Oral traditions preserve cultural heritage through storytelling, songs, and rituals passed down orally across generations. These practices maintain historical knowledge, values, and communal identity without written records. Explore the article to understand how oral traditions shape societies and influence cultural continuity.
Table of Comparison
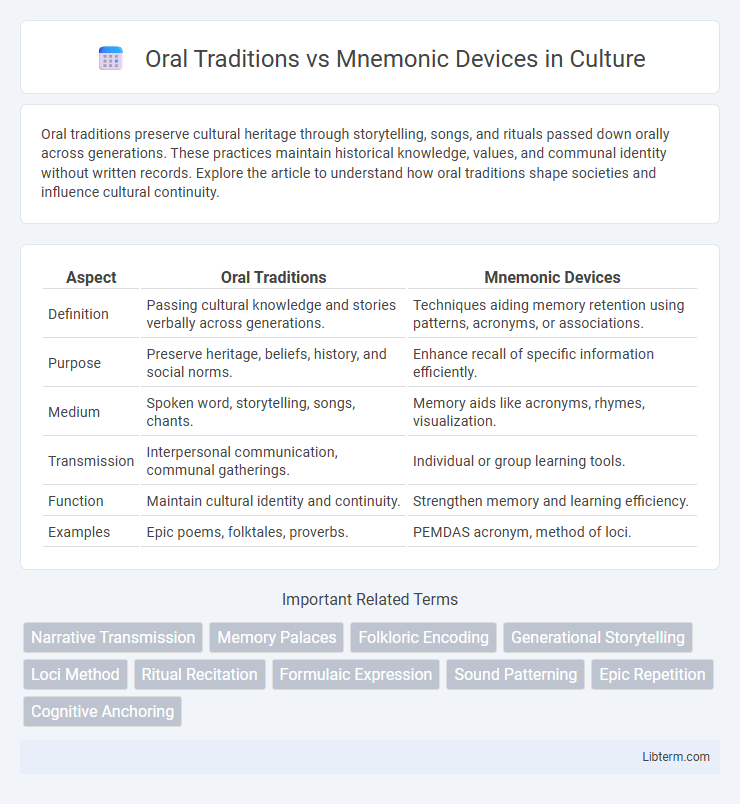
| Aspect | Oral Traditions | Mnemonic Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Passing cultural knowledge and stories verbally across generations. | Techniques aiding memory retention using patterns, acronyms, or associations. |
| Purpose | Preserve heritage, beliefs, history, and social norms. | Enhance recall of specific information efficiently. |
| Medium | Spoken word, storytelling, songs, chants. | Memory aids like acronyms, rhymes, visualization. |
| Transmission | Interpersonal communication, communal gatherings. | Individual or group learning tools. |
| Function | Maintain cultural identity and continuity. | Strengthen memory and learning efficiency. |
| Examples | Epic poems, folktales, proverbs. | PEMDAS acronym, method of loci. |
Understanding Oral Traditions: Definition and Scope
Oral traditions encompass the cultural practice of transmitting stories, knowledge, and customs verbally across generations, preserving collective memory without written records. These traditions include myths, legends, folklore, and rituals that maintain identity and historical continuity within communities. Understanding oral traditions involves recognizing their reliance on communal participation, performative storytelling, and contextual adaptation to sustain cultural heritage.
What Are Mnemonic Devices?
Mnemonic devices are cognitive tools designed to enhance memory retention and recall by associating complex information with simple, vivid cues such as acronyms, rhymes, or visual imagery. These techniques capitalize on the brain's ability to remember structured patterns, facilitating efficient encoding and retrieval of data. Widely used in education and daily life, mnemonic devices transform abstract or extensive content into accessible, memorable formats, distinguishing them from oral traditions that rely on collective storytelling and transmission.
Historical Roots: Oral Traditions Through the Ages
Oral traditions have served as the primary vehicle for preserving and transmitting cultural knowledge, stories, and histories across generations since prehistoric times. These practices rely on rhythmic patterns, storytelling techniques, and communal participation to embed information deeply into collective memory. Mnemonic devices, while often systematic and individual-focused, evolved later as cognitive tools to enhance memory retention beyond traditional oral recitation methods.
The Psychology Behind Mnemonic Techniques
Mnemonic techniques leverage cognitive psychology principles by enhancing encoding and retrieval processes through structured associations, vivid imagery, and chunking strategies. These devices capitalize on the brain's preference for meaningful patterns and spatial organization, enabling more efficient memory consolidation compared to the fluid and context-dependent nature of oral traditions. Research demonstrates that mnemonic methods activate neural pathways linked to long-term memory storage, promoting durable retention beyond the episodic recall favored by oral transmission.
Memory Transmission: Oral Versus Mnemonic Methods
Oral traditions rely on storytelling, songs, and rituals to transmit cultural knowledge and collective memory across generations through communal participation. Mnemonic devices use structured techniques such as visualization, acronyms, and chunking to enhance individual memory retention and recall efficiency. Both methods serve as powerful tools for preserving and conveying information but differ in their reliance on social interaction versus cognitive strategies.
Cultural Significance of Oral Storytelling
Oral storytelling serves as a vital cultural conduit, preserving traditions, histories, and values across generations without reliance on written records. This practice fosters community identity and social cohesion by embedding collective memory within engaging narratives that are easily transmitted. Mnemonic devices complement these methods by enhancing recall and structuring information, but oral storytelling remains paramount in maintaining intangible cultural heritage worldwide.
Cognitive Benefits of Mnemonic Devices
Mnemonic devices enhance memory retention by creating structured associations that simplify the recall process, engaging multiple cognitive pathways such as visualization, organization, and repetition. Unlike oral traditions that rely heavily on narrative and communal reinforcement, mnemonic techniques actively stimulate executive functions in the brain, improving working memory and long-term recall capabilities. Scientific studies show that mnemonic training increases neural connectivity in areas linked to memory and attention, offering superior cognitive benefits for learning and information retrieval.
Limitations and Challenges of Oral Traditions
Oral traditions face limitations such as the potential distortion of information due to memory lapses and the lack of a fixed record, resulting in variations over time. Challenges include the risk of knowledge loss when key storytellers or memory keepers pass away without transferring their knowledge. Environmental factors, language evolution, and cultural shifts can also hinder the accurate preservation and transmission of oral narratives.
Modern Applications: Integrating Both Methods
Oral traditions and mnemonic devices coexist in modern applications by enhancing memory retention through storytelling combined with structured memory aids. Educational methods increasingly integrate narrative techniques with mnemonic frameworks to improve cognitive recall and knowledge transmission. Digital tools utilize these combined approaches to support learning processes and preserve cultural heritage effectively.
Oral Traditions vs Mnemonic Devices: A Comparative Analysis
Oral traditions rely on the collective memory and storytelling techniques passed down through generations to preserve cultural knowledge, whereas mnemonic devices utilize structured cognitive strategies, such as acronyms or visualization, to enhance individual memory retention. Oral traditions encompass narratives, songs, and rituals deeply embedded in social contexts, while mnemonic devices are often systematic tools tailored for specific information recall. Comparing the two highlights the dynamic interplay between communal memory cultures and personalized cognitive methods in knowledge transmission.
Oral Traditions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com