Oral tradition preserves cultural knowledge, stories, and customs through spoken word across generations, serving as a vital link to ancestral heritage. It strengthens community identity and offers rich insight into the values and history of societies unable to record their narratives in writing. Explore the rest of this article to uncover the significance of oral tradition in shaping human culture.
Table of Comparison
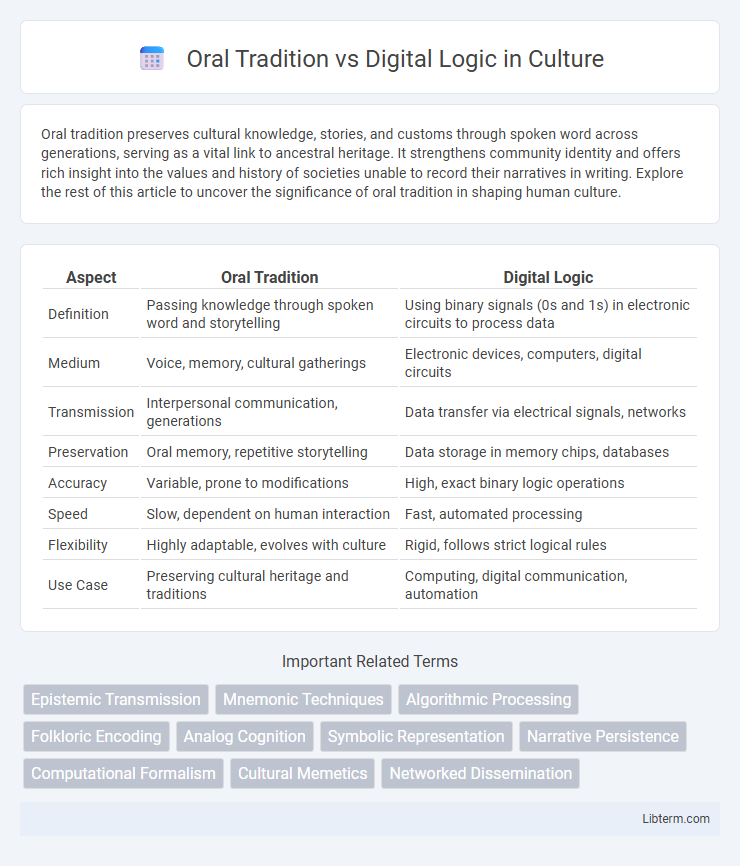
| Aspect | Oral Tradition | Digital Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passing knowledge through spoken word and storytelling | Using binary signals (0s and 1s) in electronic circuits to process data |
| Medium | Voice, memory, cultural gatherings | Electronic devices, computers, digital circuits |
| Transmission | Interpersonal communication, generations | Data transfer via electrical signals, networks |
| Preservation | Oral memory, repetitive storytelling | Data storage in memory chips, databases |
| Accuracy | Variable, prone to modifications | High, exact binary logic operations |
| Speed | Slow, dependent on human interaction | Fast, automated processing |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable, evolves with culture | Rigid, follows strict logical rules |
| Use Case | Preserving cultural heritage and traditions | Computing, digital communication, automation |
Introduction to Oral Tradition and Digital Logic
Oral tradition is the practice of passing stories, knowledge, and cultural values verbally from generation to generation without written records, relying on memory and communal interaction. Digital logic, by contrast, employs binary systems and electronic circuits to process, store, and transmit information in modern computing devices. Understanding the foundational differences in information transmission between oral tradition and digital logic reveals the evolution from human-centered communication to machine-centered data processing.
Historical Evolution of Communication
Oral tradition served as the primary mode of communication for millennia, relying on storytelling, memory, and communal participation to preserve historical knowledge and cultural values. The advent of digital logic revolutionized communication by enabling precise information processing, storage, and transmission through binary systems, which underpin modern computing and telecommunications. This shift marks a significant transformation from ephemeral oral exchanges to persistent, scalable digital data management, profoundly impacting how societies record and share information.
Core Principles of Oral Tradition
Oral tradition relies on memory, storytelling, and communal participation to transmit knowledge, emphasizing repetition, rhythm, and mnemonic devices to preserve information accurately. It prioritizes human interaction and context-dependent communication over formal structures or binary processing found in digital logic. The core principles also include adaptability, personalization, and the integration of cultural values, making knowledge transmission an evolving and social experience rather than a fixed, coded system.
Fundamentals of Digital Logic
Fundamentals of digital logic revolve around binary systems, Boolean algebra, and logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, enabling precise electronic circuit design and computation. Unlike oral tradition, which relies on human memory and verbal transmission of knowledge, digital logic provides a formal framework for encoding, processing, and storing information in digital devices. This shift to digital logic underpins modern computing technologies, facilitating reliable data manipulation and automated decision-making.
Oral Narratives vs. Digital Data
Oral narratives preserve cultural heritage through spoken storytelling, relying on memory, performance, and social interaction to transmit knowledge across generations. Digital data encodes information in binary formats, enabling precise storage, rapid processing, and scalable distribution within electronic systems. The contrast highlights the fluid, context-dependent nature of oral tradition against the structured, reproducible characteristics of digital logic.
Knowledge Transmission: Storytelling vs. Coding
Oral tradition relies on storytelling to transmit knowledge through generations, preserving cultural values, histories, and social norms via spoken word and mnemonic devices. Digital logic employs coding languages, algorithms, and binary systems to encode, process, and transmit data efficiently, enabling precise and scalable knowledge storage and retrieval. While storytelling fosters emotional connection and contextual understanding, coding ensures accuracy, reproducibility, and rapid dissemination in modern digital communication.
Memory, Authenticity, and Preservation
Oral tradition relies on human memory, which can introduce variations but maintains authenticity through communal repetition and cultural context. Digital logic ensures precise preservation of data by encoding information in binary form, minimizing errors and enabling long-term storage. While oral tradition is dynamic and adaptive, digital memory offers consistency and scalability for preserving information over generations.
Technology’s Impact on Oral Cultures
Technology's impact on oral cultures has transformed knowledge transmission from oral tradition to digital logic, profoundly altering communication methods. Oral traditions rely on memory, storytelling, and communal participation, whereas digital logic facilitates storage, retrieval, and dissemination through electronic media and algorithms. The integration of digital tools enhances preservation but also challenges authenticity and cultural context inherent in oral narratives.
Advantages and Limitations of Each System
Oral tradition preserves cultural heritage through storytelling, enabling memory-based transmission that fosters community engagement and adaptability but risks information loss and alteration over time. Digital logic offers precise, fast, and scalable data processing with high reliability and reproducibility, yet it depends on technological infrastructure and is vulnerable to cyber threats and hardware failures. Combining oral tradition with digital technology can enhance knowledge preservation and accessibility while navigating the limitations of both systems.
Future Trends: Bridging Oral and Digital Worlds
Future trends in bridging oral tradition and digital logic emphasize the integration of voice recognition and natural language processing technologies to preserve cultural narratives while enhancing accessibility. Innovations in AI-driven storytelling platforms and augmented reality experiences enable interactive engagement with oral histories, fostering deeper cultural understanding across generations. This convergence promotes the coexistence of ancient oral practices and cutting-edge digital frameworks, ensuring heritage preservation within the evolving digital landscape.
Oral Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com