Cultural competence involves understanding, respecting, and effectively interacting with people from diverse cultural backgrounds. It enhances communication, reduces biases, and promotes inclusive environments in both personal and professional settings. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for developing your cultural competence.
Table of Comparison
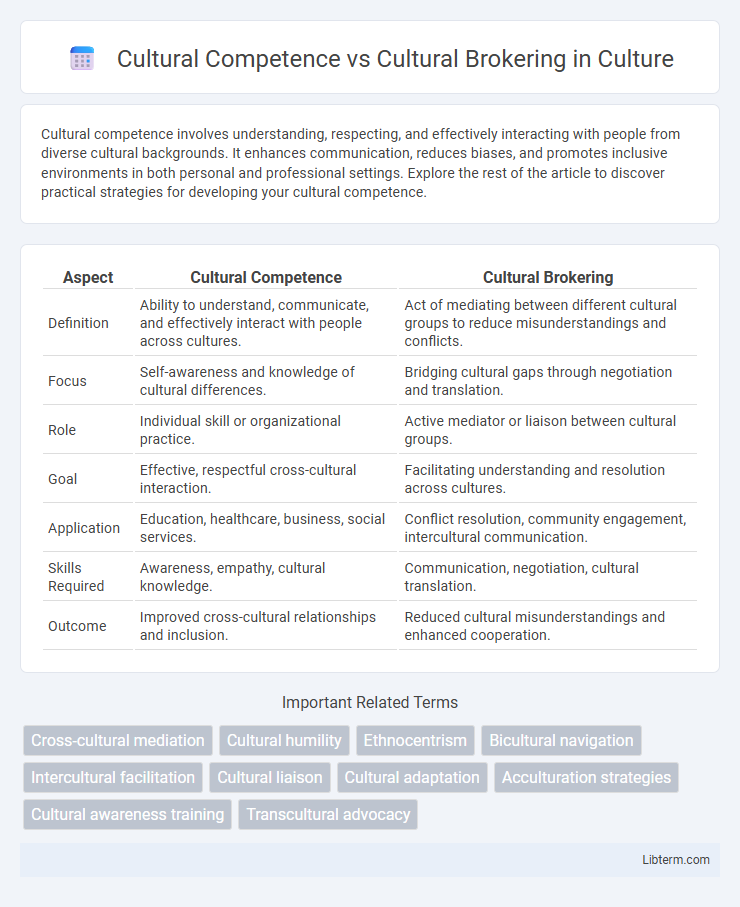
| Aspect | Cultural Competence | Cultural Brokering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to understand, communicate, and effectively interact with people across cultures. | Act of mediating between different cultural groups to reduce misunderstandings and conflicts. |
| Focus | Self-awareness and knowledge of cultural differences. | Bridging cultural gaps through negotiation and translation. |
| Role | Individual skill or organizational practice. | Active mediator or liaison between cultural groups. |
| Goal | Effective, respectful cross-cultural interaction. | Facilitating understanding and resolution across cultures. |
| Application | Education, healthcare, business, social services. | Conflict resolution, community engagement, intercultural communication. |
| Skills Required | Awareness, empathy, cultural knowledge. | Communication, negotiation, cultural translation. |
| Outcome | Improved cross-cultural relationships and inclusion. | Reduced cultural misunderstandings and enhanced cooperation. |
Defining Cultural Competence
Cultural competence refers to the ability of individuals or organizations to understand, communicate with, and effectively interact with people across cultures by recognizing and respecting cultural differences and adapting practices accordingly. It involves awareness of one's own cultural worldview, knowledge of different cultural practices and worldviews, and cross-cultural skills to engage appropriately in diverse environments. Unlike cultural brokering, which actively mediates and negotiates cultural differences between groups, cultural competence emphasizes ongoing learning and self-reflection to provide inclusive and sensitive services or support.
