Cultural preservation safeguards the traditions, languages, and heritage that define a community's unique identity. Protecting these elements fosters a deeper understanding and respect for diverse histories and practices. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can contribute to preserving cultural richness.
Table of Comparison
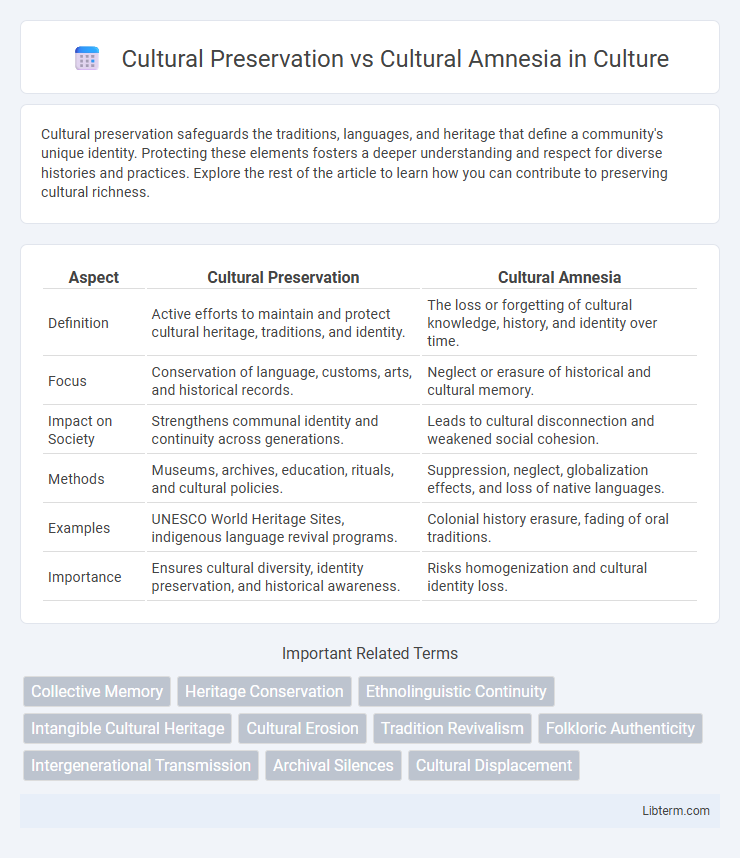
| Aspect | Cultural Preservation | Cultural Amnesia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active efforts to maintain and protect cultural heritage, traditions, and identity. | The loss or forgetting of cultural knowledge, history, and identity over time. |
| Focus | Conservation of language, customs, arts, and historical records. | Neglect or erasure of historical and cultural memory. |
| Impact on Society | Strengthens communal identity and continuity across generations. | Leads to cultural disconnection and weakened social cohesion. |
| Methods | Museums, archives, education, rituals, and cultural policies. | Suppression, neglect, globalization effects, and loss of native languages. |
| Examples | UNESCO World Heritage Sites, indigenous language revival programs. | Colonial history erasure, fading of oral traditions. |
| Importance | Ensures cultural diversity, identity preservation, and historical awareness. | Risks homogenization and cultural identity loss. |
Understanding Cultural Preservation
Understanding cultural preservation involves actively maintaining and safeguarding intangible heritage such as traditions, languages, and rituals to ensure their transmission to future generations. Effective cultural preservation requires community engagement, documentation, and educational initiatives that reinforce cultural identity and prevent loss due to globalization or modernization. Preserving cultural elements enhances social cohesion and fosters appreciation of diverse heritages within a global context.
Defining Cultural Amnesia
Cultural amnesia refers to the collective forgetting or suppression of significant historical events, traditions, and identities within a society, resulting in a loss of cultural continuity. This phenomenon often occurs due to political repression, colonization, or social upheaval, erasing critical aspects of heritage and memory. Preserving cultural knowledge through education, documentation, and community engagement is essential to counteract cultural amnesia and maintain cultural diversity.
Historical Roots of Cultural Memory
Historical roots of cultural memory anchor societies by preserving ancestral knowledge, traditions, and values, ensuring intergenerational continuity. Cultural preservation involves actively maintaining artifacts, oral histories, and rituals to combat cultural amnesia, a phenomenon where collective forgetting erases essential identities. The tension between these forces shapes national narratives and influences contemporary cultural resilience amid globalization.
The Role of Education in Cultural Continuity
Education plays a pivotal role in cultural preservation by transmitting historical knowledge, traditions, and values to younger generations, ensuring cultural continuity. Curriculum that incorporates indigenous languages, arts, and heritage fosters a strong cultural identity and counters cultural amnesia. Schools and community programs act as vital platforms for safeguarding intangible cultural assets and promoting intergenerational dialogue.
Technology’s Impact on Cultural Identity
Technology shapes cultural identity by enabling digital archives and virtual museums that preserve endangered languages, traditions, and histories for future generations. However, the rapid spread of global media and social platforms can contribute to cultural amnesia, diluting unique cultural expressions and promoting homogenization. Balancing technological innovation with mindful cultural preservation ensures that diverse heritages remain vibrant and accessible in the digital age.
Globalization and the Erosion of Traditions
Globalization accelerates cultural exchange but often contributes to the erosion of traditional practices and languages, leading to cultural amnesia among younger generations. The dominance of global media and economic systems marginalizes indigenous customs, resulting in the loss of unique cultural identities. Efforts in cultural preservation prioritize safeguarding intangible heritage, such as oral traditions and rituals, to counterbalance globalization's homogenizing effects.
Community Efforts in Safeguarding Heritage
Community efforts in safeguarding heritage play a vital role in combating cultural amnesia by actively preserving traditions, languages, and historic landmarks. Grassroots organizations, local museums, and cultural festivals unite residents to maintain collective memory and reinforce identity, ensuring intergenerational transmission of cultural knowledge. Digital archiving, oral history projects, and educational programs enhance accessibility and engagement, strengthening resilience against the erosion of cultural heritage.
Challenges Facing Indigenous Cultures
Indigenous cultures face challenges such as loss of language, erosion of traditional knowledge, and displacement from ancestral lands that jeopardize cultural preservation. The impact of globalization and modernization accelerates cultural amnesia, diminishing practices and rituals integral to community identity. Efforts to document and revitalize indigenous languages and customs are critical to counteracting these challenges and maintaining cultural heritage.
Cultural Revitalization Movements
Cultural revitalization movements actively counter cultural amnesia by restoring forgotten customs, languages, and traditions to strengthen community identity and continuity. These efforts often involve reclaiming historical narratives, promoting indigenous knowledge, and integrating ancestral practices into contemporary life. By prioritizing the transmission of cultural heritage across generations, revitalization combats the erosion caused by globalization and assimilation pressures.
Balancing Progress with Tradition
Balancing progress with tradition requires fostering cultural preservation through safeguarding indigenous languages, rituals, and historic landmarks while embracing technological and social innovations that drive modern development. Effective cultural preservation promotes identity continuity and intergenerational knowledge transfer, countering cultural amnesia, which results in the erosion of heritage and communal values. Sustainable cultural policies integrate education and community participation, ensuring that modernization respects and revitalizes traditional practices without stalling societal growth.
Cultural Preservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com