Folklore preserves the rich traditions, myths, and cultural values passed down through generations, shaping communities' identities and beliefs. Understanding these stories reveals insights into humanity's collective imagination and social history. Explore the rest of the article to discover how folklore influences modern culture and your connection to these timeless narratives.
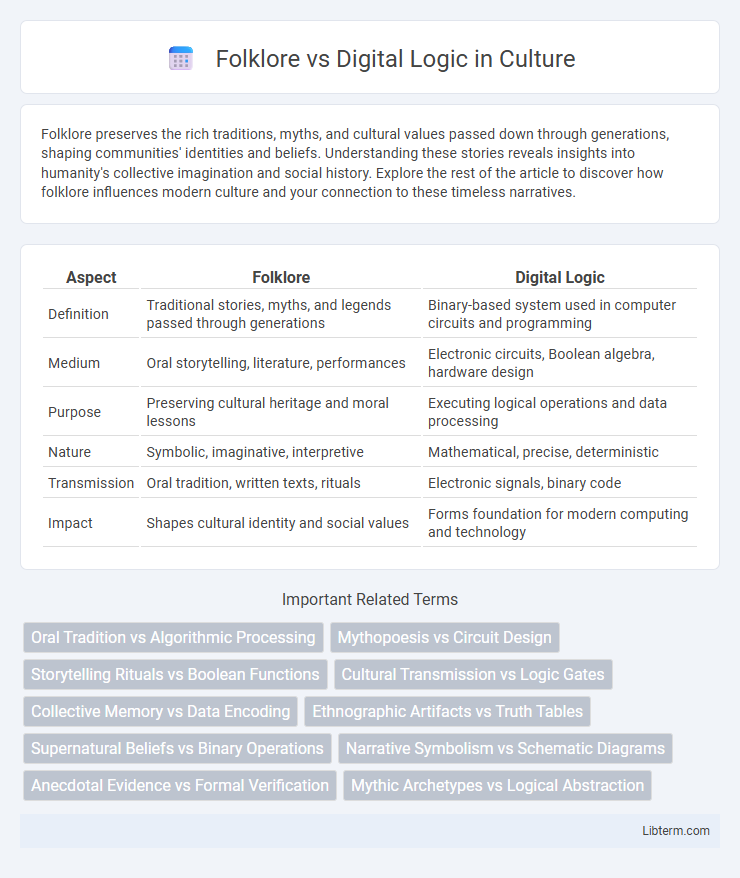
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Folklore | Digital Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional stories, myths, and legends passed through generations | Binary-based system used in computer circuits and programming |
| Medium | Oral storytelling, literature, performances | Electronic circuits, Boolean algebra, hardware design |
| Purpose | Preserving cultural heritage and moral lessons | Executing logical operations and data processing |
| Nature | Symbolic, imaginative, interpretive | Mathematical, precise, deterministic |
| Transmission | Oral tradition, written texts, rituals | Electronic signals, binary code |
| Impact | Shapes cultural identity and social values | Forms foundation for modern computing and technology |
Understanding Folklore: Origins and Definitions
Folklore encompasses the traditional beliefs, customs, stories, and practices passed down through generations orally or by example, reflecting a community's cultural heritage. Its origins trace back to pre-literate societies where knowledge and moral lessons were shared through myths, legends, and rituals, serving as a collective memory and social glue. Understanding folklore involves recognizing its role in preserving identity and values, contrasting with digital logic's foundation in binary computation and formal, systematic information processing.
What Is Digital Logic? Foundations and Principles
Digital logic forms the foundational framework for designing and implementing electronic circuits using binary signals represented by two discrete voltage levels, typically 0 and 1. It is based on Boolean algebra and employs logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT to perform basic operations that enable complex computational processes in digital systems. Key principles include signal integrity, timing, synchronization, and the hierarchical organization of combinational and sequential logic components for reliable and predictable circuit behavior.
Historical Context: Folklore in Human Societies
Folklore in human societies dates back thousands of years, serving as a primary means of preserving and transmitting cultural values, beliefs, and traditions through storytelling, music, and rituals. Unlike digital logic, which emerged in the 20th century with the development of electronic computing, folklore evolved organically within oral cultures long before written language became widespread. This historical context highlights folklore's role as a foundational element in shaping collective identity and social cohesion across diverse civilizations.
The Rise of Digital Logic in the Modern Era
The rise of digital logic in the modern era has revolutionized computing and electronics, replacing traditional folklore-based computational methods with precise binary systems and Boolean algebra. Innovations in semiconductor technology and integrated circuits have accelerated the adoption of digital logic, enabling faster, more reliable, and scalable electronic devices. This shift has driven advancements across industries, from microprocessors and communication networks to artificial intelligence and automation.
Key Differences: Storytelling vs. Binary Systems
Folklore centers on storytelling that transmits cultural values and collective memory through narratives rich in symbolism and oral tradition. Digital logic relies on binary systems using two-state values, 0 and 1, to perform computations and control electronic circuits with precise, rule-based operations. The primary distinction lies in folklore's qualitative, human-centered expression versus digital logic's quantitative, machine-oriented processing.
Cultural Transmission vs. Data Processing
Folklore serves as a vital vehicle for cultural transmission, preserving traditions, beliefs, and collective identity through oral narratives, rituals, and communal memory across generations. Digital logic, in contrast, operates as the foundational framework for data processing in computing systems, utilizing binary code and logical gates to perform precise, algorithmic tasks. The interplay between folklore and digital logic highlights the contrast between human-centered storytelling methods and machine-centered information processing techniques.
Examples: Folklore Narratives and Logic Circuits
Folklore narratives often use symbolic storytelling to explain natural phenomena or cultural values, such as the fable of the tortoise and the hare illustrating patience and perseverance. In contrast, logic circuits in digital electronics rely on precise boolean operations and gate functions like AND, OR, and NOT to perform computations and data processing. While folklore encodes meaning through metaphor and human experience, digital logic circuits encode information through binary signals and deterministic algorithms.
Impact on Society: Tradition vs. Innovation
Folklore preserves cultural identity through storytelling and rituals, fostering community bonds and shared values across generations. Digital logic drives technological innovation, transforming communication, industry, and everyday life with increased efficiency and connectivity. The interplay between tradition and innovation shapes societal evolution, balancing preservation of heritage with advancement in digital technologies.
Folklore and Digital Logic in Education
Folklore in education preserves cultural heritage through storytelling, traditional practices, and communal knowledge sharing, enriching students' understanding of historical identities and values. Digital logic education focuses on the principles of binary systems, logic gates, and circuit design, providing essential skills for understanding computer architecture and programming fundamentals. Integrating folklore and digital logic fosters a diverse learning environment where cultural context complements technological competence.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Heritage and Technology
Bridging the gap between folklore and digital logic involves leveraging traditional narratives to inspire innovative computational models and human-computer interaction designs. Embedding cultural heritage in digital frameworks enhances the relevance and accessibility of technology in diverse communities, fostering inclusivity. This integration promotes the preservation of intangible cultural assets while advancing the development of context-aware digital systems.
Folklore Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com