Tradition shapes cultural identity and preserves valuable customs passed down through generations, influencing social behaviors and community values. It provides a sense of belonging and continuity, connecting individuals with their heritage and history. Explore this article to understand how tradition impacts your life and the world around you.
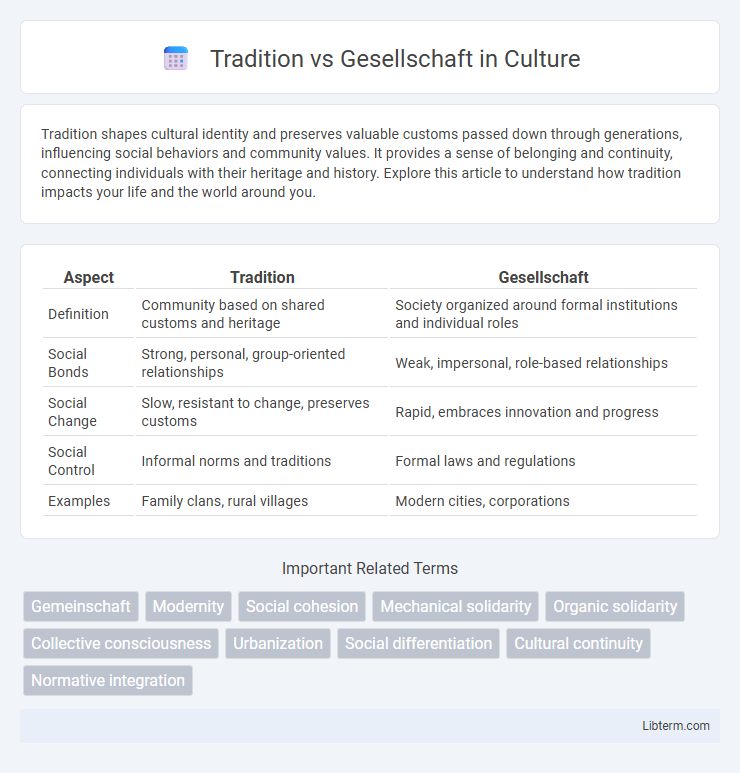
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tradition | Gesellschaft |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Community based on shared customs and heritage | Society organized around formal institutions and individual roles |
| Social Bonds | Strong, personal, group-oriented relationships | Weak, impersonal, role-based relationships |
| Social Change | Slow, resistant to change, preserves customs | Rapid, embraces innovation and progress |
| Social Control | Informal norms and traditions | Formal laws and regulations |
| Examples | Family clans, rural villages | Modern cities, corporations |
Defining Tradition and Gesellschaft
Tradition refers to long-established customs, beliefs, and practices passed down through generations that shape social behavior and cultural identity within close-knit communities. Gesellschaft describes large-scale, impersonal social structures characterized by formal institutions, contractual relationships, and individual self-interest predominant in modern societies. These concepts illustrate contrasting modes of social organization: Tradition emphasizes continuity and collective norms, while Gesellschaft highlights change and rational cooperation.
Historical Origins of Tradition
Tradition originates from long-established customs and collective social practices that developed in pre-industrial, agrarian societies, emphasizing continuity and communal bonds. These historical roots contrast with Gesellschaft, which emerged alongside industrialization and urbanization, highlighting impersonal, contractual relationships within complex, modern societies. Understanding Tradition's historical origins reveals its foundation in stable, close-knit communities governed by shared values and inherited norms.
The Emergence of Gesellschaft in Modern Society
Gesellschaft emerges in modern society as a form of social organization characterized by impersonal, formal, and contractual relationships, contrasting sharply with the intimate, community-based bonds of Tradition (Gemeinschaft). This shift is driven by industrialization, urbanization, and the rise of bureaucratic institutions, which prioritize individualism, rationality, and economic exchange over kinship and communal values. Sociologist Ferdinand Tonnies highlights how Gesellschaft reflects the complex social structures necessary for modern capitalist economies and mass societies.
Key Differences Between Tradition and Gesellschaft
Tradition is characterized by long-established customs, social roles, and cultural continuity, emphasizing community bonds and collective identity. Gesellschaft, in contrast, involves formal, impersonal relationships based on individual goals and contractual agreements typical of modern urban societies. The key differences lie in social cohesion: Tradition relies on shared values and emotional ties, while Gesellschaft depends on rationality, legal systems, and self-interest.
Social Bonds: Community vs. Society
Traditional societies emphasize strong social bonds rooted in kinship, shared values, and collective identity, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support within tight-knit communities. Gesellschaft, or modern societies, rely on impersonal, contract-based relationships where social ties are more fragmented and driven by individual goals and economic transactions. The shift from community-centered bonds to society-oriented networks reflects changes in social cohesion, trust, and the nature of interpersonal connections in contemporary life.
The Role of Traditions in Shaping Identity
Traditions play a crucial role in shaping identity by providing individuals and communities with a sense of continuity and belonging rooted in shared cultural practices and values. They reinforce social cohesion within Gemeinschaft societies, where relationships are based on close, personal connections and long-standing customs. In contrast, Gesellschaft societies emphasize formal associations and individual goals, leading to a more fluid identity influenced by social contracts rather than inherited traditions.
Gesellschaft and the Rise of Individualism
Gesellschaft, a concept introduced by sociologist Ferdinand Tonnies, characterizes modern societies where relationships are impersonal and goal-oriented, contrasting sharply with traditional Gemeinschaft communities based on close personal ties. The rise of individualism within Gesellschaft reflects a shift towards autonomy, contractual associations, and rational self-interest, fostering social structures driven by legal systems and economic transactions. This transformation emphasizes efficiency and formal organizations, promoting individual rights and freedoms over collective customs and obligations.
Impacts on Social Cohesion and Stability
Traditional societies prioritize long-standing customs and collective values, fostering strong social cohesion through shared norms and reciprocal relationships. Gesellschaft societies emphasize individual goals and formal institutions, which can lead to weaker social ties but greater adaptability and economic development. The shift from Tradition to Gesellschaft often challenges social stability by altering trust patterns and community integration, impacting collective identity and cooperation.
Challenges of Transitioning from Tradition to Gesellschaft
Transitioning from Tradition to Gesellschaft presents significant challenges including the erosion of close-knit community bonds, increased social fragmentation, and the rise of impersonal relations characterized by contractual obligations rather than emotional ties. Individuals often struggle with identity shifts as traditional values give way to rational, individualistic norms, leading to social alienation and weakened collective responsibility. Economic modernization and urbanization further exacerbate disparities, complicating governance and social cohesion in Gesellschaft societies.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Tradition and Gesellschaft
Balancing Tradition and Gesellschaft requires integrating long-standing cultural values with modern societal dynamics to foster sustainable development and social cohesion. Future perspectives emphasize adaptive frameworks that respect heritage while embracing innovation, ensuring communities retain identity amid rapid globalization and technological advancement. Strategic policies and inclusive governance models can support this equilibrium, promoting resilience and progressive transformation.
Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com