Understanding Cultural Brokering
Cultural brokering involves actively mediating between diverse cultural groups to facilitate communication, understanding, and trust, often resolving conflicts rooted in cultural differences. Unlike cultural competence, which emphasizes an individual's awareness and respect for cultural diversity, cultural brokering requires dynamic interaction and negotiation skills to bridge gaps in values, beliefs, and practices. Effective cultural brokers utilize deep knowledge of multiple cultural frameworks to advocate for equitable outcomes in healthcare, education, and social services.
Key Differences Between Cultural Competence and Cultural Brokering
Cultural competence involves acquiring knowledge, attitudes, and skills to effectively interact with diverse populations, focusing on understanding and respecting cultural differences. Cultural brokering goes beyond competence by actively mediating and bridging gaps between cultures to resolve conflicts and facilitate access to resources. The key difference lies in cultural brokering's role as an intermediary, while cultural competence centers on personal awareness and skill development.
Importance of Cultural Competence in Diverse Settings
Cultural competence enhances communication and service delivery by enabling individuals and organizations to understand and respect diverse cultural perspectives, which is vital in multicultural environments such as healthcare, education, and social services. It fosters trust, reduces misunderstandings, and improves outcomes by promoting inclusivity and responsiveness to cultural differences. While cultural brokering involves mediating between cultures, cultural competence equips professionals with the ongoing skills and knowledge necessary to effectively engage with diverse populations independently.
The Role of Cultural Brokers in Bridging Gaps
Cultural brokers play a crucial role in bridging gaps by facilitating understanding and communication between diverse cultural groups, enhancing service delivery and community engagement. They possess deep cultural knowledge and negotiation skills that help navigate cultural nuances, reduce misunderstandings, and build trust among stakeholders. This role goes beyond cultural competence by actively mediating conflicts, interpreting cultural contexts, and promoting inclusive practices in healthcare, education, and social services.
Skills Required for Effective Cultural Competence
Effective cultural competence requires skills such as active listening, empathy, adaptability, and a deep understanding of diverse cultural norms and values. These skills enable professionals to navigate cultural differences respectfully and avoid biases during interactions. In contrast, cultural brokering emphasizes mediation and negotiation abilities, translating not just language but also cultural contexts to bridge gaps between disparate groups.
Essential Qualities of a Successful Cultural Broker
Successful cultural brokers demonstrate deep cultural awareness, empathy, and effective communication skills, enabling them to bridge gaps between diverse communities and service providers. They possess adaptability and conflict resolution abilities to navigate complex intercultural interactions sensitively. Strong ethical standards and trustworthiness are essential to facilitate mutual respect and understanding among all parties involved.
Benefits of Integrating Both Approaches
Integrating cultural competence and cultural brokering enhances communication and understanding between diverse populations and service providers by combining knowledge of cultural nuances with active mediation skills. This dual approach reduces misunderstandings, improves client trust, and promotes equitable access to resources and services. Organizations adopting both strategies achieve higher client satisfaction and more effective outcomes in multicultural settings.
Challenges in Achieving Cultural Competency and Brokering
Cultural competence involves understanding and respecting diverse cultural backgrounds, but achieving it is challenged by inherent biases, limited cultural knowledge, and dynamic cultural identities. Cultural brokering requires mediating between cultures to facilitate understanding, yet faces difficulties such as language barriers, conflicting cultural norms, and mistrust between parties. Both processes demand ongoing education, empathy, and effective communication skills to overcome obstacles and foster inclusive environments.
Best Practices for Fostering Culturally Responsive Environments
Fostering culturally responsive environments requires embracing both cultural competence and cultural brokering to effectively navigate diverse perspectives and communication styles. Best practices include ongoing cultural awareness training, active listening, and engaging community stakeholders to bridge cultural gaps and promote mutual respect. Implementing these strategies enhances organizational inclusivity and ensures services are accessible and relevant to diverse populations.
Cultural Competence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com