Haptics technology enhances user experience by providing tactile feedback through vibrations, forces, or motions, making interactions more intuitive and immersive. It is widely used in smartphones, gaming controllers, and virtual reality systems to simulate real-world touch sensations. Explore the rest of this article to discover how haptics can transform Your digital interactions and everyday devices.
Table of Comparison
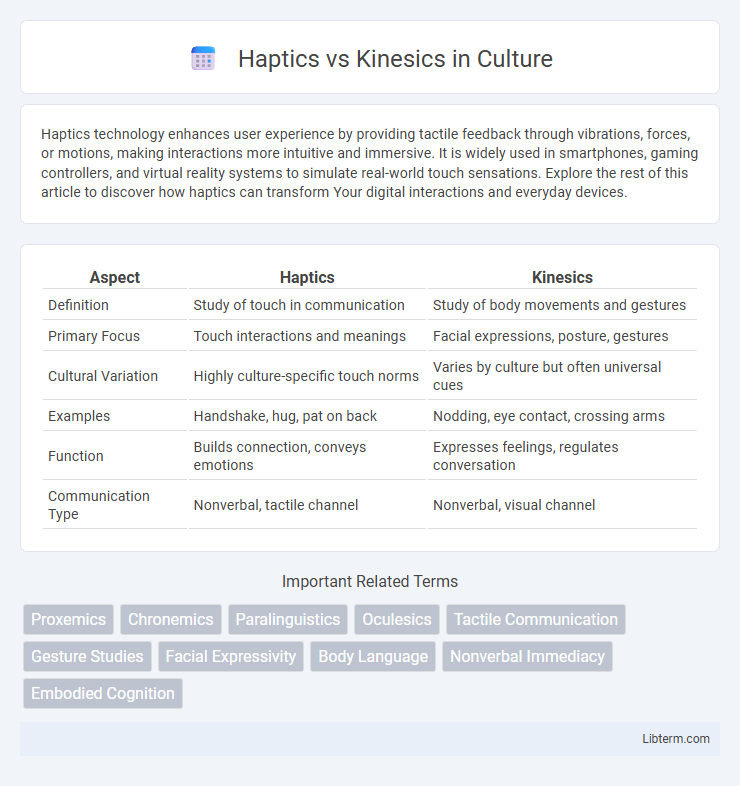
| Aspect | Haptics | Kinesics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of touch in communication | Study of body movements and gestures |
| Primary Focus | Touch interactions and meanings | Facial expressions, posture, gestures |
| Cultural Variation | Highly culture-specific touch norms | Varies by culture but often universal cues |
| Examples | Handshake, hug, pat on back | Nodding, eye contact, crossing arms |
| Function | Builds connection, conveys emotions | Expresses feelings, regulates conversation |
| Communication Type | Nonverbal, tactile channel | Nonverbal, visual channel |
Introduction to Haptics and Kinesics
Haptics explores the role of touch in communication, examining how physical contact conveys emotions and social cues in various contexts. Kinesics studies body movements such as gestures, facial expressions, and posture to interpret nonverbal messages in human interaction. Both haptics and kinesics are essential components of nonverbal communication, providing insight into underlying feelings and intentions beyond spoken language.
Defining Haptics: The Power of Touch
Haptics refers to the study and use of touch as a form of nonverbal communication, conveying emotions and intentions through physical contact. It plays a critical role in human interaction by establishing connection, comfort, and social bonding. The power of touch can influence perceptions, trust, and emotional responses more profoundly than verbal or visual cues.
Understanding Kinesics: Body Language Essentials
Kinesics, the study of body language, encompasses gestures, facial expressions, posture, and eye movements, revealing unspoken emotions and intentions. Understanding kinesics enhances communication by interpreting nonverbal cues that often convey more than verbal messages alone. Mastery of body language essentials improves interpersonal interactions, enabling clearer, more empathetic exchanges in personal and professional contexts.
Key Differences Between Haptics and Kinesics
Haptics refers to the study and use of touch as a form of nonverbal communication, involving physical contact like handshakes, hugs, or pats, while kinesics focuses on body movements, gestures, facial expressions, and posture to convey messages. Haptics primarily deals with tactile signals and their social, emotional, or cultural meanings, whereas kinesics interprets visual cues and body language that indicate feelings, intentions, or attitudes. The key difference lies in the sensory modality used--haptics relies on touch, while kinesics depends on motion and visual observation.
The Role of Culture in Haptics and Kinesics
Haptics and kinesics are deeply influenced by cultural norms that dictate acceptable touch and body language behaviors within different societies. In haptics, cultures vary in touch frequency and intensity, with some cultures valuing physical contact as a form of connection, while others prioritize personal space and minimal touch. Kinesics also reflects cultural differences in gestures, facial expressions, and posture, where specific movements may convey respect, aggression, or emotional states uniquely interpreted by cultural context.
Haptics in Communication: Examples and Impact
Haptics in communication refers to the use of touch to convey messages, such as a handshake signaling greeting, a pat on the back expressing encouragement, or a hug providing comfort. The impact of haptics is profound, as it can build trust, establish social bonds, and enhance emotional understanding between individuals. In contrast to kinesics, which involves body movements and gestures, haptics directly influences interpersonal connection through physical contact.
Kinesics in Communication: Gestures, Posture, and Facial Expressions
Kinesics in communication encompasses gestures, posture, and facial expressions, which serve as powerful nonverbal signals that convey emotions, intentions, and social cues. Gestures like hand movements and nodding complement verbal messages, enhancing clarity and engagement, while posture reflects confidence, openness, or defensiveness during interactions. Facial expressions, such as smiles, frowns, and eye contact, provide immediate emotional feedback and strengthen interpersonal connections, making kinesics a vital component of effective communication.
Haptics vs Kinesics in Professional Settings
Haptics in professional settings refers to the use of touch, such as handshakes or pats on the back, to establish rapport, demonstrate support, or convey confidence, while kinesics involves body language including gestures, posture, and facial expressions to communicate nonverbally. Effective use of haptics can build trust and reinforce messages in business interactions, whereas kinesics provides insight into true emotions and engagement levels during meetings or negotiations. Cultural norms significantly influence both haptics and kinesics, requiring professionals to adapt their nonverbal communication to maintain appropriateness and respect.
Challenges in Interpreting Haptics and Kinesics
Interpreting haptics, which involves communication through touch, poses challenges due to cultural differences and personal boundaries that affect the perception of touch behaviors. Kinesics, the study of body movements and gestures, is complicated by the variability in nonverbal cues across contexts and the ambiguity in assigning specific meanings to gestures. Both forms of nonverbal communication require careful contextual understanding to avoid misinterpretation in interpersonal interactions.
Future Trends in Nonverbal Communication
Haptics and kinesics are evolving rapidly in nonverbal communication with advancements in wearable technology and virtual reality. Future trends indicate increased integration of haptic feedback devices to simulate touch, enhancing remote interactions and emotional connectivity. Simultaneously, kinesics will benefit from AI-driven gesture recognition, enabling more precise interpretation of body language in digital environments.
Haptics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com