Reality shapes your perceptions and influences every decision you make, rooted in the tangible and intangible elements around you. Understanding the layers of reality can enhance your awareness and improve how you interact with the world. Explore the rest of this article to uncover deeper insights into the nature of reality and its impact on your life.
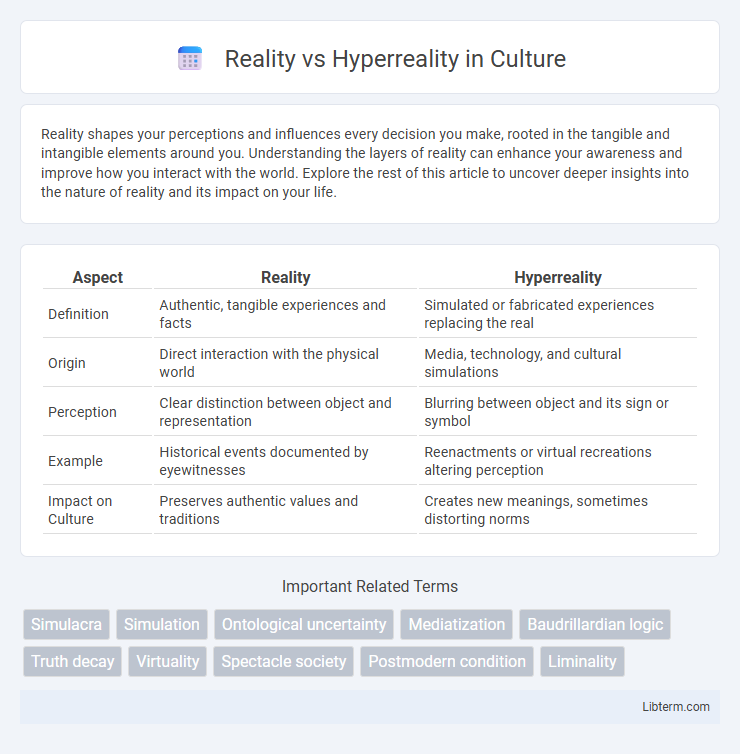
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reality | Hyperreality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authentic, tangible experiences and facts | Simulated or fabricated experiences replacing the real |
| Origin | Direct interaction with the physical world | Media, technology, and cultural simulations |
| Perception | Clear distinction between object and representation | Blurring between object and its sign or symbol |
| Example | Historical events documented by eyewitnesses | Reenactments or virtual recreations altering perception |
| Impact on Culture | Preserves authentic values and traditions | Creates new meanings, sometimes distorting norms |
Understanding Reality: The Foundation of Human Perception
Understanding reality forms the foundation of human perception by grounding experiences in objective facts and sensory input. Reality consists of tangible, observable phenomena that shape cognitive frameworks and influence decision-making. Distinguishing between reality and hyperreality involves recognizing the authentic context versus simulated or constructed representations that can distort perception.
Defining Hyperreality: Beyond the Real
Hyperreality is a concept in postmodern philosophy where the distinction between reality and simulation blurs, creating a condition in which representations or models of reality become more real than reality itself. This phenomenon, extensively analyzed by theorists like Jean Baudrillard, challenges traditional perceptions by presenting simulations as a new form of reality that shapes human experience and social interactions. The hyperreal transcends objective truth, constructing a fabricated world where signs and symbols replace authentic experiences, ultimately redefining cultural and existential understanding.
Historical Context: From Baudrillard to the Digital Age
Jean Baudrillard's concept of hyperreality emerged in the late 20th century as a critique of media-saturated societies where simulations replace or distort reality. The transition from traditional media to digital platforms intensified hyperreal experiences by blending virtual environments with everyday life, blurring the distinction between the real and the fabricated. This historical progression highlights how technological advancements have transformed social perceptions, creating a world dominated by constructed images and signs rather than direct reality.
The Role of Media in Shaping Hyperreality
Media plays a crucial role in constructing hyperreality by blending real and simulated experiences, creating a mediated environment where representations often replace or distort actual reality. Through constant framing, editing, and sensationalism, media outlets generate perceptions that prioritize spectacle and entertainment over factual accuracy, influencing public consciousness and social behavior. This manufactured reality blurs the line between truth and fiction, making hyperreality a dominant lens through which individuals interpret everyday life.
Everyday Examples: Hyperreality in Modern Life
Hyperreality in modern life manifests through social media platforms where curated images and filtered experiences often replace authentic interactions, creating simulated realities more influential than actual events. Advertising blurs the line between product and lifestyle, crafting idealized versions of consumption that shape consumer desires beyond tangible benefits. Virtual reality gaming immerses users in expertly designed digital environments, making the simulated experiences feel more vivid and compelling than real-life activities.
Simulation and Simulacra: Blurring the Boundaries
Simulation and simulacra challenge traditional notions of reality by creating representations that no longer correspond to any original, leading to a hyperreal experience where distinctions between the real and the fabricated dissolve. This blurring of boundaries results in environments dominated by signs and images that replace and shape perception, making the simulation appear more authentic than reality itself. Consequently, hyperreality transforms social and cultural experiences, complicating the ability to discern genuine existence from constructed illusions.
Psychological Effects of Living in Hyperreality
Living in hyperreality blurs the distinction between reality and simulation, leading to altered perceptions of self and environment. This psychological state often results in increased anxiety, identity confusion, and a detachment from authentic experiences. Studies show that prolonged exposure to hyperreal environments, such as social media and virtual realities, can diminish emotional resilience and impair critical thinking.
Hyperreality and Social Media Influences
Hyperreality in social media blurs the boundaries between authentic experiences and digitally constructed identities, where curated content often replaces genuine interactions. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok amplify idealized lifestyles through filters, influencers, and algorithm-driven feeds, creating a simulated reality that users consume as truth. This phenomenon shifts social perception, fostering desires based on fabricated norms rather than authentic reality, impacting self-esteem and social behavior.
Consequences: Truth, Authenticity, and Identity
The collapse of reality into hyperreality blurs the boundaries between what is genuine and simulated, eroding the foundation of truth by replacing authentic experiences with manufactured representations. This shift challenges individual and collective identity, as people increasingly base their sense of self on fabricated images and narratives rather than factual existence. The consequence is a society where authenticity becomes elusive, posing profound implications for cultural integrity and personal meaning.
Navigating the Divide: Strategies for Distinguishing Reality from Hyperreality
Navigating the divide between reality and hyperreality requires critical media literacy to discern authentic experiences from simulated ones crafted by digital technologies. Employing strategies such as cross-referencing multiple information sources, engaging in reflective self-awareness, and prioritizing direct sensory experiences enhances the ability to identify distortions propagated through social media, virtual reality, and augmented reality platforms. Adopting these methods reduces susceptibility to manipulated perceptions, fostering a grounded understanding of the real world amidst increasingly sophisticated hyperreal environments.
Reality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com