Identity shapes how individuals perceive themselves and are recognized by others, encompassing aspects like personal traits, beliefs, and cultural background. Understanding the complexities of identity helps you navigate social interactions and fosters a deeper connection to your sense of self. Explore the full article to uncover the layers of identity and their impact on your life.
Table of Comparison
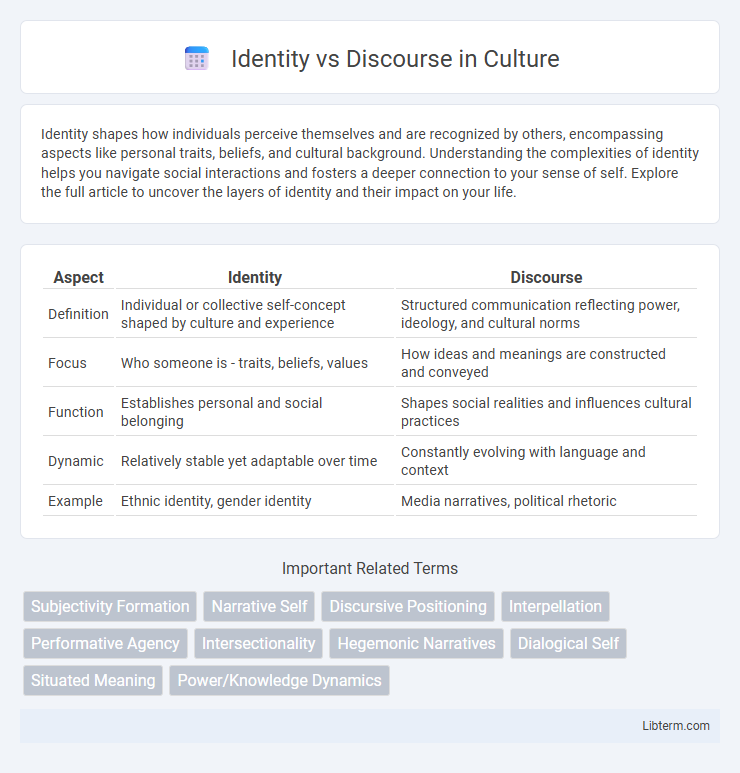
| Aspect | Identity | Discourse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or collective self-concept shaped by culture and experience | Structured communication reflecting power, ideology, and cultural norms |
| Focus | Who someone is - traits, beliefs, values | How ideas and meanings are constructed and conveyed |
| Function | Establishes personal and social belonging | Shapes social realities and influences cultural practices |
| Dynamic | Relatively stable yet adaptable over time | Constantly evolving with language and context |
| Example | Ethnic identity, gender identity | Media narratives, political rhetoric |
Understanding Identity: Core Concepts
Identity encompasses an individual's sense of self shaped by personal experiences, social roles, and cultural contexts. Core concepts include self-concept, which reflects how one perceives oneself, and social identity, defined by group memberships such as ethnicity, nationality, or profession. Understanding identity requires examining both stable traits and fluid aspects influenced by discourse and interpersonal interactions.
Defining Discourse: Language, Power, and Practice
Discourse encompasses structured language use that shapes social realities and power relations within cultural and institutional contexts. It functions as a set of practices that legitimize certain identities while marginalizing others through dominant narratives and linguistic frameworks. Analyzing discourse reveals how language operates as a tool for constructing knowledge, reinforcing authority, and influencing societal behavior.
The Intersection of Identity and Discourse
The intersection of identity and discourse reveals how language both shapes and reflects individual and group identities within social contexts. Discourse practices construct identities by enabling individuals to express, negotiate, and transform their social roles and cultural affiliations through communicative acts. Understanding this dynamic interplay is essential for analyzing power relations, social positioning, and the continuous reconfiguration of selfhood in diverse communities.
Historical Perspectives on Identity and Discourse
Historical perspectives on identity and discourse reveal the evolving interplay between personal and collective self-understandings shaped by language, culture, and power structures. Scholars trace identity formation through discourse analysis, emphasizing how narratives, myths, and social practices historically construct and negotiate group affiliations and individual subjectivities. The examination of historical texts and communication practices highlights shifts in identity markers influenced by colonialism, nationalism, and social movements, demonstrating discourse's role in both reinforcing and challenging dominant identities.
Social Construction of Identity Through Discourse
Identity is dynamically shaped through discourse, where social interactions and language practices contribute to constructing and negotiating individual and group identities. Discursive frameworks provide categories and narratives that individuals use to position themselves and others within social contexts, reflecting power relations and cultural norms. This process highlights identity as fluid and contingent, continuously formed through communicative acts and social meaning-making.
Power Dynamics: Who Shapes Identity in Discourse?
Power dynamics significantly influence who shapes identity within discourse, as dominant groups often control the narratives and define social norms. Institutions such as media, education, and government play critical roles in reinforcing these identities by privileging certain voices while marginalizing others. Understanding these mechanisms reveals how identity is not fixed but continuously negotiated through unequal power relations embedded in discourse.
Digital Spaces: Identity Performance Online
Digital spaces amplify identity performance through curated profiles and interactive content, allowing users to selectively present facets of themselves. Online platforms enable identity exploration and experimentation, often blurring lines between authentic self and performed personas. Algorithmic targeting and social feedback shape digital identity construction, influencing how individuals negotiate self-presentation in virtual environments.
Discourse and Identity in Multicultural Contexts
Discourse shapes identity by constructing social realities through language, particularly in multicultural contexts where diverse narratives intersect and influence individual and group self-perceptions. Identity in multicultural settings is fluid, negotiated through continuous interactions that reflect power dynamics, cultural norms, and social practices embedded in discourse. Understanding the interplay of discourse and identity highlights how individuals navigate belonging and difference within complex cultural landscapes.
Challenges and Controversies: Identity Politics and Discourse
Identity politics challenges discourse by emphasizing group-based experiences and marginalized voices, often leading to polarized debates about representation and inclusion. Critics argue that this focus can fragment public dialogue, prioritizing identity over shared values and hindering consensus-building. The controversy intensifies around how identity-driven discourse shapes social policies and impacts free speech in diverse societies.
Towards Inclusive Discourse: Rethinking Identity for the Future
Inclusive discourse requires rethinking identity beyond fixed categories to embrace fluidity and intersectionality, promoting diverse voices and experiences. Emphasizing narrative plurality and cultural hybridity enables more equitable communication practices that challenge exclusion and bias. Future frameworks must integrate dynamic identity constructs to foster understanding and collaborative dialogue in increasingly globalized societies.
Identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com