Explicit context refers to the clear and direct information presented within a text or communication, leaving little room for interpretation or ambiguity. Understanding explicit context helps you grasp the precise meaning intended by the author or speaker, enhancing comprehension and effective response. Explore the rest of the article to discover how recognizing explicit context can improve your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
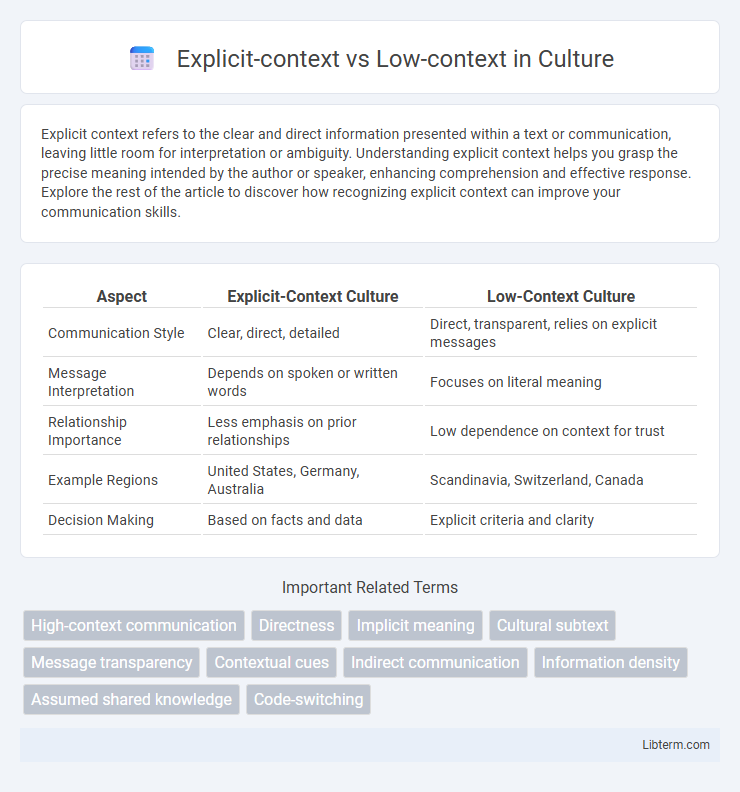
| Aspect | Explicit-Context Culture | Low-Context Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Clear, direct, detailed | Direct, transparent, relies on explicit messages |
| Message Interpretation | Depends on spoken or written words | Focuses on literal meaning |
| Relationship Importance | Less emphasis on prior relationships | Low dependence on context for trust |
| Example Regions | United States, Germany, Australia | Scandinavia, Switzerland, Canada |
| Decision Making | Based on facts and data | Explicit criteria and clarity |
Understanding Explicit-Context and Low-Context Communication
Explicit-context communication relies on clear, direct, and detailed messages where meaning is spelled out, minimizing ambiguity and ensuring that information is fully conveyed through words alone. Low-context communication emphasizes transparency and straightforwardness, typically found in cultures where individuals depend less on shared backgrounds and more on explicit verbal expression to understand intentions and facts. Mastering these communication styles enhances cross-cultural understanding by recognizing when clarity comes from explicit statements versus relying on implicit social cues.
Defining Explicit-Context Cultures
Explicit-context cultures rely on clear, direct communication where messages are spelled out and unambiguous, minimizing reliance on situational or nonverbal cues. These cultures prioritize detailed verbal expression and explicit instructions to convey meaning effectively, often found in Western societies such as the United States and Germany. Understanding explicit-context communication is essential for cross-cultural interactions to avoid misunderstandings and ensure clarity.
Key Features of Low-Context Communication
Low-context communication relies heavily on explicit verbal messages where information is clearly and directly conveyed through precise language. Key features include straightforward expression, detailed instructions, and minimal reliance on shared background or nonverbal cues, making messages clear even to those outside the immediate social context. This communication style is common in cultures prioritizing clarity, efficiency, and individualism, such as the United States and Germany.
Major Differences Between Explicit-Context and Low-Context
Explicit-context communication relies heavily on clear, precise, and detailed verbal messages to convey meaning, ensuring minimal reliance on shared background knowledge. Low-context communication, often found in cultures like the United States and Germany, emphasizes straightforward, direct exchanges where information is explicitly stated within the message itself. The major differences between explicit-context and low-context communication lie in the degree of message clarity, dependence on contextual cues, and the role of shared experience in understanding.
Advantages of Explicit-Context Approaches
Explicit-context approaches enhance communication clarity by providing detailed and unambiguous information, which reduces misunderstandings in global and multicultural interactions. These approaches support efficient knowledge transfer by clearly stating expectations, rules, and procedures, thereby improving collaboration in diverse teams. The explicit-context method also facilitates data documentation and learning processes by making critical information accessible and easily interpretable for all stakeholders.
Challenges in Low-Context Communication
Low-context communication relies heavily on explicit verbal expression, presenting challenges such as potential misunderstandings due to lack of shared background knowledge and cultural nuances. This communication style often demands clearer, more detailed explanations to avoid ambiguity in international business or multicultural environments. Misinterpretations can arise from the absence of nonverbal cues, requiring individuals to develop skills in clear articulation and active listening.
Cultural Examples of Low-Context Societies
Low-context societies such as the United States, Germany, and Switzerland rely heavily on explicit verbal communication where messages are clear, direct, and spelled out to avoid misunderstandings. In these cultures, individualism and transparency are emphasized, leading to straightforward business interactions and daily conversations. Social norms prioritize clarity over implied meaning, contrasting sharply with high-context cultures where communication depends more on shared background and nonverbal cues.
Explicit-Context in Business and Negotiations
Explicit-context communication in business and negotiations prioritizes clear, direct, and detailed exchanges to avoid misunderstandings. This style thrives in environments where precise instructions, comprehensive documentation, and straightforward language reduce ambiguity and enhance accountability. Organizations operating in multicultural settings often adopt explicit-context approaches to ensure clarity and foster trust among diverse stakeholders.
Miscommunication in Low-Context Settings
Low-context communication relies heavily on explicit verbal messages, reducing ambiguity to minimize miscommunication. In contrast, low-context settings often experience miscommunication due to the lack of shared background knowledge, causing messages to be interpreted narrowly or incorrectly. Clear, detailed information exchange and confirming understanding are critical strategies to overcome misunderstandings in low-context environments.
Strategies for Bridging Contextual Communication Gaps
Explicit-context communication relies heavily on clear, direct messages where meaning is spelled out through words, while low-context communication minimizes implicit cues and prioritizes straightforwardness. Strategies for bridging these contextual communication gaps include employing explicit language to clarify intentions, confirming understanding through feedback loops, and adapting messaging styles to meet the receiver's cultural and contextual expectations. Utilizing visual aids, detailed documentation, and consistent terminologies effectively reduces ambiguity and fosters clearer intercultural dialogue.
Explicit-context Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com