Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that have similar or identical meanings, enhancing clarity and variety in communication. Understanding how to use synonyms effectively can improve your writing by avoiding repetition and enriching expression. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips and examples for mastering synonymy.
Table of Comparison
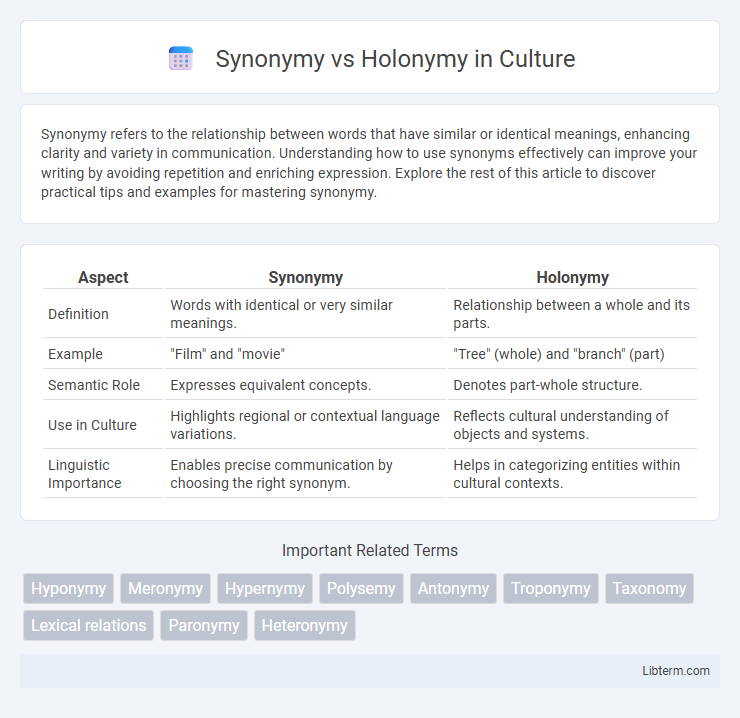
| Aspect | Synonymy | Holonymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words with identical or very similar meanings. | Relationship between a whole and its parts. |
| Example | "Film" and "movie" | "Tree" (whole) and "branch" (part) |
| Semantic Role | Expresses equivalent concepts. | Denotes part-whole structure. |
| Use in Culture | Highlights regional or contextual language variations. | Reflects cultural understanding of objects and systems. |
| Linguistic Importance | Enables precise communication by choosing the right synonym. | Helps in categorizing entities within cultural contexts. |
Understanding Synonymy: Definition and Examples
Synonymy refers to the linguistic phenomenon where two or more words share the same or very similar meanings, such as "big" and "large." It plays a crucial role in language by allowing variation in expression without altering the intended message. Understanding synonymy aids in enhancing vocabulary, improving writing style, and facilitating accurate communication.
Exploring Holonymy: Meaning and Illustrations
Holonymy refers to the semantic relationship where a term denotes a whole whose parts are represented by other related terms, such as "tree" being a holonym of "branch" and "leaf." This concept contrasts with synonymy, which involves different words with almost identical meanings, like "big" and "large." Understanding holonymy helps in fields like linguistics and natural language processing by clarifying hierarchical structures within language and improving semantic analysis.
Key Differences Between Synonymy and Holonymy
Synonymy involves words that have identical or very similar meanings, such as "big" and "large," whereas holonymy denotes a whole-part relationship, like "tree" being a holonym of "branch." Synonyms are interchangeable in many contexts without changing the meaning, but holonyms and their parts are related by inclusion rather than equivalence. This fundamental difference in semantic relation distinguishes synonymy as similarity-based and holonymy as part-whole based.
Linguistic Roles of Synonymy in Language
Synonymy plays a crucial linguistic role by providing lexical variety and enabling nuanced expression without altering meaning, enhancing communication efficiency and stylistic richness. It allows speakers and writers to choose words that best fit context, tone, or register, thereby supporting semantic precision and language creativity. Unlike holonymy, which relates to part-whole relationships in lexical semantics, synonymy centers on equivalency in meaning across different lexical items.
The Function of Holonymy in Semantic Networks
Holonymy plays a crucial role in semantic networks by representing part-whole relationships, where a holonym denotes the whole entity encompassing its parts, called meronyms. This relationship enhances semantic understanding by linking concepts hierarchically, aiding in knowledge organization and natural language processing tasks such as word sense disambiguation and ontology construction. Unlike synonymy, which connects words with similar meanings, holonymy structures information based on inclusion, supporting more complex reasoning about entities and their components.
Synonymy vs Holonymy: Contextual Usage
Synonymy and holonymy differ fundamentally in their semantic relationships; synonymy involves words with similar meanings used interchangeably in specific contexts, while holonymy relates to a whole-part relationship where one term denotes the whole entity, and the other refers to its part. Contextual usage determines the choice between synonyms to convey precise meaning, whereas holonyms require understanding the connection between the whole and its constituents, impacting comprehension in discourse. Effective communication relies on recognizing these distinctions to enhance clarity and semantic accuracy in language processing and lexical semantics.
Importance of Synonymy and Holonymy in Lexicography
Synonymy enhances lexicography by providing multiple lexical options with similar meanings, enriching language comprehension and aiding precise word choice. Holonymy organizes vocabulary through part-whole relationships, enabling comprehensive thematic grouping and a better semantic network within dictionaries. Together, synonymy and holonymy improve lexical databases, supporting more effective language learning, natural language processing, and semantic analysis.
Cognitive Processing of Synonymy and Holonymy
Cognitive processing of synonymy involves recognizing different words that share the same or very similar meanings, facilitating efficient vocabulary retrieval and semantic understanding in language comprehension. Holonymy processing requires identifying part-whole relationships between concepts, such as understanding that "wheel" is part of a "car," which aids in organizing and categorizing knowledge hierarchically. These distinct semantic relationships engage different neural mechanisms and cognitive strategies, reflecting how the brain integrates lexical synonyms versus conceptual wholes during language processing.
Common Misconceptions About Synonymy and Holonymy
Synonymy is often confused with holonymy, but they represent distinct semantic relationships: synonymy refers to words with similar meanings, while holonymy denotes a whole-to-part relationship. A common misconception is that synonyms are interchangeable in all contexts, ignoring nuances of connotation and usage that affect meaning. Holonymy is sometimes incorrectly assumed to be synonymous with synonymy, yet it specifically involves a broader term encompassing its parts, such as "tree" being the holonym of "branch.
Practical Applications in Natural Language Processing
Synonymy enhances Natural Language Processing (NLP) by improving search engines and keyword matching through recognizing different words that convey the same meaning, thereby increasing accuracy in information retrieval. Holonymy plays a crucial role in text summarization and ontology building by identifying part-whole relationships, which helps systems understand contextual hierarchies and semantic structures. Leveraging synonymy and holonymy together enables NLP models to perform more precise entity recognition and semantic analysis, supporting advanced applications like question answering and machine translation.
Synonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com