Polysemy refers to a single word or phrase having multiple related meanings, which can enrich communication by adding layers of interpretation. Understanding polysemy allows you to appreciate the nuance and complexity of language, improving both comprehension and expression. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how polysemy shapes everyday language and influences your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
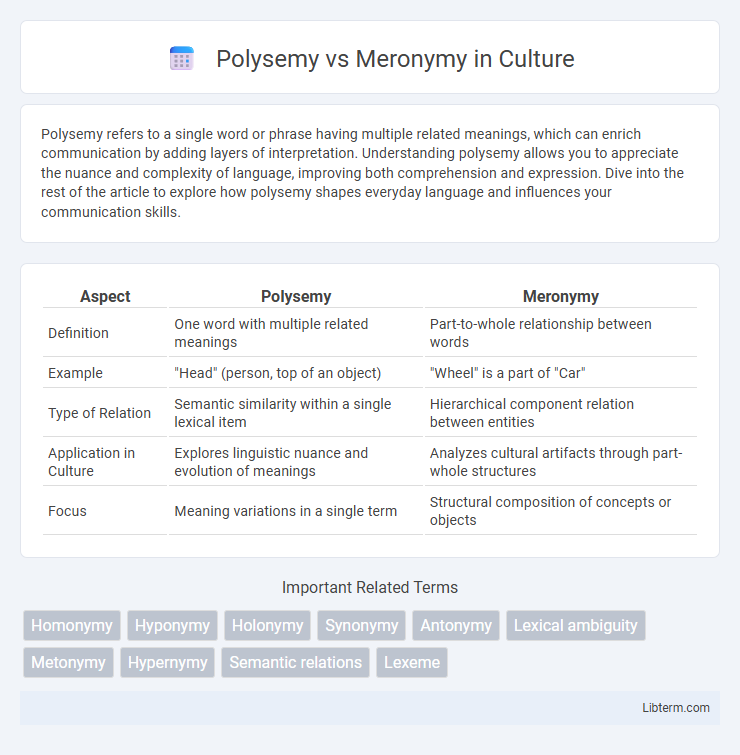
| Aspect | Polysemy | Meronymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One word with multiple related meanings | Part-to-whole relationship between words |
| Example | "Head" (person, top of an object) | "Wheel" is a part of "Car" |
| Type of Relation | Semantic similarity within a single lexical item | Hierarchical component relation between entities |
| Application in Culture | Explores linguistic nuance and evolution of meanings | Analyzes cultural artifacts through part-whole structures |
| Focus | Meaning variations in a single term | Structural composition of concepts or objects |
Introduction to Polysemy and Meronymy
Polysemy refers to a single word having multiple related meanings, such as the word "bank," which can mean a financial institution or the side of a river. Meronymy denotes a part-whole relationship between terms, where one word represents a part of something else, such as "wheel" being a meronym of "car." Understanding polysemy and meronymy is essential in semantic analysis for accurately interpreting word meanings and their relational structures in language processing.
Defining Polysemy: Multiple Meanings of Words
Polysemy refers to a single word having multiple related meanings, such as the word "bank," which can mean the side of a river or a financial institution. This linguistic phenomenon contrasts with meronymy, where the relationship is part-to-whole, like "wheel" being a part of a "car." Understanding polysemy is crucial for natural language processing and semantic analysis because it helps disambiguate word meanings in context.
Understanding Meronymy: Part-Whole Relationships
Meronymy defines the part-whole relationship between words, where a meronym represents a part of a larger whole, such as "wheel" being a meronym of "car." This semantic relationship helps in understanding how complex objects or concepts are composed of smaller, constituent parts. Recognizing meronymy is crucial for language processing tasks like taxonomy building and knowledge representation in natural language understanding.
Key Differences Between Polysemy and Meronymy
Polysemy refers to a single word having multiple related meanings, such as the word "bank" meaning both a financial institution and the side of a river. Meronymy denotes a part-whole relationship between terms, like "wheel" being a part of a "car." The key difference lies in polysemy involving multiple senses of one word, whereas meronymy connects two distinct but related entities through a part-to-whole hierarchy.
Examples of Polysemy in Everyday Language
Polysemy occurs when a single word has multiple related meanings, such as "bank," which can refer to the edge of a river or a financial institution. Another example is "head," meaning the top part of the body or a leader of a group. These multiple meanings depend on context and reflect the flexible nature of language semantics.
Real-World Applications of Meronymy
Meronymy, the semantic relationship where one term denotes a part of something else, plays a critical role in fields like natural language processing and knowledge representation by enabling machines to understand part-whole hierarchies. Real-world applications include enhancing search engines through more precise query interpretation, improving image recognition systems by identifying object components, and supporting medical diagnosis by mapping symptoms to organ systems. In contrast to polysemy, which deals with multiple meanings of a single word, meronymy provides structured insights into the composition of entities, essential for semantic web technologies and ontology development.
Cognitive Processing of Polysemous and Meronymous Terms
Cognitive processing of polysemous terms involves activating multiple related meanings within a single lexical entry, which requires context to disambiguate and efficiently access the intended sense. Meronymous terms engage a hierarchical cognitive framework where parts and wholes are represented relationally, facilitating understanding through spatial or functional relationships. Neuroimaging studies reveal differential brain activation patterns, with polysemy relying more on semantic network integration and meronymy engaging relational and feature-based processing regions.
Polysemy and Meronymy in Linguistic Theory
Polysemy refers to a single word having multiple related meanings, such as "bank" meaning a financial institution or the side of a river, highlighting semantic flexibility within lexical items. Meronymy describes a part-whole relationship between words, where one term denotes a component of another, as in "wheel" being a meronym of "car." Linguistic theory uses polysemy to analyze semantic ambiguity and cognitive categorization, while meronymy informs hierarchical lexical organization and structural semantics.
Challenges in NLP: Distinguishing Polysemy from Meronymy
Distinguishing polysemy, where a single word has multiple related meanings, from meronymy, which involves part-whole relationships between words, poses significant challenges in NLP due to context-dependent semantic nuances. Word sense disambiguation techniques often struggle to accurately categorize terms when semantic boundaries blur, affecting tasks like named entity recognition and semantic parsing. Advanced contextual embeddings and knowledge graph integration are crucial for effectively resolving these ambiguities in natural language understanding systems.
Conclusion: The Importance of Semantic Distinctions
Recognizing the difference between polysemy and meronymy is crucial for accurate semantic interpretation and natural language processing applications. Polysemy involves a single word having multiple related meanings, while meronymy concerns the part-whole relationship between words. Establishing clear semantic distinctions enhances linguistic analysis, improves information retrieval, and facilitates more precise communication.
Polysemy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com