Cultural appreciation involves respecting and valuing the traditions, customs, and expressions of different cultures without appropriating or disrespecting them. Understanding the significance behind cultural elements enriches your perspective and fosters genuine connections. Explore the article to learn how to embrace cultural appreciation thoughtfully and meaningfully.
Table of Comparison
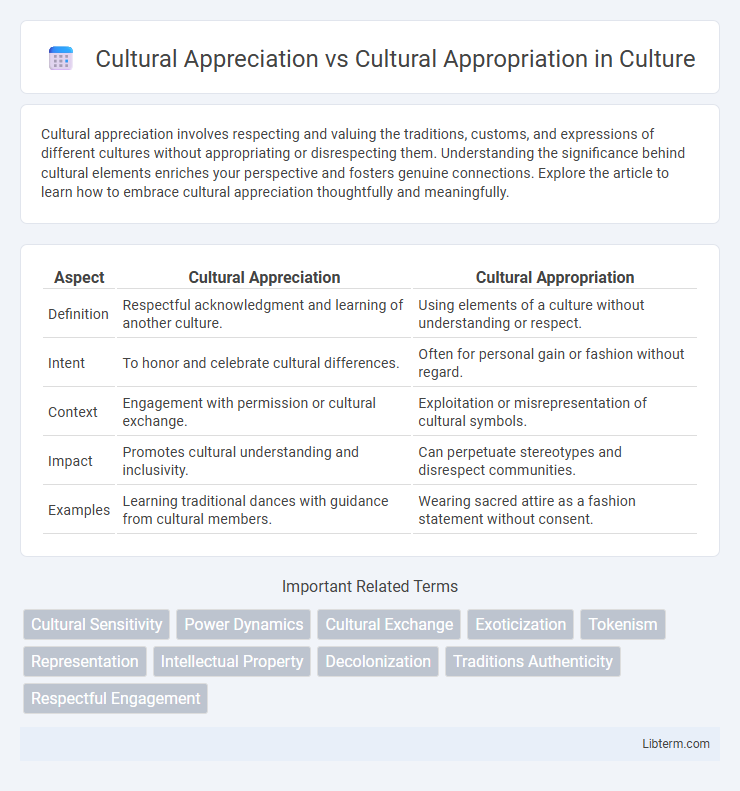
| Aspect | Cultural Appreciation | Cultural Appropriation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Respectful acknowledgment and learning of another culture. | Using elements of a culture without understanding or respect. |
| Intent | To honor and celebrate cultural differences. | Often for personal gain or fashion without regard. |
| Context | Engagement with permission or cultural exchange. | Exploitation or misrepresentation of cultural symbols. |
| Impact | Promotes cultural understanding and inclusivity. | Can perpetuate stereotypes and disrespect communities. |
| Examples | Learning traditional dances with guidance from cultural members. | Wearing sacred attire as a fashion statement without consent. |
Understanding Cultural Appreciation and Appropriation
Cultural appreciation involves respectfully engaging with and learning about another culture's traditions, art, and practices, fostering mutual respect and understanding. In contrast, cultural appropriation occurs when elements of a culture are taken out of context, often by a dominant group, without permission or acknowledgement, leading to misrepresentation and exploitation. Recognizing the boundaries and significance behind cultural symbols helps distinguish appreciation from appropriation, promoting ethical cultural exchange.
Defining Key Terms: Appreciation vs Appropriation
Cultural appreciation involves respectfully engaging with and valuing another culture's customs, traditions, and artifacts, ensuring acknowledgment and understanding of their significance. Cultural appropriation occurs when elements of a marginalized culture are taken out of context, exploited, or used without permission, often perpetuating stereotypes or contributing to cultural erasure. The key distinction lies in intention, respect, and the power dynamics between the cultures involved.
Historical Context of Cultural Exchange
Cultural appreciation involves respectful engagement with another culture's traditions, often rooted in a historical context of mutual exchange and influence between societies. Historical examples include the Silk Road, where goods, ideas, and cultural practices were shared, fostering understanding rather than exploitation. In contrast, cultural appropriation frequently stems from unequal power dynamics, where dominant groups adopt elements of marginalized cultures without acknowledgment or respect for their historical significance.
Signs of Cultural Appreciation
Signs of cultural appreciation include respectful engagement with traditions, such as learning the history and meaning behind cultural practices rather than merely adopting superficial elements. Genuine appreciation involves supporting and crediting the original creators or communities, ensuring their voices and contributions are acknowledged. Respectful cultural appreciation fosters understanding and celebration of diversity without exploiting or misrepresenting the culture.
Red Flags of Cultural Appropriation
Cultural appropriation often involves using symbols, clothing, or rituals from marginalized cultures without understanding their significance, leading to disrespect and perpetuation of stereotypes. Red flags include commodifying sacred traditions, ignoring the historical context, and profiting from elements of another culture without consent or acknowledgment. This behavior can contribute to cultural erasure and reinforce power imbalances between dominant and marginalized communities.
Power Dynamics and Privilege in Culture Sharing
Cultural appreciation involves respectful engagement with traditions and practices, recognizing the historical context and power imbalances that shape cultural interactions. Cultural appropriation occurs when individuals from dominant groups exploit elements of marginalized cultures without permission, often reinforcing systemic inequalities and erasing the original meaning. Understanding power dynamics and privilege is essential to differentiate between honoring cultural heritage and perpetuating cultural harm.
Impact on Marginalized Communities
Cultural appropriation often perpetuates stereotypes and reinforces power imbalances by exploiting marginalized communities without proper respect or understanding. In contrast, cultural appreciation involves honoring traditions and practices with acknowledgment and consent, fostering mutual respect and cultural exchange. The impact on marginalized groups can be profound, as appropriation may lead to cultural erasure and economic disenfranchisement, while appreciation promotes empowerment and preservation of cultural identity.
Examples of Positive Cultural Appreciation
Positive cultural appreciation occurs when individuals respectfully engage with traditions, such as participating in traditional Japanese tea ceremonies while honoring their origins and significance. Wearing indigenous clothing with permission and understanding the cultural symbolism reflects genuine admiration rather than exploitation. Learning and sharing authentic recipes from diverse cultures, like preparing Indian cuisine while acknowledging its rich culinary history, exemplifies respectful cultural appreciation.
Famous Cases of Cultural Appropriation
Famous cases of cultural appropriation include the fashion industry's use of Indigenous patterns without permission, sparking widespread criticism for disrespecting Native American heritage. Celebrities like Kylie Jenner faced backlash for using traditional African hairstyles such as cornrows, highlighting the ongoing debate between cultural appreciation and exploitation. The controversy surrounding the Coachella festival's adoption of Native American headdresses further exemplifies the clash between admiration and cultural insensitivity.
Guidelines for Respectful Cultural Engagement
Respectful cultural engagement requires understanding and honoring the origins and significance of cultural elements, ensuring permission and collaboration with members of the culture involved. Avoiding stereotypes, commodification, and misrepresentation promotes genuine appreciation instead of exploitation. Prioritizing education, empathy, and reciprocal exchange helps maintain cultural integrity and fosters meaningful cross-cultural connections.
Cultural Appreciation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com