the fundamental laws governing spacetime, seeking to explain the universe's history and predict its future.
Historical Perspectives: Science and Cosmology
Historical perspectives on science and cosmology reveal a progression from mythological explanations of the universe to empirical investigations grounded in observation and mathematics. Early civilizations like the Babylonians and Greeks laid foundational cosmological models, while the Scientific Revolution introduced methods that transformed cosmology into a rigorous science, exemplified by Copernicus' heliocentric theory and Newton's laws of motion. The integration of telescopic discoveries and Einstein's theory of relativity further refined cosmological understanding, bridging empirical science and the study of the cosmos.
The Interplay Between Science and Cosmology
Science and cosmology intersect through the systematic study of the universe's origin, structure, and evolution, employing empirical methods and theoretical physics. Advances in cosmology, including the Big Bang theory and cosmic microwave background radiation, rely heavily on scientific experimentation and observation techniques such as spectroscopy and telescope data analysis. This interplay enhances understanding of fundamental forces, dark matter, and dark energy, driving progress in both astrophysics and particle physics.
Key Differences in Approach and Methodology
Science relies on empirical evidence and experimental methods to test hypotheses and validate theories through observation, measurement, and reproducible results. Cosmology, a branch of science, specifically studies the origin, structure, and evolution of the universe using observational data like cosmic microwave background radiation, redshift of galaxies, and theoretical models based on physics and mathematics. The key difference lies in cosmology's heavy reliance on indirect observation and theoretical constructs due to the universe's vast scale and inability to perform controlled experiments, whereas general science often benefits from direct experimentation and more immediate data collection.
Major Discoveries in Cosmology Through Science
Major discoveries in cosmology through science include the identification of the cosmic microwave background radiation, which provided strong evidence for the Big Bang theory. Observations of galaxy redshifts led to the understanding of the expanding universe, establishing Hubble's law as a key scientific principle. Advances in telescope technology and satellite missions like the Planck satellite have refined measurements of the universe's age, composition, and large-scale structure, deepening our knowledge of dark matter and dark energy.
Philosophical Questions: Science vs Cosmology
Philosophical questions in science and cosmology explore the origins and fundamental nature of the universe, questioning what can be empirically tested versus what remains speculative. Science relies on observable evidence and falsifiable hypotheses, while cosmology often grapples with metaphysical concepts such as the multiverse, the nature of space-time, and the existence of a cosmic beginning. The distinction highlights challenges in defining the limits of scientific inquiry and the role of philosophy in interpreting cosmological phenomena.
Contemporary Debates and Challenges
Contemporary debates in science and cosmology center on the interpretation of dark matter, dark energy, and the advancement of quantum gravity theories, challenging the limits of current astrophysical models. The tension between observational data from telescopes and theoretical frameworks, such as string theory and loop quantum gravity, fuels ongoing discussions about the universe's origin and structure. These challenges drive innovation in experimental cosmology, including deep-space probes and cosmic microwave background measurements, essential for refining or refuting existing hypotheses.
Future Directions in Science and Cosmological Research
Future directions in science emphasize interdisciplinary approaches combining quantum mechanics, astrophysics, and computational modeling to deepen understanding of the universe's origins and structure. Advances in telescopic technologies and space missions aim to probe dark matter, dark energy, and cosmic inflation with unprecedented precision. Integration of artificial intelligence in data analysis accelerates discoveries in cosmology, potentially unraveling fundamental mysteries about the multiverse and the ultimate fate of the cosmos.
Science Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com