Globalization drives unprecedented connectivity and economic integration, reshaping markets and cultures worldwide. It influences everything from trade and technology to social norms, creating both opportunities and challenges for businesses and individuals. Explore the rest of the article to understand how globalization impacts your daily life and future prospects.
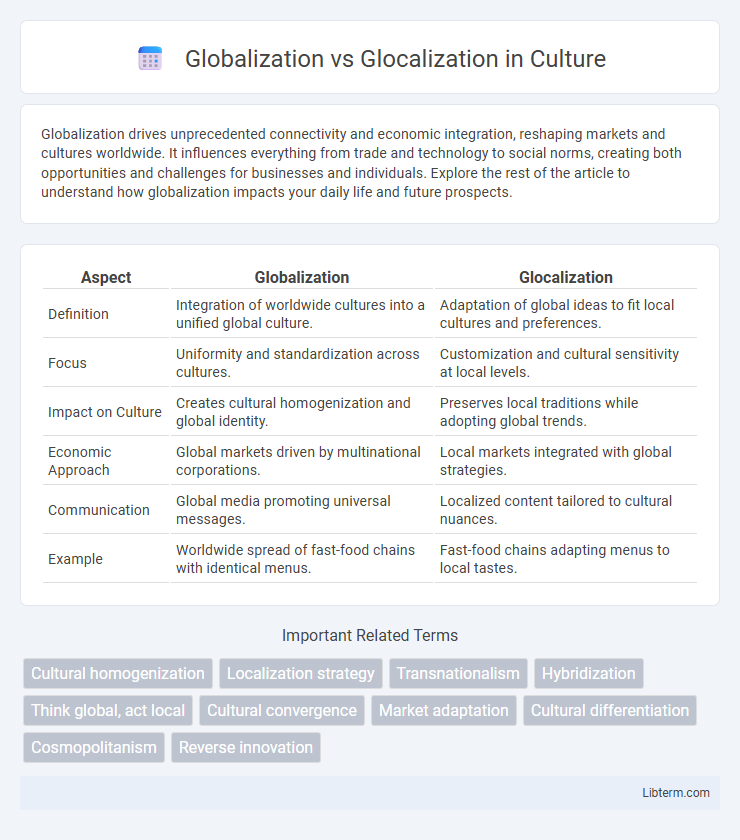
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Globalization | Glocalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of worldwide cultures into a unified global culture. | Adaptation of global ideas to fit local cultures and preferences. |
| Focus | Uniformity and standardization across cultures. | Customization and cultural sensitivity at local levels. |
| Impact on Culture | Creates cultural homogenization and global identity. | Preserves local traditions while adopting global trends. |
| Economic Approach | Global markets driven by multinational corporations. | Local markets integrated with global strategies. |
| Communication | Global media promoting universal messages. | Localized content tailored to cultural nuances. |
| Example | Worldwide spread of fast-food chains with identical menus. | Fast-food chains adapting menus to local tastes. |
Understanding Globalization: A Macro Perspective
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of countries through trade, communication, and cultural exchange, driving economic growth and innovation on a macro scale. It involves the expansion of multinational corporations, global supply chains, and international institutions shaping policies and market dynamics worldwide. Understanding globalization from a macro perspective highlights its role in integrating markets, harmonizing regulations, and influencing socio-economic structures across nations.
Defining Glocalization: Bridging Global and Local
Glocalization integrates global business strategies with local cultural, economic, and social nuances to create tailored products and services that resonate with specific markets. This approach enhances competitive advantage by blending worldwide reach with community relevance, ensuring adaptability in diverse environments. Emphasizing local consumer behavior and preferences within a global framework maximizes engagement and market success.
Key Differences Between Globalization and Glocalization
Globalization emphasizes the worldwide integration of economies, cultures, and technologies, promoting uniformity and standardized products across global markets. Glocalization adapts global products or services to fit local cultures, preferences, and regulations, ensuring relevance and acceptance within specific regions. The key difference lies in globalization's pursuit of global homogeneity versus glocalization's strategy of local customization within a global framework.
Economic Impacts: Global Reach vs Local Adaptation
Globalization drives economic growth by enabling companies to access international markets, facilitating economies of scale and cross-border investments that boost productivity and innovation. Glocalization emphasizes local adaptation, allowing businesses to tailor products and marketing strategies to specific cultural preferences and regulatory environments, enhancing consumer satisfaction and competitive advantage. Combining global reach with local responsiveness optimizes supply chains and maximizes market penetration, fostering sustainable economic development in diverse regions.
Cultural Integration or Preservation?
Globalization promotes cultural integration by encouraging the exchange of ideas, values, and customs across borders, leading to a more interconnected world culture. Glocalization, however, emphasizes cultural preservation by adapting global products or ideas to fit local traditions and identities, maintaining unique cultural expressions. Balancing these approaches helps societies benefit from global influences while protecting and celebrating their distinct cultural heritage.
Case Studies: Global Brands Embracing Glocalization
Global brands like McDonald's and Starbucks illustrate glocalization by adapting menus and marketing strategies to reflect local tastes and cultural preferences, enhancing customer connection and market acceptance. McDonald's offers region-specific items such as the McSpicy Paneer in India and Teriyaki Burgers in Japan, aligning global brand identity with local flavors. Starbucks customizes store designs and product offerings globally, integrating local culture to create a unique customer experience while maintaining its core brand values.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Global and Local Strategies
Technology serves as a critical driver in balancing globalization and glocalization by enabling seamless communication, data analytics, and supply chain management across borders while allowing for local adaptation. Digital platforms, AI, and IoT facilitate global reach and scale yet provide customizable solutions to meet regional consumer preferences and regulatory requirements. Companies leverage technological tools to integrate global efficiencies with local responsiveness, optimizing market penetration and innovation strategies in diverse environments.
Consumer Behavior: Global Trends vs Local Preferences
Consumer behavior reflects a dynamic interplay between global trends and local preferences, where globalization promotes widespread adoption of international brands and standardized products. Glocalization tailors these offerings by integrating cultural nuances, adapting marketing strategies, and customizing products to fit regional tastes and values. This balance ensures that while consumers benefit from global innovations, their local identities and preferences remain influential in purchasing decisions.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Globalization faces criticism for homogenizing cultures, widening economic disparities, and undermining local identities, leading to resistance from communities seeking to preserve their unique traditions. Glocalization challenges include the complexity of balancing global integration with local adaptation, which can result in inconsistent brand messaging and operational inefficiencies. Both approaches struggle with managing cultural sensitivity, regulatory compliance, and the dynamic expectations of diverse consumer bases in an interconnected world.
Future Outlook: Balancing Globalization and Glocalization
The future outlook for balancing globalization and glocalization emphasizes adaptive strategies that integrate global market trends with local cultural nuances to optimize business growth and consumer engagement. Advances in technology, such as AI and big data analytics, enable companies to tailor products and services dynamically for diverse regional markets while maintaining scalable global operations. Sustainable development goals and increasing demand for local authenticity will drive businesses to foster coexistence between global efficiency and localized customization, ensuring resilience in evolving economic landscapes.
Globalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com