Living tradition embodies cultural practices that evolve while preserving their core values across generations, forming a dynamic link between past and present. These traditions influence your identity and community cohesion by adapting to contemporary contexts without losing their essence. Explore the article to discover how living traditions continue to shape societies worldwide.
Table of Comparison
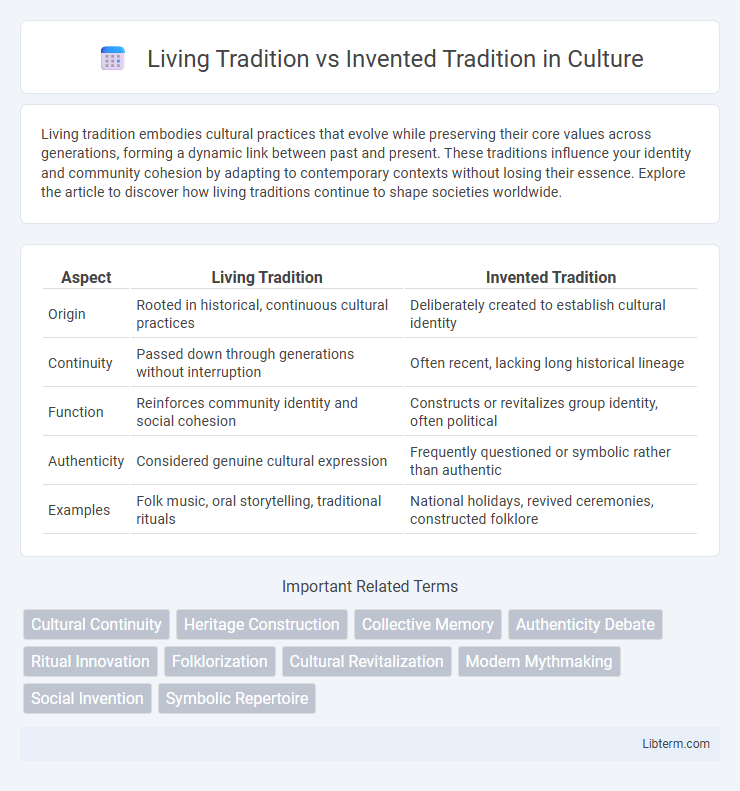
| Aspect | Living Tradition | Invented Tradition |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Rooted in historical, continuous cultural practices | Deliberately created to establish cultural identity |
| Continuity | Passed down through generations without interruption | Often recent, lacking long historical lineage |
| Function | Reinforces community identity and social cohesion | Constructs or revitalizes group identity, often political |
| Authenticity | Considered genuine cultural expression | Frequently questioned or symbolic rather than authentic |
| Examples | Folk music, oral storytelling, traditional rituals | National holidays, revived ceremonies, constructed folklore |
Understanding Living Tradition and Invented Tradition
Living tradition refers to cultural practices and customs continuously passed down through generations, evolving organically within communities and reflecting their collective identity. Invented tradition involves deliberately created rituals or symbols designed to establish social cohesion or legitimize institutions, often constructed in recent history to appear as longstanding practices. Understanding the distinction helps analyze how societies maintain continuity or shape collective memory through either genuine historical transmission or purposeful invention.
Defining Characteristics of Living Traditions
Living traditions are characterized by continuous practice and adaptation, deeply rooted in the community's evolving cultural context, ensuring relevance across generations. They exhibit dynamic transmission through active participation and oral or performative forms, allowing organic growth and transformation. Their authenticity is derived from lived experience and communal validation rather than static, prescribed rules or recent invention.
Traits and Origins of Invented Traditions
Invented traditions often feature traits such as formalization, ritualization, and symbolic gestures designed to establish continuity with a suitable historic past, despite their recent origins. These traditions typically emerge in response to social or political needs, serving to legitimize institutions or foster group identity by creating a constructed sense of historical continuity. Unlike living traditions, invented traditions are deliberately fabricated, relying on selective representations of history rather than genuine unbroken practices.
Historical Contexts of Tradition Formation
Living traditions evolve organically over centuries within specific cultural and historical contexts, maintaining continuous practices that reflect the community's identity and values. Invented traditions emerge more recently, often created intentionally to establish social cohesion or legitimize institutions by mimicking older practices, sometimes lacking deep historical roots. Understanding the historical contexts of tradition formation reveals how power dynamics, societal changes, and cultural needs influence whether traditions are preserved or constructed.
Role of Community in Sustaining Traditions
The role of community in sustaining traditions is crucial, as living traditions thrive through continuous practice and adaptation by generations within a social group. Invented traditions often rely on deliberate creation or revival by authority figures but require community acceptance and participation to achieve legitimacy. Collective memory, shared rituals, and social cohesion enable communities to maintain and evolve living traditions more organically than the constructed narratives of invented ones.
Examples of Living vs Invented Traditions
Living traditions such as the Japanese tea ceremony and Native American powwows embody practices continuously passed down through generations, reflecting authentic historical and cultural continuity. Invented traditions like the Scottish Highland games and the modern Olympic ceremonies were consciously created or revived in recent centuries to promote social cohesion or national identity, often lacking direct historical precedent. These distinctions highlight how living traditions evolve organically, whereas invented traditions serve constructed purposes with symbolic meanings.
The Impact of Modernization on Tradition
Modernization often redefines living traditions by introducing new technologies and social structures that alter practices without erasing their core meanings. Invented traditions emerge as deliberate creations to forge identity or social cohesion, often reflecting contemporary values rather than historical continuity. The impact of modernization thus blurs the line between authentic heritage and constructed rituals, reshaping cultural expression in dynamic and complex ways.
Authenticity and Legitimacy in Traditions
Authenticity in living traditions stems from continuous practice and genuine cultural transmission across generations, ensuring their legitimacy through communal acceptance and historical continuity. Invented traditions, while often constructed to promote social cohesion or political legitimacy, may lack deep-rooted historical authenticity but gain legitimacy by embedding themselves into collective identity over time. The tension between authenticity and legitimacy highlights the dynamic nature of traditions, where perceived legitimacy can sometimes supersede historical origins in defining cultural significance.
How Traditions Shape Collective Identity
Traditions, whether living or invented, play a crucial role in shaping collective identity by reinforcing shared values, customs, and historical narratives within a community. Living traditions evolve naturally over time through continuous practice, reflecting authentic cultural experiences and fostering a sense of belonging. Invented traditions, often consciously created or revived, serve to legitimize social cohesion and collective memory by providing symbolic rituals that connect present generations to an idealized past.
The Future of Tradition in a Globalized World
Living traditions evolve organically within communities, adapting to contemporary contexts while preserving cultural identity, whereas invented traditions are consciously created to serve specific social or political purposes. In a globalized world, the future of tradition hinges on balancing authenticity with innovation, enabling cultural practices to remain relevant amid rapid technological and social changes. Digital platforms facilitate the dissemination and transformation of traditions, fostering intercultural dialogue and hybrid identities that redefine heritage in dynamic, inclusive ways.
Living Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com