Laws are essential for maintaining order and protecting individual rights within society, providing a structured framework that guides behavior and resolves conflicts. Understanding the various types of laws, including criminal, civil, and regulatory, can help you navigate legal complexities more effectively. Explore the following article to gain deeper insights into how laws impact your everyday life and legal obligations.
Table of Comparison
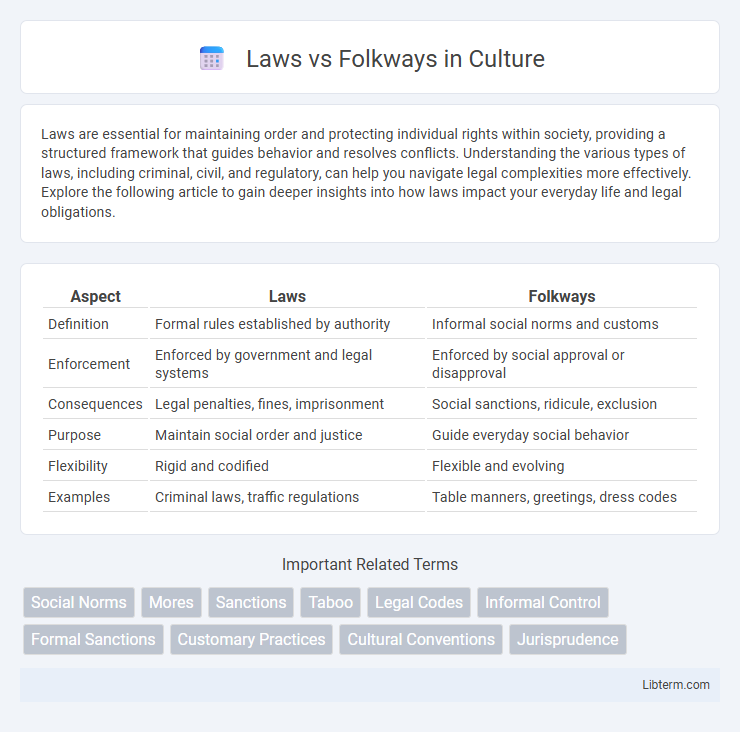
| Aspect | Laws | Folkways |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal rules established by authority | Informal social norms and customs |
| Enforcement | Enforced by government and legal systems | Enforced by social approval or disapproval |
| Consequences | Legal penalties, fines, imprisonment | Social sanctions, ridicule, exclusion |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and justice | Guide everyday social behavior |
| Flexibility | Rigid and codified | Flexible and evolving |
| Examples | Criminal laws, traffic regulations | Table manners, greetings, dress codes |
Understanding the Concept of Laws
Laws are formal, codified rules established by governments to regulate behavior and maintain social order, backed by official sanctions and enforcement mechanisms. Unlike folkways, which are informal norms guiding everyday conduct without legal consequence, laws provide clear, authoritative guidelines that individuals and institutions must follow. Understanding laws involves recognizing their role in defining rights, responsibilities, and penalties within a structured legal framework.
Defining Folkways in Society
Folkways are informal social norms that govern everyday behavior within a society, reflecting cultural habits and traditions rather than legal requirements. These unwritten rules guide routine interactions, such as dress codes, greetings, and dining etiquette, helping maintain social order through collective expectations. Unlike laws, folkways do not carry official sanctions but influence social approval and acceptance within communities.
Key Differences Between Laws and Folkways
Laws are formal rules enacted by governmental authorities that carry legal penalties when violated, designed to maintain social order and justice. Folkways are informal social norms based on cultural customs and everyday behaviors, lacking formal enforcement but influencing social acceptance and etiquette. While laws require official sanctions, folkways rely on social approval and informal consequences to regulate behavior within a community.
Origins and Development of Laws
Laws originate from formalized rules established by governing authorities to regulate behavior and maintain social order, evolving through codification and legal institutions. Folkways, by contrast, arise organically from cultural customs and social practices that guide everyday conduct without formal enforcement mechanisms. Over time, some folkways may influence or transform into laws as societies seek to formalize widely accepted norms for greater consistency and authority.
How Folkways Shape Social Behavior
Folkways, as informal norms, guide everyday social interactions by establishing expectations for behavior that maintain social order without legal enforcement. They influence routines such as greetings, dress codes, and table manners, reinforcing community values and promoting cultural cohesion. Through socialization, adherence to folkways fosters predictability, helping individuals navigate social environments smoothly.
The Role of Authority in Enforcing Laws
Laws are formal rules established and enforced by governmental authorities to maintain social order, whereas folkways are informal norms upheld by social expectations and traditions. The role of authority in enforcing laws involves agencies like the police, judiciary, and regulatory bodies that ensure compliance through penalties and sanctions. Unlike folkways, which rely on social pressure, laws depend on institutional power for their legitimacy and effectiveness.
Social Sanctions and Folkway Violations
Social sanctions for law violations are formal and enforced by official institutions, such as fines, imprisonment, or legal penalties, ensuring societal order through codified rules. Folkway violations incur informal social sanctions like disapproval, ridicule, or ostracism, relying on community norms to guide everyday behavior without legal consequences. The distinction between laws and folkways highlights the varying degrees of social control based on the severity and codification of norms.
Impact of Laws on Social Order
Laws establish formal rules and regulations that govern behavior, ensuring consistent enforcement of social norms and promoting public safety. They create clear consequences for violations, which deters deviant actions and reduces social disorder. By institutionalizing norms, laws reinforce social cohesion and stability more effectively than informal folkways.
Cultural Significance of Folkways
Folkways hold significant cultural value as informal norms that guide everyday social behavior, reflecting the shared values and traditions within a community. Unlike laws, which are formally codified and enforced by institutions, folkways influence social cohesion by promoting conformity and mutual understanding through habitual practices. Their cultural significance lies in preserving social order and identity without the need for legal intervention.
Interrelationship Between Laws and Folkways
Laws and folkways are deeply interconnected as folkways often serve as the cultural foundation from which formal laws evolve, reflecting society's moral standards and everyday behaviors. While laws codify and enforce rules with legal consequences, folkways guide informal social conduct and reinforce community norms without formal sanctions. The interplay between laws and folkways ensures social order by aligning legal statutes with prevailing cultural practices and collective values.
Laws Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com