Integration enhances efficiency by seamlessly connecting systems, enabling data to flow smoothly across platforms and reducing manual effort. It supports better decision-making through real-time access to consolidated information and automates workflows to save time and resources. Discover how integration can transform Your business operations by reading the rest of this article.
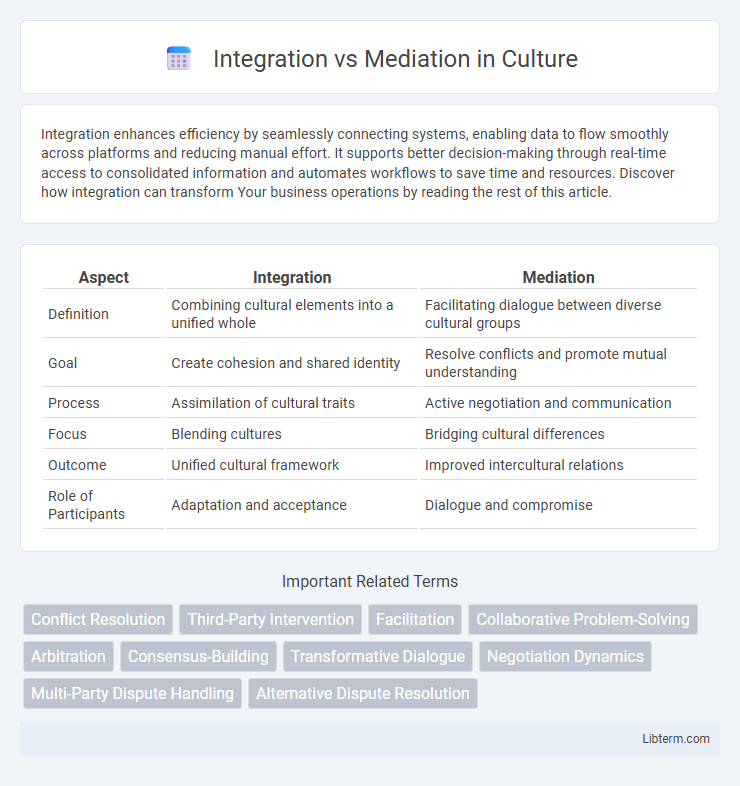
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Integration | Mediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining cultural elements into a unified whole | Facilitating dialogue between diverse cultural groups |
| Goal | Create cohesion and shared identity | Resolve conflicts and promote mutual understanding |
| Process | Assimilation of cultural traits | Active negotiation and communication |
| Focus | Blending cultures | Bridging cultural differences |
| Outcome | Unified cultural framework | Improved intercultural relations |
| Role of Participants | Adaptation and acceptance | Dialogue and compromise |
Understanding Integration and Mediation
Integration involves directly connecting multiple systems or applications to enable seamless data exchange and unified workflows, enhancing operational efficiency. Mediation acts as an intermediary layer that transforms, filters, or routes messages between disparate systems, ensuring compatibility and managing communication protocols. Understanding the distinction highlights integration's role in system unification, while mediation focuses on facilitating interoperability through message handling.
Key Differences Between Integration and Mediation
Integration involves combining multiple systems or components into a unified whole to work seamlessly together, while mediation acts as an intermediary layer facilitating communication and data exchange between disparate systems without merging them. Key differences include integration's focus on consolidation and shared processes, whereas mediation prioritizes protocol translation, message routing, and decoupling system dependencies. Integration often requires tightly coupled architectures, whereas mediation supports loosely coupled, flexible service interactions.
How Integration Works in Modern Systems
Integration in modern systems works by connecting disparate applications and data sources through APIs, middleware, or integration platforms, enabling seamless data exchange and process automation across diverse environments. It creates unified workflows by synchronizing information in real-time or through scheduled data transfers, reducing silos and improving operational efficiency. Technologies like iPaaS and microservices architecture play a crucial role in facilitating scalable, flexible integration solutions that support evolving business needs.
The Role of Mediation in Digital Ecosystems
Mediation in digital ecosystems serves as an intermediary layer that enables seamless communication and data exchange between disparate systems, platforms, and services. This approach facilitates interoperability by transforming, routing, and aggregating data in real-time, enhancing system flexibility and scalability. Unlike direct integration, mediation reduces complexity and dependency on tightly coupled connections, allowing digital ecosystems to evolve dynamically and support diverse business processes.
Pros and Cons of Integration Solutions
Integration solutions streamline data flow across multiple systems, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing manual data entry errors. However, they can involve complex implementation processes and high upfront costs, requiring specialized expertise for maintenance and troubleshooting. Scalability may be limited if the solution is tightly coupled with specific applications, potentially hindering flexibility in adapting to future business needs.
Advantages and Challenges of Mediation Approaches
Mediation approaches offer advantages such as enhancing flexibility by enabling loosely coupled services and simplifying complex system interactions through message transformation and routing. They improve scalability and adaptability in heterogeneous environments by decoupling service consumers and providers, facilitating seamless protocol and data format integration. Challenges include increased complexity in managing and configuring mediation components, potential performance overhead, and difficulties in ensuring reliability and consistency across distributed systems.
Common Use Cases for Integration
Integration is commonly used in scenarios requiring seamless data exchange between disparate systems such as ERP and CRM platforms, enabling unified business processes and real-time analytics. It supports automation in supply chain management by connecting inventory, order processing, and logistics systems for improved efficiency. Integration also facilitates customer data synchronization across marketing, sales, and support applications, ensuring consistent and personalized user experiences.
Typical Scenarios Favoring Mediation
Mediation is favored in scenarios requiring complex message transformations, routing, and protocol bridging between disparate systems. It excels in environments where loose coupling and message enrichment enhance system flexibility and scalability, such as integrating legacy applications with modern services. Typical use cases include service orchestration, event-driven architectures, and enterprise service buses facilitating asynchronous communication.
Choosing Between Integration and Mediation
Choosing between integration and mediation depends on the specific needs of system interoperability and data flow. Integration involves directly connecting systems for seamless data exchange and unified functionality, ideal for tightly coupled environments requiring real-time processing. Mediation acts as an intermediary layer transforming and routing messages between disparate systems, suited for loosely coupled architectures needing flexibility and protocol adaptation.
Future Trends in Integration and Mediation Technologies
Future trends in integration technologies emphasize the adoption of AI-driven automation, real-time data processing, and cloud-native architectures to enhance scalability and flexibility. Mediation technologies are evolving towards intelligent API gateways and microservices-based platforms, enabling seamless connectivity and dynamic routing for complex, distributed environments. Both integration and mediation will increasingly leverage edge computing and machine learning to optimize data flow and decision-making across diverse enterprise ecosystems.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com